Why can’t you exercise after breast augmentation?
Sports activities after mammoplasty are prohibited for a simple reason - the likelihood of bleeding and trauma to the breast during forceful exercise. Physical exercises that patients perform in the early stages after plastic surgery on the breast can lead to divergence of postoperative sutures and the formation of large hematomas. According to statistics, most complications after augmentation mammoplasty occur precisely because women do not comply with the rest regimen that the plastic surgeon recommends during rehabilitation.
Sports after mammoplasty: when can you return to exercise?
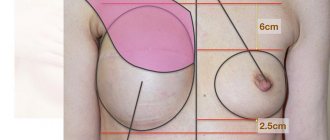
This is one of the most popular questions that every woman asks during a consultation before breast augmentation or reduction surgery with a plastic surgeon. Any doctor will tell a patient that after major surgery, the body needs time to regain its strength. As practice shows, the pectoral muscles return to normal within 3-6 months after breast augmentation. During the same time, tissue swelling subsides and scars heal completely. The mammary glands acquire a new beautiful shape. Only limiting physical activity and activity will minimize the postoperative risks of silicone implant displacement.
Therefore, during the period of rehabilitation after augmentation or reduction mammoplasty, the following are prohibited:
- lifting weights;
- running, swimming;
- bodybuilding classes;
- push-ups, lifting dumbbells and barbells;
- dancing.
After examining the mammary glands 3 months after breast augmentation, the plastic surgeon may allow athletics and jogging. At the same time, it is very important to observe a gentle regime for the shoulder girdle. More serious physical activity is possible only 6 months after surgery.
When can you exercise after mammoplasty? This is determined by the plastic surgeon after examining the mammary glands, since the timing for each patient is strictly individual. The time it takes to complete rehabilitation after breast augmentation, reduction or lift depends on many factors, in particular:
- on the size and shape of the silicone implant that the plastic surgeon used during the operation;
- type of plastic surgery and method of implant placement;
- density of breast tissue.
If a woman has enlarged her breasts by several sizes at once, then the time frame for returning to physical activity and sports may increase several times. And if during augmentation mammoplasty the implant is installed under the pectoral muscle, then physical stress on the shoulder girdle should be excluded for up to 6 weeks.
Recovery after mammoplasty
Internal absorbable sutures do not require removal. It should be borne in mind that such a seam or such a thread for a long enough time (more than a month) can affect the appearance and consistency of the seam itself. Because of this, the seam is dense, inactive and often compressed. The absorbable material loses its strength and disintegrates into fragments within 1-2 months. By this time, the scar itself relaxes.
If the absorbable sutures are separate subcutaneous loops, then with thin skin (this is especially typical for internal sutures in the areola area during a breast lift or breast augmentation through the areola), pustules may appear in these places during the second month. When opened or squeezed out, a small amount of cloudy liquid is released. This is precisely the partially dissolved suture material. In some patients this can be quite pronounced. The solution is opening the abscess and using an alcohol or vodka compress.
A special topic is the use of liquids such as brilliant green, fucorcin, potassium permanganate and miramistin. If you leave aqueous Miramistin for use in the intimate area, for which, in fact, it is recommended, then other liquids can be safely excluded from the methods of treating postoperative sutures.
If you want to use something other miraculous than a vodka or alcohol solution, then you can confidently recommend an iodine solution. You need to be careful with it, do not apply napkins well soaked in it to the skin, do not leave it under bandages, because. Iodine skin burns occur frequently. It is better to dilute pharmaceutical 5% iodine with alcohol or vodka in half. With this dilution, iodine burns do not occur.
For compresses or for any other purpose, you can use Betadine ointment or solution. This is a form of iodine with a slow and prolonged release and a very effective disinfecting effect. The disadvantage of iodine preparations is their coloring effect.
Crusts on the surgical suture.
It must be said that if the seam is well adapted, i.e. the edges are brought together and evenly touch each other, and care for it is regular and as described above (washing, treatment, antiseptic), then no crusts form. Anything that has accumulated or dried in the seam area can be easily washed off with water during the first shower for 2-3 days. Crusts can form at the location of the drains, at the site of uneven skin adhesion, at the site where there was or is developing an infection. On one side, the crust on the suture covers the defect and healing occurs underneath it. On the other hand, it can cover or cover the abscess, and the lack of outlet for pus aggravates the inflammation. It follows that it is necessary to carefully monitor such crusts, soak them when washing, carefully remove them if possible, and if there are signs of infection (new: redness, pain, swelling), rush to see a doctor.
Now we can postulate basic recommendations after mammoplasty or breast augmentation surgery
What to do with these seams, crusts and threads?
- It is imperative and imperative to take a shower and wash your body, surgical site and sutures with soap or something similar once or twice a day.
- After wiping or drying the surgical site and sutures, wipe the suture with an alcohol solution, vodka or an alcoholic antiseptic solution. Morning and evening, twice a day is an excellent option.
- Betadine can be considered as an effective alternative water-based antiseptic.
- You should forget about brilliant green, potassium permanganate or fucorcin.
- Ointments “for healing” are definitely not needed at this stage.
- In principle, it makes no sense to seal a wound or seam with a plaster or tight bandages. You can add gauze or a napkin to prevent friction on the laundry. In the first days, this may be justified by the possible release of ichor from the wound.
- Special silicone patches for the prevention of hypertrophic and keloid scars can be applied after the sutures are removed. The same applies to various ointments, such as dermatix or silicone.
- Ointments such as Solcoseryl or Contratubes do not have any proven therapeutic effect, so their use is not justified. Moreover, their inefficiency is costly to the consumer.
- Hydrogen peroxide can be used to dissolve dried blood or superficial crusts and stop superficial bleeding. It is hardly suitable for other purposes.
What can you do after breast surgery?
Sports after mammoplasty under the muscle are a necessary condition for the body’s recovery, but only if you return to physical activity gradually and moderately.
- In the first 3 weeks after breast augmentation, reduction or lifting, when the implant is being fixed and the sutures are healing, the patient is allowed only short walks. It is strictly forbidden to lift even light weights.
- Starting from 4 to 6 weeks after mammoplasty, the patient should raise his arms up, thereby developing the shoulder girdle. To do this, you should perform a simple “cheerful person” exercise.
- After 4 weeks after augmentation mammoplasty, the patient can begin swimming short distances. You can also lift small dumbbells whose weight does not exceed 2 kg.
- 3 months after surgical breast augmentation, you are allowed to do abdominal exercises, stretching, and raise your arms above your shoulders.
- Stretching the pectoral muscles, push-ups, and chest presses can only be performed 6 months after mammoplasty.
It is necessary to play sports for the first 4 weeks in compression underwear, and after this period in a sports bra. Strictly follow the recommendations of the plastic surgeon, only in this case the new breast will delight you with the beauty of its shape and size.
The information on the site was personally verified by plastic surgeon Maxim Aleksandrovich Osin; if you have any additional questions, call the phone number listed on the site.
Quality of life of patients after reconstruction with implants and their own tissues
Early diagnosis of a tumor, treatment, including surgery, followed by radiation and chemotherapy are different stages of the fight against breast cancer, the goal of which is to increase the patient’s life expectancy and only indirectly improve its quality. Breast reconstruction is aimed primarily at improving the patient’s quality of life, which makes this type of surgery the most important step in an integrated approach in the fight against cancer in a woman.
Most often, reconstruction of the mammary glands consists of several stage operations: restoration of the volume and shape of the breast, reconstruction of the nipple-areolar complex and elimination of asymmetry, which involves correction of the volume and shape of the healthy mammary gland.
Breast reconstruction can be performed simultaneously (immediately after removal of the breast in one surgical procedure) or delayed (the operation is performed some time after chemotherapy or radiation therapy). Depending on the type of surgery chosen, patients perceive the result of reconstruction differently. The delayed type causes greater damage to the moral and psychological state of a woman, since for some time she will have to live without a mammary gland. For these patients, any result of the operation will be a priori more satisfactory than the complete absence of breasts.
Reconstruction methods
Currently, there are several methods of breast reconstruction in plastic surgery. The method of autotransplantation of one's own tissue involves the transplantation of free revascularized tissue flaps or tissue flaps on a feeding pedicle. Free autotransplantation of adipose tissue - lipofilling - is being introduced into practice quite actively. The use of breast implants is often justified, but may require the prior installation of a tissue expander. An alternative option is to install a permanent expander implant. Each type of operation has its own indications and contraindications, pros and cons, and the surgeon decides individually which type of reconstruction to choose. The choice depends on many factors, including the method of previous mastectomy and the therapy performed. There is a significant difference between a radical mastectomy (Halstead) and a subcutaneous mastectomy. These operations have different results and different indications for one or another type of reconstruction. But it cannot be said that reconstruction methods are mutually exclusive; they often complement each other.
Autotransplantation involves taking various types of flaps of the patient’s own tissue and moving them to the area of the removed mammary gland. Previously, the TDL (thoracodorsal flap) was widely used - a flap based on the latissimus dorsi muscle, consisting of skin, fat and muscle tissue. It moved on a vascular pedicle to the area of the developing mammary gland. Despite the lack of volume of tissue grafted from the back, this provided sufficient tissue coverage for subsequent placement of the implant (or expander and then implant). Most often, transplantation of a thoracodorsal flap involved further increasing the volume of the mammary gland using an implant.
The most common method of breast reconstruction today is reconstruction with a TRAM flap (rectus abdominis flap). The disadvantage of the operation is the reduction of the frame function of the anterior abdominal wall. This entails subsequent problems in the abdominal area: the formation of prolapse of the anterior abdominal wall. Attempts to close this defect with various mesh materials made it possible to improve the situation, but not radically.
The development of vascular microsurgery gave a powerful impetus to the development of reconstructive surgery. Plastic surgeons have a unique opportunity to use free revascularized tissue flaps in reconstruction, in which the blood supply is surgically restored.
The most modern method of breast reconstruction is considered to be a DIEP flap (free revascularized skin-fat flap of the anterior abdominal wall). The surgeon takes a flap from the lower abdomen, which is only skin and fat tissue (the closest in softness, texture and appearance to breast tissue), and moves it to the reconstruction area, restoring blood circulation using microsurgical techniques. This method is complex and requires the surgeon to have extensive surgical experience, deep knowledge of vascular anatomy and perfect command of microsurgical techniques. If the operation using the DIEP FLAP method is performed correctly and according to indications, without serious complications, then its result will be very impressive. The method may not be suitable for thin patients, since not everyone has a sufficient amount of subcutaneous tissue in the abdominal area. If the mammary glands are small, the operation does not require the removal of a large volume of tissue; flap transplantation can be supplemented with an implant.
Features of breast reconstruction
In the area where a particular flap is harvested, a tissue defect always occurs—a donor site defect. If the operation is not planned correctly, a donor site problem may arise. When moving a flap to the breast area, it is necessary to cover the defect in the area from which it was taken. In cases where patients have a deficiency of their own tissues (thin physique, stretched and insufficiently elastic skin, scars from previous operations), it becomes difficult to close the defect. That is why reconstruction with abdominal flaps is always preferable: it is easier to close such a defect, a low postoperative scar is less noticeable and hidden by underwear. Also, the patient simultaneously receives the benefits of abdominoplasty, getting rid of excess skin and fat and the apron in the lower abdomen. A striking example of this is reconstruction with a DIEP flap, in which the defect is easiest to close, and only an inconspicuous scar remains at the operation site. The use of a thoracodorsal flap in breast reconstruction, on the contrary, has significantly more disadvantages (including due to the presence of a noticeable scar in the donor area).
The problem of the donor zone does not exist in the case of breast reconstruction with implants or when using the method of autotransplantation of free adipose tissue - lipofilling.
In this regard, breast reconstruction using implants is a rational solution. But only on the condition that the patient has not undergone a course of radiation therapy (their own tissues are damaged and become quite dense, scarring changes appear). The deficiency of your own tissues, which are not enough to “cover” the implants, also becomes a contraindication to their installation. In such cases, immediate implantation is practically impossible, and preliminary dermatension (skin stretching) by implanting an expander is often required. Only after this stage is it possible to replace the expander with implants. It is also possible to install a permanent expander implant, which does not require replacement.
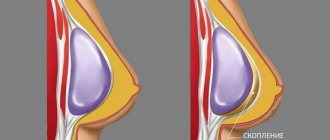
The main problem with silicone implants is that they are made of foreign material. Although there is usually no rejection reaction, there is a risk of capsular contracture (reaction of surrounding tissues to a foreign body). In the case of radiation therapy, this risk increases significantly. The breast may become dense, its shape will undergo changes, and it will bear little resemblance to its own mammary gland. Therefore, installing an implant is not always a viable solution and rarely satisfies patients. In cases where there is no radiation therapy and when a subcutaneous mastectomy is performed, replacing the volume of the mammary gland using implants is quite acceptable and gives a good result.
The breast reconstruction method should not be contrasted with your own tissues and implants - they complement each other and are often used together. There are cases when patients who have undergone a mastectomy and selection of exoprostheses have a high quality of life and do not plan to undergo breast reconstruction at all.