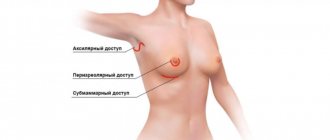
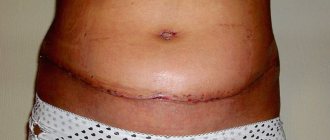
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy is the reconstruction of the breast using plastic and reconstructive surgery after it has been completely or partially removed (mastectomy).
Breasts are one of the main symbols of femininity, so removal of the mammary gland during a mastectomy is especially difficult for women. Reconstructive plastic surgery allows you to recreate one or both mammary glands after their removal, helping the patient return to a full life after an illness and again feel like an attractive and confident woman.
Breast reconstruction after breast removal can be delayed (performed after a mastectomy), or one-stage, when the procedure is performed simultaneously with the main breast surgery.
Visually and to the touch, your breasts after reconstruction will look absolutely natural, you will again be able to wear a cleavage and beautiful underwear, sunbathe on the beach in a swimsuit, and not be embarrassed by tight-fitting clothes.
Existing types of breast reconstruction
Breast reconstruction surgery can be performed in different ways. There are several types of reconstruction: immediate and delayed, with the installation of implants or transplantation of one’s own tissues, unilateral or bilateral. The choice of a specific technique is made by a doctor and depends on the following factors:
- Features of the tumor removal: excision of a sector of the mammary gland or complete removal, type of operation performed. So, during a subcutaneous mastectomy, the surgeon preserves the skin, sometimes the areola and nipple. In this case, installing an implant is sufficient. With total removal, the skin, nipple-areolar complex, glandular tissue and part of the pectoral muscle are completely excised. In this situation, a more complex operation is required, which will be performed in several stages, since it will definitely not be possible to solve all the problems at once.
- Breast conditions. The doctor finds out whether sufficient amounts of skin are present, whether the muscles are preserved, and what is the shape and size of the preserved mammary gland.
- Forms and stages of cancer. The surgeon must clarify whether remission has been achieved and whether continuation of treatment is planned.
- General condition of the patient's body. The surgeon must find out how healthy the woman is, whether she can undergo extensive surgery, and whether there are the required volumes of donor tissue (if a transplant operation is performed).
- Patient's wishes. The plastic surgeon finds out what the patient is ready for and what results she expects after the operation.
Below we discuss in detail the existing types of breast reconstruction performed by modern plastic surgeons.
| Immediate and delayed breast reconstruction | Simultaneous reconstruction is performed simultaneously with a mastectomy. Immediately after removal of the part of the breast affected by the tumor, a physiologically normal shape is created. But this option is possible if a woman has reserves of skin and soft tissue. Delayed breast reconstruction after mastectomy occurs later and becomes the final stage of a woman’s rehabilitation. As a rule, plastic surgery is prescribed after tissue healing and completion of treatment. |
| One-stage reconstruction | In one-stage reconstruction, plastic surgery is performed in one stage when the woman has a sufficient musculocutaneous pocket to install the prosthesis. If the skin and muscles are completely excised, then prosthetics will be problematic. One-stage restoration is carried out with implants or using a Becker prosthesis - a combination of an expander and an implant. In the latter case, a hollow prosthesis is placed into the mammary gland cavity and then filled with contents, gradually stretching the formed pocket to obtain the final result. |
| Two-stage breast reconstruction | In two-stage breast reconstruction, plastic surgery is performed in two stages. At the first stage, an expander is placed into the mammary gland (under the pectoralis major muscle or above it), which initially remains empty inside. Then, weekly, a solution is injected through the valve (hole) to fill the expander and stretch pocket. It takes 3-6 months to stretch the tissue to the desired state. A permanent, individually selected implant is placed in the prepared pocket (cavity). The incisions are made along the previous stitches, so that no new scars remain. |
| Unilateral and bilateral reconstruction | With unilateral reconstruction, only one breast is operated on, while with bilateral reconstruction, surgery is performed on both breasts. As a rule, bilateral plastic surgery is performed, since with a unilateral technique the bust often becomes asymmetrical. When both breasts are corrected, the second one can undergo a lift, augmentation with an implant, or, conversely, reduction. |
Types of surgical operations
According to the clinical recommendations of the Association of Oncologists of Russia, partial resection of the mammary gland, that is, organ-sparing surgery, can be considered a sufficient method of treatment only at the 1st stage of breast cancer. Starting from stage 2, removal of the gland, that is, mastectomy, is recommended.
Depending on the extent of the spread of cancer cells, mastectomy surgery for breast cancer can be performed using one of three methods:
- Madden mastectomy preserves the skin of the breast. Only the nipple and areola of the breast are removed. The mammary gland is excised completely. This method is used in the absence of metastases in muscle tissue.
- Skin-sparing surgery allows you to reconstruct the mammary gland, that is, restore its volume and shape. At the international clinic Medica24, this is done simultaneously with a mastectomy, using a polyurethane implant. This technique has a number of serious advantages.
- Patey's mastectomy is a more extensive operation. It involves removing not only the breast, but also the axillary lymph nodes and the pectoralis minor muscle.
- A Halstead mastectomy involves removing the breast, axillary nodes, pectoral muscles and fat. It is performed for advanced cancer with deep metastases.
Before choosing one or another surgical plan, the international clinic Medica24 conducts a thorough and thorough diagnosis. Using MRI or CT with contrast, the boundaries of tissue damage by cancer cells are determined.
Until relatively recently, surgeons preferred to play it safe and remove lymph nodes just in case, in order to minimize the risk of relapse as much as possible.
Currently, the method of studying “sentinel” lymph nodes is considered preferable. For this purpose, a radioactive or fluorescent drug is used. The first lymph node to which it spreads is determined. A piece of tissue is taken from this node using a biopsy and subjected to histological examination. If no cancer cells are found in it, this means that there are no metastases in the lymph nodes and they do not need to be removed.
Removal of lymph nodes reduces the quality of life and can cause edema. Meanwhile, in some cases it has virtually no effect on the risk of disease relapse after surgery.
When choosing a treatment plan, we always lean toward organ-sparing surgery. But in the case of breast cancer, this is not always advisable, since it has been proven that its complete removal significantly affects the prognosis of the disease.
The main reason why women seek to avoid radical surgery is the desire to maintain an attractive appearance. But the development of modern reconstructive plastic surgery makes this argument untenable.
The methods of oncoplastic surgery used in the international clinic Medica24 make it possible to fully comply with the safety requirement - unconditional and complete removal of the tumor, minimizing the risk of relapse, preserving the health and life of the patient. And at the same time maintain an aesthetic appearance, attractiveness, not cause psychological trauma to a woman, preserve her self-esteem and social self-awareness.
The optimal option for oncoplastic surgery is skin-sparing mastectomy with simultaneous breast reconstruction.
Materials used
Two groups of materials are used for breast reconstruction operations:
- Prosthetics with implants. Prostheses replace the natural physiological tissue of the breast and help achieve an ideal anatomical shape. This option is suitable if it is impossible to use your own tissues, for example, when the patient has a thin or slight build. But to install the prosthesis, sufficient volumes of skin are required, since it is necessary to have your own tissues to cover the implant. In addition, prosthetic breasts may differ significantly from natural breasts, sometimes requiring mammoplasty on the second breast to achieve symmetry. It is also worth noting that silicone implants are not recommended for installation if the woman will subsequently undergo radiation therapy.
- Autologous plastic surgery. The breast is reconstructed with tissue taken from the patient’s body, for example, from the back, hips, abdomen, buttocks.
The appropriate option is selected during consultation after the examination.
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION USING AUTOLOGIC TISSUE
An operation to restore the chest muscles can be performed using the patient’s tissue - a flap is taken from the back, abdomen, buttocks. In some cases, reconstruction is limited to using only the skin, fat layer, and blood vessels - the muscle is not affected, which reduces trauma.
Thoracodorsal technology involves the use of a flap from the back. Since the fat layer in this area is usually not very developed, an implant can be used to add volume.
How is the operation performed? The formed flap is transplanted to the site of the removed breast through a tunnel under the skin. Blood vessels are preserved to the maximum. The operation ends with the formation of the mammary gland and suturing. This method is suitable for women with small breasts. The muscular function of the back is not damaged, but the scar remains (slight disproportion of the back may appear).
If the bulk of adipose tissue is concentrated in the abdominal region, a flap is taken from the rectus abdominis muscle and then moved through a tunnel to the transplantation site. Additionally, an implant can be used during reconstruction. If a vessel has to be cut during surgery, it is sutured to the flap using microsurgical equipment. The TRAM Flap method is accompanied by abdominoplasty and reconstruction of the navel (displacement occurs when the material is taken).
The abdominal flap is transferred using the DIEP FLAP method. Unlike the previous reconstruction method, the material contains only skin, adipose tissue, and blood vessels. This reduces the trauma of the operation and avoids abdominal muscle weakness. Due to the need to suture all vessels, reconstruction and restoration of breast elasticity takes about five hours.
S-GAP and I-GAP are used if the bulk of adipose tissue is concentrated on the buttocks. A flap taken from the upper or lower part of the buttocks is used. Skin, fat, and blood vessels are transplanted, but the muscles are not affected. Since surgeons have to completely restore the vessels, the duration of the operation can reach 10-12 hours. To balance the proportions, liposuction of the second buttock is usually performed. The advantage of S-GAP and I-GAP reconstruction is the possibility of repeat surgery if the graft does not take root. When using other recovery methods, this is not possible.
Complications of the operation include pain and the formation of a rough scar at the site where the material was taken. If the surgeon is insufficiently qualified, tissue rejection (necrosis) is possible. That is why it is so important to contact a trustworthy medical institution. The clinic has professional technical equipment. There are comfortable rooms with 24-hour medical care.
What implants are used
For female breast reconstruction, you can use the same implants as for breast augmentation or lifting with shape or size correction. Prostheses vary in shape, volume and materials. They can be rough and smooth, teardrop-shaped and round.
Implant shells are made from silicone. Its advantages include biocompatibility with human tissue, strength, elasticity, durability, hypoallergenicity and resistance to various influences.
There are several types of implant fillings: saline solution (saline solution), biogel, silicone cohesive gel. Each filler has its own pros and cons, so your doctor will help you choose the appropriate option during a consultation, taking into account your specific situation. The most common ones at the moment are implants filled with silicone gel.
Using your own tissue: existing transplantation methods
Transplantation of your own tissue allows you to achieve the most natural structure. But the intervention is complex, and the recovery is long and difficult. Complications include blood clots, necrosis of donor fragments, scarring, prolonged healing, and deformation of tissue collection areas.
Two types of flaps are used as grafting materials: free and pedicled. In the first case, tissues move along with the vessels that penetrate them, which during surgery are sutured to the vessels in the transplantation area. This is a microsurgical intervention performed under a microscope with multiple magnification. In the second case, the flap is not separated from the vascular network, but remains on the so-called feeding pedicle, consisting of vessels. This piece is delivered to the chest through a subcutaneous tunnel in the body.
All transplanted flaps are divided into groups:
- thin, consisting of layers of skin and subcutaneous fat: SGAP, SIEA, IGAP, DIEP (abbreviations of medical names that describe the structure and localization of tissue fragments);
- more dense, including not only skin and fat cells, but also muscles: TRAM, LD, TUG.
The transplantation technique involves several steps:
- Creating a pattern of the flap, cutting it out. The fragment is created on such parts of the body as the buttock, abdomen (lower part), and area of the latissimus dorsi muscle.
- Giving the flap its final shape.
- Transplantation itself is the fixation of the fragment at the site of the removed breast.
- Stitching of vessels and tissues.
- Performing plastic surgery of the donor area - where the flap was borrowed.
Sometimes the use of one's own tissue is combined with the use of implants. You can also additionally use your own fat tissue (from the abdomen, thighs, buttocks), and this method is called lipofilling.
Breast reconstruction using your own tissue
An alternative to silicone implants in breast reconstruction can be the use of one’s own tissue in the form of flaps, which include skin with subcutaneous tissue, as well as a fragment of muscle through which the blood supply to this flap occurs (see Figure 3).
Figure 3. Breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Scheme
Most often, these techniques are used to create a large mammary gland, as well as in cases where the stretching of the reconstruction area is compromised by scar changes or radiation therapy.
The most common site for tissue collection for reconstruction is the lower abdomen. Some women develop excess fatty tissue in this area with age and are not averse to getting rid of it. They remove this excess in the same way as an abdominoplasty, but this tissue is then used to create volume and shape to the lost breast.
This is a rather complex and labor-intensive operation that lasts several hours and may require a stay in the intensive care unit, blood transfusions and a hospital stay of 7 to 10 days. In this regard, the cost of reconstruction using your own tissues is significantly higher than using silicone implants.
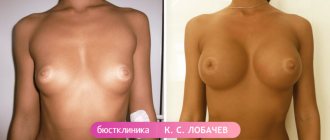
However, reconstruction with your own tissue rarely requires repeated interventions, and also allows you to create symmetrical breasts of almost any size compared to the opposite one (see photos 11-16).
Photo 11. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 1
Photo 12. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 1
Photo 13. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 1
Photo 14. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 2
Photo 15. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 2
Photo 16. Before and after breast reconstruction using your own tissue. Patient 2
Areola and nipple formation
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy usually includes nipple and areola formation. This stage is final and very important. The nipple-areolar complex is restored either simultaneously with the reconstruction, or later, when the tissue has healed.
The nipple can be created from the skin of the reconstructed breast (if there is a sufficient amount of free skin) or from the epithelial tissues of other parts of the body, for example, the areola of a healthy breast (if it is large), the earlobe or the labia minora.
The areola around the nipple is formed through tattooing, which gives the skin the desired dark shade, imitating natural pigment. If you get a medical tattoo, the nipple-areola complex looks more natural.
Breast reconstruction using combined techniques
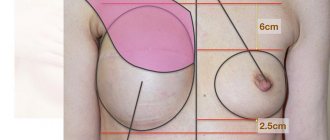
There are situations where your own tissue is required, but it is not enough to create sufficient breast volume. In such cases, combined techniques are used, when a small flap from the back is used, moved to the chest wall area and a silicone implant of the required volume and shape (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. Combined breast reconstruction. Scheme
This reconstruction method is used in women who have had radiation therapy. To reduce the risk of complications and improve blood supply to the area, these patients require repositioning of vascular-rich tissue that will provide long-lasting aesthetic results (see Figure 17).
Photo 17. Result of combined breast reconstruction
Preparation for the operation
Preparation for breast reconstruction involves undergoing a full examination, during which the patient’s condition is assessed and contraindications are identified. Preoperative diagnostics includes preliminary examinations by specialized specialists: surgeon, oncologist, mammologist, gynecologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist.
An electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the mammary glands, and in some cases MRI or CT are prescribed. The woman also takes blood tests for Rh factor and blood group, for infections (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis), biochemistry, coagulation, general, and some hormones (if necessary). A urine test is performed.
The preparatory period includes some restrictions and recommendations:
- A week before the scheduled date of surgery, the patient stops drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Two weeks before surgery, medications that affect the blood coagulation system are discontinued (this group of drugs includes acetylsalicylic acid and oral hormonal contraceptives).
- On the eve of the operation, the patient takes a bath or shower.
- 12 hours before the exact time of the operation, stop drinking any liquids and food.
Possible complications after breast reconstruction
For most patients, the operation proceeds without complications. If you follow all the recommendations of your attending physician and constant monitoring by the clinic’s surgeons in the early rehabilitation period, you will be able to avoid or promptly prevent the possibility of any surgical complication.
Breast reconstruction in Moscow | Author's techniques and prices at the clinic of Professor S.N. Blokhin
Breast reconstruction is a plastic and reconstructive surgery aimed at restoring the breast after a mastectomy. Options for performing the operation, features of the rehabilitation period.
Recovery period
The duration of rehabilitation will depend on the complexity of the operation performed and on the individual characteristics of the particular patient. On average, recovery can take from several weeks to several months.
The patient remains in the hospital from 4-5 days to two weeks, depending on the speed of tissue recovery and healing. At first, surgical sutures are treated; severe pain is relieved with painkillers.
Important! In the first day or two after reconstructive breast surgery, it may be difficult for the patient to move, and yet during this difficult time, one must begin to maintain minimal physical activity in order to maintain normal blood supply to the extremities and prevent the formation of blood clots. You need to get up and walk a little.
Recovery after breast reconstruction surgery involves following several rules:
- For the first two to four weeks, the patient should not raise her arms and sleep on her side and stomach.
- For 1.5-3 months, the woman will wear special compression garments on an ongoing basis, without taking them off even at night. Then, for a year, a support bra should be worn before exercising.
- You can resume physical activity no earlier than three months after the operation. This should be done gradually, starting with simple exercises. You can return to full training later – about six months after breast reconstruction.
- For two months you cannot go to baths, saunas, or solariums. Visiting public bodies of water, including swimming pools, is prohibited.
- Recovery also requires regular visits to the doctor, both the surgeon who performed the operation and the treating oncologist (if the reconstruction was performed after a mastectomy due to oncology).
It is important to understand that the terms defined above are individual, and the surgeon’s recommendations must be strictly followed.
Photos and videos taken after the mastectomy prove that in the short term after the operation, swelling persists, which gradually goes away. The final results are assessed after complete healing of the tissues and completion of scar formation. This usually takes about a year.
REHABILITATION AFTER BREAST RECONSTRUCTION SURGERY
The first days after reconstruction will have to be spent in a hospital under the supervision of doctors - our clinic offers patients 14 comfortable rooms. The stitches will be removed in two weeks. For about six months after breast reconstruction, you need to wear a special bra or bandage. If drainage has been installed, you will have to take care of the system and measure the amount of fluid released. Since painful sensations are observed at first, the doctor may prescribe painkillers.
After the procedure, you should avoid heavy lifting, physical activity, and intimate contact for 4-6 weeks. It is advisable to delegate most of the household chores to your loved ones. Swelling and hematomas will persist for about 8 weeks after reconstruction, so it will not be possible to immediately assess the aesthetic result of the operation. Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, or hot countries is excluded (this opportunity will appear 3 months after the operation or later). At the frequency prescribed by the doctor, the woman will need to undergo follow-up examinations, as well as mammographic examinations.
Clothing during the recovery period should be comfortable - not squeezing the mammary glands and the site where the flap is taken. It is advisable that the blouse or blouse have a fastener (buttons, zipper). The doctor usually recommends breast reconstruction with massages in case of implant installation. If autologous tissue was used in the reconstruction, then physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed to overcome the muscle weakness of the donor site.
Possible complications
Complications can develop both during the first time after plastic surgery and in the delayed period. The beginning of recovery can be overshadowed by the following troubles:
- seam divergence;
- suppuration of postoperative sutures;
- formation of keloid scars;
- infection of the skin and fat or deeper tissues, sepsis;
- necrosis (especially during transplantations);
- hematomas, hemorrhages;
- seromas.
If we are talking about delayed consequences, then reconstruction of the mammary glands after mastectomy with the help of implants can cause capsular contractures (pathological fibrosis of the tissue around the implant), displacement and rejection of prostheses, as well as implant ruptures. In these cases, repeat plastic surgery will be required to eliminate complications.
Why remove the second breast?
Clinical studies conducted in the second half of the twentieth century showed that the development of breast cancer is influenced by a hereditary factor - mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
BRCA genes prevent the formation of malignant tumors. But if a mutation occurs in them, they cease to perform their function, and the development of breast cancer becomes almost inevitable.
In this case, removal of the mammary glands reduces the risk of cancer by 97%, this is proven by all clinical studies conducted to date.
In 2013, the famous American actress Angelina Jolie had both mammary glands removed after doctors discovered that she had a hereditary mutation of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. This caused a great public outcry and became a kind of precedent and example for other women with a similar genetic factor.
Unfortunately, the legislation of the Russian Federation prohibits the performance of such preventive procedures in public clinics. Breast removal can only be performed if cancer is diagnosed. If there is no tumor in the mammary gland yet, it will not be removed, even if the risk of its occurrence is very high.
This forced many women to go abroad and undergo operations in the USA and Western Europe. Today there is no such need. Preventive surgery can be performed in Moscow, at the international clinic Medica24. And at the same time, not only get rid of the risk of cancer, but also lose practically nothing in terms of appearance. Indeed, in our clinic, mastectomy is performed with simultaneous breast reconstruction. Installing a polyurethane implant will not just recreate the breast, but can make its shape even more harmonious and attractive.
In 2010, such preventive operations were officially approved by the Ministry of Health and included in the List of technologies permitted in medical practice in the Russian Federation. This practice complies with the clinical recommendations of the Russian Association of Oncologists.
However, such operations are still not available in public medical institutions and are performed only in private clinics, such as the International Clinic Medica24, where surgical interventions are performed in accordance with international protocols adopted in Western Europe and the United States.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Prices
| Medical | from |
| Mastopexy areolar | 75 000 ₽ |
| Mastopexy circumvertical | 110 000 ₽ |
| Mastopexy anchor | 150 000 ₽ |
| Mammoplasty (enlargement) | 80 000 ₽ |
| Mammoplasty (reduction) | 170 000 ₽ |
| Areola correction (1 nipple) | 20 000 ₽ |
| Areola correction (2 nipples) | 40 000 ₽ |
Installment plan
You can find out more about prices here