from 280,000 rub.
Cost of the operation
This plastic surgery allows you to make the nose more proportional, give the face a more harmonious and attractive appearance, and model an elegant or, conversely, masculine profile. Both individual parts of the nose - tip, back, wings - and the entire nose can be corrected.
The nose is a significant detail of a person’s appearance, playing an important role in the perception of his image. One of the main reasons for turning to rhinoplasty specialists is the desire to reduce the tip of the nose or the entire nose. It is nose reduction that in most cases helps to achieve ideal facial proportions.
There are many indications for nose reduction surgery, and they are not always purely aesthetic. Indications may be:
- large size of the nose or some of its parts (wings, tip, back);
- the bridge of the nose is too wide;
- the presence of a bone or cartilaginous hump;
- some types of breathing disorders.
Before the operation, in an individual consultation with the surgeon, computer modeling is performed, which allows you to assess future changes in appearance and take into account all the patient’s wishes. A detailed operation plan is drawn up. Often, along with nose reduction, endoscopic operations are performed on the deep structures of the nasal cavity in order to eliminate breathing problems or other unpleasant phenomena.
Rhinoplasty – Price in our clinics
| Classic rhinoplasty | Price: from 129,900 rub. | Price: 264,000 rub. |
| Nose wing correction | Price: from 44,000 rub. | Price: 57,500 rub. |
| Plastic surgery of the tip of the nose | Price: from 75,100 rub. | Price: 123,200 rub. |
| Rhinoseptoplasty | Price: from 164,900 rub. | Price: 305,000 rub. |
If you are interested in rhinoplasty, please note that the cost of the operation varies significantly from one clinic to another and largely depends on the type of operation.
At Novoklinik, classic rhinoplasty costs 129,900 rubles, but changing the tip of the nose or slightly correcting the shape of the wings will cost less - from 44,000 rubles.
Effect of the operation
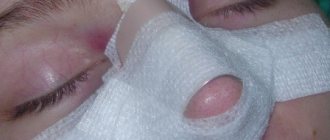
After rhinoplasty, the patient wears a plaster cast for two weeks. Swelling and hematomas disappear 15-20 days after surgery.
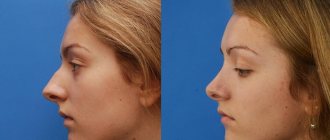
Rhinoplasty allows the patient to significantly change their appearance, become more attractive, and gain self-confidence.
The result of the procedure largely depends on the experience and professionalism of the plastic surgeon.
Therefore, if you are looking for where to get a nose job, contact the specialists at SM-Plastika. To make an appointment, clarify the details of the operation and prices for rhinoplasty, please call +7 (495) 777-48-05 .
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Modern equipment
Free consultation
Affordable prices
European service
Indications for rhinoplasty
Surgery on the nasal structures is preferable for patients who want to change the shape of the nose, shorten or lengthen it, adjust the size of the wings, get rid of a hump or deviated nasal septum, or improve facial features.
Plastic surgery is also indicated in cases where there has been an injury or post-traumatic scars remain, there are congenital problems with respiratory function, or unsuccessful plastic surgery has previously been performed.
There are no strict medical indications for this procedure - most patients seek to change the shape of their nose due to dissatisfaction with what nature has given them.
A plastic surgeon is able to change the condition of the nasal structures, giving them a different shape and eliminating the following aesthetic defects:
- saddle shape;
- wide nostrils;
- thickened or bifurcated tip of the nose;
- disproportionate relationship between the nose and other parts of the face;
- "eagle beak";
- nasal deformation caused by old injuries;
- pronounced hump on the back;
- difficult nasal breathing.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the age at which plastic surgery is acceptable. The lower level ranges from 18 to 21 years - it is at this age that bone and cartilage tissues in the body are finally formed. It is undesirable to perform this operation after 35-40 years of age due to the high likelihood of complications. However, the upper age limit is determined individually for each patient. For example, rhinoplasty of a broken nose can be performed at any age.
The doctors of the Novoklinik Aesthetic Medicine Centers will help you get rhinoplasty in Moscow - in our clinic you will get a qualitative change in appearance at an affordable price.
What is conservation rhinoplasty?
In most cases, when patients contact a plastic surgeon for rhinoplasty, the number one problem is the presence of a nasal hump . Therefore, reducing the nasal hump is an important surgical step in rhinoplasty. In classical rhinoplasty, after reducing the height of the dorsum, the nasal arch is destroyed and must be reconstructed. For the past few years, this technique has been a standard procedure used by surgeons to remove the hump and reshape the nose. The bony hump was removed using an osteotome and hammer and then removed, resulting in an open roof of the nasal dorsum, which had to be reconstructed using cartilage grafts and sutures.
Think of the nose as a multi-story building with the top floor being the hump. In standard rhinoplasty, the surgeon removes the top floor or hump to reduce the size of the building. This method leaves the roof exposed, which will then need to be repaired.
⇒ INFORMATION: Open and closed rhinoplasty: differences and features
Types of plastic surgery of the nose
Depending on the volume and specific purpose, several types of correction are distinguished.
Rhinoplasty of the tip of the nose
This type of rhinoplasty allows you to restore the harmonious contours of the nose without affecting the supporting structures. The variety of anatomical options requires the development of an individual correction plan in each specific case.
Rhinoplasty of the wings of the nose
This type of operation allows you to change the width, thickness, and symmetry of the nostrils. Correction of the wings can be either an independent operation or one of the stages of a more extensive plastic surgery.
Correction of a hump
Removing the nose from excessive osteochondral protrusion is achieved by excision of excess cartilage tissue. Rhinoplasty to eliminate such a defect leads to a smaller nose and helps to harmonize the appearance as a whole.
Correction of the nasal septum
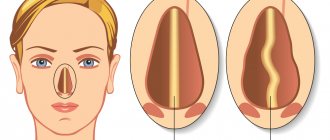
Septoplasty is a medical service to correct a deformed nasal septum. Most often it is performed with difficulty in nasal breathing and is not accompanied by visible changes in the face.
Columella correction
Aesthetic surgery to correct the shape and size of the skin fold separating the nostrils. Allows you to significantly change the aesthetic perception of the face as a whole. The columella is considered harmonious if it is located below the level of the wings.
Rhinoseptoplasty
This is a type of combined intervention, during which the septum and adjacent structures are affected. As a result, a radical change in the shape of the nose occurs and respiratory function is restored.
After nose correction
The postoperative period requires a lot of patience and self-discipline. In the first days after rhinoplasty, there is severe swelling of the nose and lower eyelids, difficulty in nasal breathing and pain. In order to fix the changed shape, a plaster bandage in the shape of a butterfly is applied to the nose, and turundas are inserted into the nasal passages.
In the early postoperative period, physical activity is contraindicated, you cannot wear glasses, you cannot sleep on your stomach, or sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium. Anti-inflammatories and cold compresses can be used to reduce discomfort and swelling.
If all recommendations are followed, the plaster is removed after 7-10 days. Swelling in the eye area goes away within 10-14 days, and you will be able to evaluate the aesthetic result of the operation 3-4 months after rhinoplasty.
Contraindications for rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty is not performed on patients under 18 years of age. The only exception is a bent nose due to injury.
Medical contraindications include chronic diseases, against the background of which surgery is accompanied by a high risk of complications. These include:
- diabetes;
- cancer;
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- acute infectious diseases;
- hypertension and any problems with the heart and lungs accompanied by respiratory or heart failure.
Contraindications are determined at the stage of preliminary examination and examination of the patient.
Predicted result
To visually assess the predicted result, Novoklinik uses computer modeling. To do this, the doctor takes several photographs of the patient - in front and profile, and then processes the image using a computer program. The data after such processing is provided to the patient.
Important! Working with living tissues is much more complex and the results may differ from those presented using computer simulations. Deviations sometimes reach 30-40% of those expected, so the computer model serves only as a guide and a sign that the patient and doctor understand each other.
Preparing for anesthesia
The procedure for correcting the shape of the nose is carried out under general anesthesia in combination with local (infiltration) anesthesia, so preparation for it includes a consultation with an anesthesiologist. The doctor carefully examines the patient, asks him about diseases and treatment, the presence or absence of allergic reactions. Then he talks about the peculiarities of anesthesia, possible side effects and complications.
For safety reasons, you should refrain from eating food 8-12 hours before surgery and drinking liquids 4 hours before surgery. If you are constantly taking medications, you need to inform your anesthesiologist about this - he will decide whether they need to be taken as usual or whether the regimen and dosage need to be changed.
The cost of anesthesia is already included in the price of nose plastic surgery.
Preparing for surgery
An integral element of preparation for rhinoplasty is a consultation with a plastic surgeon. During the interview, the patient and the doctor discuss possible plastic surgery options, facial modeling and rhinoscopy are performed.
In addition, preoperative preparation includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- study of the blood coagulation system (coagulogram);
- electrocardiogram;
- general urine test;
- laboratory testing for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis.
These tests can be performed in our laboratory.
If there are concomitant diseases that may affect the course of the operation or increase the likelihood of complications, a consultation with a specialist is scheduled. Thus, for cardiac pathology, a consultation with a cardiologist is required, for pulmonary pathology, a pulmonologist, and for endocrine diseases, an endocrinologist.
Article on the topic
How to remove a hump on your nose?
Can't come to terms with a hump on your nose? We'll tell you what it will cost you to get rid of it.
Read more
Carrying out rhinoplasty surgery
For Novoklinik patients, any cosmetic surgery, including rhinoplasty of the nostrils, is completely painless, under general anesthesia. During the intervention, the doctor makes an incision on the inner surface of the nostrils up to 2 cm in size and carries out all the necessary manipulations through it.
To provide a better view of the surgical area, an endoscope is inserted endonasally (through the nostrils). In this case, the tissue image is displayed on a large monitor, which provides convenience for the surgeon and reduces the risk of complications.
The very essence of the operation is the redistribution of tissues that form the nasal structures: skin and cartilage are removed where there is an excess of them (in the area of the hump), and they are built up where there is a lack of them (on the wings, for example).
The duration of rhinoplasty depends on the volume and specific technology and ranges from 30 minutes to 3 hours. The end of the operation is marked by the application of miniature sutures to the incision and a polymer or plaster bandage to the outer surface of the nose. Rhinoprotectors and hemostatic sponges (turundas) are installed in the nasal passages.
In exceptional situations, open rhinoplasty is performed, when the surgeon cuts the columella and performs intervention on the open structures of the nose. This method is used in the most difficult cases - after serious injuries, with massive fractures, when carrying out extensive work on the nasal bones.
A long nose is not measured in centimeters, it is simply disproportionate to the vertical lines of the face. It's a matter of proportions, not distances.
If you draw horizontal lines along the bridge of your nose and under the tip of your nose and see that the middle part of your face is larger than the top and bottom, then you have a long nose.
What to do with a long nose? Is this a mandatory reason to undergo plastic surgery? Of course not. But if you are concerned about this disharmony in your facial features, you can come for a consultation with a plastic surgeon, leading rhinoplasty at the Beauty Doctor clinic, Sergei Arkadyevich Kharitonov.
You will have a long conversation, measurements of your nose in different projections and modeling of a new nose in a computer program.
The clinic’s specialists spare no time in initial consultations, understanding that the assessment of the result depends on how correctly the patient understands the essence of what will happen.
Sometimes a clinic visitor asks not so much about the result as about how long the operation will take, whether it can be done under local anesthesia, how long it will take for the face to recover after the intervention, and whether the nose will lose its sensitivity.
Let’s answer briefly right away to dispel fears and doubts, and let’s get to the heart of the matter (how to reduce a long nose):
Long nose rhinoplasty surgery lasts for an hour or an hour and a half.
It can be done under local anesthesia, but this is a big test for the patient’s psyche: he will not feel pain, but he will feel all the touches, see the surgeon’s hands, scalpel, needles, skin flap - this, you know, is not something everyone can do. At the Beauty Doctor clinic, rhinoplasty is performed under general anesthesia, the entire process of artificial ventilation of the lungs is controlled by devices, the clinic’s experienced anesthesiologist-resuscitator Igor Valentinovich Arkhipov has many years of practice, and observes the patient until he is sure that the patient’s well-being is normal.
The nose does not lose its sensitivity after long nose surgery, but if there was intervention in the mucous membranes, then within a week a dullness of smell is possible, much the same as during a runny nose. This is caused by the same reasons - tissue swelling.
During surgery to reduce the length of the nose (nose shortening), after two to three weeks the patient is fully social and can go to work.
And now about how the nose is shortened?
A feature of visual perception at work here is the assessment of proportions. It seems to us that a nose is disproportionate if the ratio of the length of the back of the nose to the distance from the base to the tip is disturbed. Normally this is three to one. If not three, but more, then the nose seems long. Therefore, if you raise the tip of the nose upward, the distance from the root to the tip will increase, and the proportions will be harmonious.
To do this, resection (cutting off) of the lateral cartilages is done and the caudal (that is, tail, terminal) section of the cartilaginous septum is shortened. Then a suture is applied, which tightens the medial, that is, those located closer to the middle, legs of the cartilage to the nasal septum, and the result is achieved!
If the disproportion between the length of the back and the distance from the root to the tip of the nose is too great, then plastic surgeons perform resection of the cartilage in the septal part.
What about the skin, you ask? Yes, it seems to be getting bigger. In order to tighten, notches are made on the inside of the nose, they tighten the skin and there is no sagging left.
It is surprising that almost all patients who have undergone surgery to reduce the length of the nose hear the same thing when they come to work. Colleagues ask if she has had a facelift? No traces are visible, but the general feeling of youth is clear. Indeed, a long nose gives the face a somewhat dull appearance, while a slightly shortened one, on the contrary, visibly adds energy, optimism and, accordingly, youth.
Possible complications
In addition to purely medical consequences (nosebleeds, tissue necrosis), rhinoplasty is sometimes accompanied by minor aesthetic defects of the face.
As practice shows, even with high-quality intervention, up to 10-15% of patients experience dissatisfaction with the “new” part of the body. Thanks to the competent work of our doctors, the likelihood of such a situation at Novoklinik is minimized.
Postoperative period after rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty surgery involves postoperative observation for 24 hours, during which the patient is in the hospital.
For 6-7 days, the patient is observed on an outpatient basis - on days 2-3, rhinoprotectors and a hemostatic sponge are removed from the nostrils, on days 7-14 the bandage is removed and the person returns to normal life. The result of rhinoplasty is assessed 2-3 weeks after rehabilitation and complete resolution of hematomas and swelling. The nose will take its final shape in 6-8 months.
Correction of the nasofrontal angle in rhinoplasty
Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, ORL-HNS Research Center, Iran Medical University, Tehran
Abstract
The root of the nose and the nasofrontal angle occupy a special place in aesthetic rhinoplasty. Minimal changes in the location or size of the nasofrontal angle affect the perception of nasal length and the length of the middle third of the face. In patients with a high root of the nose, the line of the forehead smoothly continues into the line of the bridge of the nose when viewed in profile, creating the illusion of an overly long nose. Conversely, a deep nasofrontal angle in patients with a low nasal root creates the illusion of a shortened nose. The ideal height of the nasal root, as well as methods for achieving it if correction is necessary, is the subject of ongoing debate and the topic of this article.
Key words: root of the nose; nasofrontal angle; nasion; augmentation
Introduction
The root of the nose is the narrowest and most distant part of the nose, delimiting the nose and forehead and defining two important angles on the face, 1 nasofrontal and nasofacial, so its slightest horizontal or vertical displacement can result in a significant change in the appearance and projection of the nose.
The ideal height and level of the nasion (the bony part of the root of the nose/bridge), as well as surgical options for correcting them, are the subject of ongoing debate. These interventions are aimed at correcting the width and height of the nasion. They can be divided into two categories: augmentation interventions for suboptimal root projection in order to elevate it and make the bone profile more prominent; and reduction interventions in individuals with an excessively high root and flattened nasofrontal angle to reduce root height and deepen the angle, which represents one of the main challenges for rhinoplasty.
This review discusses the ideal position of nasion on the face and various surgical interventions to correct it.
Anatomy and ideal nasion position
The nasion is the deepest point of the nasofrontal cavity. As an anthropometric landmark and reference point for soft tissue, the nasion lies midway between the nasofrontal suture and the top of the nasal bones, and corresponds to the most concave point on the dorsum of the nose.2
In the lateral projection, the forehead is slightly tilted posteriorly - by 10±40 degrees in men and 6±50 in women, forming an angle with the bridge of the nose - the so-called. nasofrontal angle (Figure 1). The nasofrontal angle is determined between tangent (tangential) lines drawn from the root to the bridge of the nose and from the root to the tip of the nose.2 The latter can simultaneously be located tangentially to the dorsum of the nose.3 Normal values of the nasofrontal angle are 130±70 in men and 134±70 in women.2
The location of the nasion is assessed in two aspects: vertically, the width (or level) of the nasion is determined as the distance from the nasion to the Frankfurt line; horizontally, nasion depth/height (or root projection) is defined as the distance from the nasion to the glabella (gdabella), or as the distance from the nasion to the corneal plane (Figure 1).
The ideal location of the nasion in the vertical plane is between the supratarsal fold and the lash line of the upper eyelid.4 Guyuron5 suggested that the ideal location of the nasion should be considered at the level of the lower edge of the upper eyelid when looking forward. (Figure 3).
Figure 1: Nasofrontal angle and nasion position; N: nasion, C: corneal plane; F: Frankfurt line, G: glabella
Figure 3: Options for positioning the nasion in the horizontal plane when fixed in the vertical plane.
In some cases, placement at the level of the pupils is acceptable, which, in principle, softens the profile.6 Changing the vertical position of the nasion creates the illusion of lengthening the nose in lateral projection (Fig. 2). If in the vertical plane the nasion is close to the Frankfurt line, then the nose looks shorter and its projection is higher, and vice versa, when the nasion moves away from the Frankfurt line, the nose appears longer.
Drawing. 2: Options for positioning the nasion in the vertical plane when fixed in the horizontal plane.
The position of the nasion in the horizontal plane is described in two different ways. It is determined either relative to the glabella or relative to the plane of the cornea. The ideal position of the nasion in the horizontal plane is 4-6 mm from the glabella,2 or 9-14 mm from the plane of the cornea.1 Deviations in the position of the nasion in the horizontal plane also affect the perception of the length and projection of the nose.
Byrand Hobar1 proposed a convenient method for determining the harmonious proportion between the projection (height) of the tip of the nose, the length of the nose and the projection of the root of the nose. It is generally accepted that the ideal length of the nose is 2/3 of the length of the midface, and the ideal projection of the tip of the nose is 2/3 of the length of the nose, provided that the projection of the root of the nose from the junction of the nasal bones with the edge of the orbit is ideally 0.28 of the length nose In this case, the reference point is the projection of the root onto the plane of the cornea.
It should be remembered that slight changes in the position of the nasion or nasofrontal angle create the impression of different lengths of the nose and middle third of the face in lateral projection (Figure 4).
Drawing. 4: Increasing the height of the nasal root
Nose root reduction
Deepening of the nasofrontal angle is indicated for patients with a high nasal root projection (high nasal root) (Figure 5). Sometimes, simultaneously with resection of soft tissues, resection of the nasal bones is also performed. In the root area, the thick soft tissue of the bridge of the nose gradually turns into the thin skin of the dorsum of the nose and eyelids.4 The soft tissues of the nasal root are formed by adipose tissue and the procerus muscle. The average thickness of the soft tissues of the nasion according to cephalohexography is 7 mm in women and 7.5 mm in men, and varies in the range of 3.5-9 mm.4 The degree of retraction after bone removal does not exceed 25%.7 To reduce the thickness of the soft tissues of the root, it is sometimes necessary to resect the muscle and subcutaneous fat, keeping in mind that the vacated space may subsequently be filled with scar tissue.3
Figure 5: Nasal root reduction
Preoperative assessment
After a preliminary assessment of the glabella, the degree of deepening of the nasofrontal angle is planned in accordance with the desired height of the dorsum and tip of the nose.4 Another tactic is possible: first determine the ideal nasion, then plan the necessary displacement of the nasal tip to achieve the ideal size of the nasofacial angle of 360.4 According to Tardy8 when planning the degree of correction nasal hump, the depth and location of the nasofrontal angle are secondary to the position of the nasal tip.
To determine the projection of the root, the distance from the nasion to the plane of the cornea is measured, and for clarification, it is checked with the distance to the plane of the glabella. This is important in cases where the eyes are set deep. Additionally, the position of the nasion in the vertical plane is determined.
Surgical correction
Various techniques are used to resect the nasal bones, including sawing, osteotomy, and the use of burrs and incisors. When simultaneously correcting a high root and a pronounced nasal hump, preference is given to osteotomy, since the latter allows one to achieve a one-step clear resection without leaving bone fragments. The disadvantages of osteotomy are the possibility of excessive or asymmetrical bone resection, which, however, can be easily corrected later. The osteotome allows you to set clear lines and a clear angle.8 Sawing achieves step-by-step removal of excess bone tissue with simultaneous excessive trauma to soft tissue, and therefore the method is not applicable in cases of very high nasal root. Another disadvantage of sawing is the inability to set the exact location of the corner.8
To deepen the nasofrontal angle, different osteotomes are used. A flat osteotome with or without a transverse percutaneous osteotomy of 2 mm of bone tissue is recommended to weaken the osseous skeleton of the root.8 Quisling and Rubin osteotomes eliminate the need for percutaneous osteotomy, but are subject to inaccuracy if one is necessary.8
A Parkes chisel is also used for resection of the root skeleton. For clear visualization and manipulation of the blade, Aiach et al proposed a T-shaped osteotome with a semi-flexible guide parallel to the blade, which, being located on the surface of the skin, allows one to clearly determine and control the specified osteotomy depth.
Guyuron9 introduced a safety cutter used for minor root deepening when a very limited - conservative - osteotomy is indicated. The main complications of using the incisor are the development of seroma and penetration into the frontal sinus. In this regard, sequentially staged bone removal has been proposed instead of continuous, in order to avoid movements in the cephalo-caudal direction in favor of the lateral ones. If additional resection of soft tissue is necessary, a superficial dissection is performed, then the bone is removed along with the procerus muscle attached to it.7 After surgery, in order to avoid the development of a hematoma and further development of fibrosis and connective tissue scar, a dense pressure bandage8 or a special splint is recommended for several days.
Increasing the height of the nasal root
Although in the past, the height of the nasal bridge flush with the root was considered as an aesthetic standard, nowadays preference is given to a natural, enhanced nasal profile. In this regard, anatomically reduced nasal root has become one of the reasons for seeking rhinoplasty.10 According to a study by Mowlavi et al.6 Nasal root augmentation is becoming an increasingly popular procedure in North Americans, especially in men. The preferred nasion height of both sexes was 10 mm, and was practically unacceptable below 7 mm.
Augmentation of the nasal root softens the expression of anger on the face, as well as the severity of pseudohypertelorism (increased distance between the palpebral fissures).10 A low nasal root creates the impression of a flattened, wide face with blurred contours; adequately increasing nasion height with enhanced profile and clear orbital framing improves appearance10. Nasofrontal augmentation in some cases helps to correct the bridge of the nose without additional tissue resection, and also visually lengthens a short nose11, since a smoother nasofrontal angle creates the impression of lengthening the nose, while a deep nasofrontal angle creates the impression of shortening12.
Surgical technique
The doctor decides on the type (natural or synthetic), as well as the size, shape and location of the implant.
Implants
The patient’s own cartilage, previously taken from the nasal septum or auricle, can be used as an implant, but in this case there is a risk of partial resorption of the implant or displacement. The temporo-parietal fascia can also be used as a source of autograft in patients with a low nasal root.13 In addition, synthetic implants made of polytetrafluoroethylene (Gore-Tex)10,14 are widely used. Unlike manipulation of the lower dorsum of the nose, the use of Gore-Tex for root correction does not pose the risk of infection or extrusion, provided that the mucosa remains intact during surgery11. In Asian countries, silicone implants are most often used for nasal root augmentation, mainly in the form of factory-made silicone rubber or wafers15. When using synthetic materials, the most likely complications are implant extrusion, foreign body reaction, infection, or implant migration, although these reactions are extremely rare with newer biomaterials.
Implant size
The dimensions of the implant vary, but rarely exceed 1.2 cm vertically and 2 cm horizontally.10
Implant shape
According to Daniels16, overcorrection, implant visibility and suture line displacement are the main technical errors of the operation when using natural cartilage as an implant. To avoid these problems, the upper pole of the cartilage implant should be cut thicker than the lower one, which will allow it to be hidden in the dorsum of the nose. In addition, the lateral edges of the implant should be rounded and proportionate10. The outer and lower edges of the Gore-Tex synthetic implant should be beveled11.
Implant placement
A pocket for placing the implant is formed in the subperiosteal space, and its size must strictly correspond to the size of the implant in order to avoid displacement in the future. Multilayer implants can be used. The implant is placed slightly above the desired point, since contractions of the procerus tend to displace the implant downward. If the procerus is overactive, the use of botulinum toxin is indicated.10 If a pocket is too large, it is recommended to sut the implant to the skin to prevent displacement. First, the implant is sutured using an absorbable thread, then the skin. The stitches are removed after a few days8. To reduce the likelihood of implant displacement, it is additionally fixed with sutures to the AlloDerm matrix strip, or the latter is used as an overlay graft10.
Conclusion
The nose is the most prominent and central part of the face. From an aesthetic point of view, the nasal root separates the nose and forehead. Any change in this area of the face has immediate consequences for the perception of the face in general and the nose in particular, namely, its length and projection. Anatomical analysis is an important step for performing high-quality rhinoplasty when deciding on the surgical plan, i.e., increasing or decreasing the height of the nasal root. The use of the latest biomaterials guarantees a reduced incidence of complications and better aesthetic results when performing rhinoplasty to correct a sunken nasal root.
References
- Byrd HS, Hobar PC. Rhinoplasty: a practical guide for surgical planning. Plast Reconstr Surg 1993;91:642-54. [8446718]
- Mathes SJ. Plastic Surgery Vol 2, part 1 (2nd ed), Philadelphia, PA, El-sevier, 2006.
- Conrad K, Gillman G. Refining os-teotomy techniques in rhinoplasty. J Otolaryngol 1998;27:1-9. [9511112]
- Aiach G, Laxenaire A, Vendroux J. Deepening the nasofrontal angle. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2002;26 Suppl 1:S5. [12454715] [doi:10.1007/s002 66-002-4309-3]
- Guerrerosantos J. Nose and paranasal augmentation: autogenous, fascia, and cartilage. Clin Plast Surg 1991;18:65-86. [2015751]
- Mowlavi A, Meldrum DG, Wilhelmi BJ. Implications for nasal recontouring: national position preferences as determined by a survey of white North Americans. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2003;27:438-45. [15029456] [doi:10.1007/s00266-004-3083-9]
- Guyuron B. Precision rhinoplasty. Part II: Prediction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1988;81:500-5. [3347658]
- Tardy ME. Rhinoplasty: The art and the science. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders Co, 1997.
- Guyuron B. Guarded burr For Dee-pening of Nasofrontal Junction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1989;84:513-6. [2762410] [doi:10.1097/00006534-198909000-00023]
- Becker DG, Pastorek NJ. The radix graft in cosmetic rhinoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2001; 3:115-9. [11368664] [doi:10.1001/archfaci. 3.2.115]
- Johnson CM Jr, Alsarraf R. The radix graft in cosmetic rhinoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2001;3:120-1. [11368665] [doi:10.1001/archfaci. 3.2.120]
- Tardy ME Jr, Becker D, Weinberger M. Illusions in rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 1995;11:117-37. [904 6602] [doi:10.1055/s-2008-1064529]
- Guerrerosantos J. Nose and paranasal augmentation: autogenous, fascia, and cartilage. Clin Plast Surg 1991;18:65-86. [2015751]
- Godin MS, Waldman SR, Johnson CM Jr. Nasal augmentation using Gore-Tex. A 10-year experience. Arch Facial Plast Surg 1999;1:118-21. [10937089] [doi:10.1001/arch-faci.1.2.118]
- Wang JH, Lee BJ, Jang YJ. Use of silicone sheets for dorsal augmentation in rhinoplasty for Asian noses. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 2007; (558):115-20. [17882581] [doi:10. 1080/03655230701624996]
- Daniel R.K. Diced cartilage grafts in rhinoplasty surgery: current technologies and applications. Plast Re-constr Surg 2008;122:1883-91. [19050542] [doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013 e31818d2104]