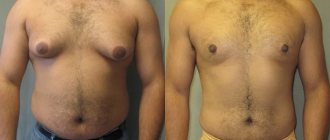
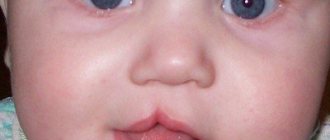
Acne (inflammatory formations on the skin, acne) is the most common disease of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles of the skin, which occurs from the neonatal period to old age.
Acne is the second most common skin disease in the world after eczema. Women are more often affected, but in men the disease is more severe. In some patients, acne is a hereditary disease (explained by the structural features of the sebaceous glands and genetic sensitivity to pathogens).
There are known cases of spontaneous recovery up to 25 years of age, but it happens that, on the contrary, the disease becomes chronic. It is very difficult to give an accurate prognosis, so it is very important to find out the causes of the disease and eliminate them as much as possible so that there are no sad consequences.
How do acne occur? Let us explain this process in more detail.
How does acne occur?
The skin is the largest human organ in terms of mass and area.
It performs a number of important functions: metabolic, heat-regulating, receptor, protective. The skin consists of three layers:
- epidermis - the outer layer of the skin, includes five layers located above the dermis and primarily perform a barrier function,
- dermis - the skin itself, connective tissue located between the epidermis and the underlying organs, from which it is separated by a layer of connective tissue - subcutaneous tissue,
- subcutaneous tissue - loose connective tissue, often rich in fatty deposits,
The topmost layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum, performs a protective function. and has no living cells, but consists of dead cells. The thickness of this layer can be different, depending on the intensity of the mechanical load on the skin area. The water-lipid mantle covers the stratum corneum of the epidermis like a space suit and protects the skin from harmful external influences, microorganisms and moisture loss. Its normal acidity level (PH) is 4.5-5.5. However, with acne, fungal and other diseases, the acidity of the skin changes.
The water-lipid mantle has its own microflora; staphylococcus epidermidis, acne bacteria and some fungi live on it in symbiosis in a certain proportion, which is strictly individual. These bacteria maintain an acidic environment on the skin and prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering it. However, if this balance is disturbed, some bacteria begin to multiply too actively. In addition, disturbances in the upper layer of the epidermis reduce its protective barrier function and can lead to the penetration of foreign infection from the external environment into the skin (especially with a certain pathology within the body). All this together leads to the development of acne.
Changes in the chemical composition of the water-lipid mantle can be caused by many reasons. Thus, during puberty (adolescence), acidity changes and sebum production increases due to hormonal changes. The thin ducts of the sebaceous glands become clogged and deformed, as a result, comedones, wen appear, and with the active development of pathogenic microflora - acne.
Thus, acne is a disease of lipid metabolism. We can say that acne patients have a special hypersensitivity (like a kind of allergy) to bacteria.
How to get rid of acne on your face using pharmaceutical products
You can buy many effective acne treatments at the pharmacy; the main thing is to read the instructions and possible side reactions first.
Here are some of them:
- The following are used as creams and ointments: Naphthalone, Ichthyol and Metronidazole.
- Facial gels: Skinoren and Metrogyl.
- It is recommended to perform cold soaks. For this purpose, the pharmacy sells herbal tinctures: infusion of yarrow or celandine.
- Colorless henna. The product allows you to get rid of the inflammatory process of the skin and fights red and black formations. The substance is based on natural ingredients and is completely safe for the body. Henna helps tighten pores and produce the required amount of sebum. You need to prepare a mask based on two large spoons of henna, a couple of drops of oil (for example, use tea tree, jojoba or lavender oils) and warm water. Apply the product up to three times a week. The procedure lasts 15 minutes, then the mask is washed off.
- Zinc paste. The paste is applied in a targeted manner, only areas of inflammation and acne are treated. Perform the procedure at night, by the morning the entire rash will dry out and not a trace will remain of it.
- Tincture of calendula. Calendula has the ability to dry the skin, so it is not recommended to use it in its pure form. A refreshing tonic is made from calendula for daily use. The tincture is diluted in equal proportions with still mineral water. The face is wiped with tonic every morning and evening.
The products are effective, but only if used regularly.
How acne forms.
The actual process of acne formation looks like this. As a result of pathogenic influences or hormonal disorders, changes occur in the chemical composition in the upper layers of the epidermis. The secretion of the sebaceous glands increases and the composition of sebum changes. The renewal process of hair follicle cells is disrupted and the stratum corneum thickens (follicular hyperkeratosis). A bacterial imbalance occurs (the proliferation of some bacteria and the inhibition of others). As a result, an inflammatory reaction begins.
If redness, inflammation, pimples, and subcutaneous painful elements appear on the skin, this is a signal from the body that the person is not healthy!
Cosmetics made from simple ingredients
You can also treat acne with other substances prepared at home. Calendula decoction will help eliminate acne. It is prepared like this: two teaspoons of dried flowers are poured with 400 milliliters of hot water and left for some time. Wipe your face with the strained tincture twice a day.
Soda-based lotions also provide good treatment. You need to dilute enough soda in water to create a thick porridge. Dip a piece of cotton wool into it and apply it to the inflamed areas for a couple of minutes.
Compresses made from green tea will also help get rid of red pimples.
A disease such as acne can be treated by wiping painful areas of the face with juice from freshly squeezed potatoes.
Aloe is a magical plant, the juice of which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the epidermis. If you have a pot with this representative of the flora on your windowsill, then you can safely use it for facial care. Cut a few aloe leaves and hide them in the refrigerator for three days. Later, finely chop the culture and squeeze the juice out of it. Before going to bed, simply wipe each pimple.
Diagnosis of acne
What does acne skin look like?
The appearance of acne skin differs from normal skin - the skin is shiny and has a greasy appearance. Various types of rashes (acne) are observed.
Skin rashes come in different types, and can look like a small cosmetic defect that does not cause much trouble, or be of a pronounced inflammatory nature, which can cause significant suffering to the patient.
The areas of acne rash are quite traditional. Most often this is the face, the so-called T-zone (forehead, nose, chin), where the sebaceous glands that nourish the hair follicle are most concentrated. In more severe cases, it can affect not only the face, but also the back, chest, shoulders, and sometimes even the buttocks and scalp.
Acne is characterized by the presence of several types of skin defects. Let's take a closer look at them.
Open comedones
Most often, blackheads in the pores are present on the skin - these are open comedones. They arise as a result of blockage of the mouth of the sebaceous glands with sebum, cosmetics, dust, etc. Open comedones are usually localized in those areas where there is a significant number of sebaceous glands, as a rule, this is the forehead, chin and wings of the nose. Single comedones are usually eliminated with proper skin care. However, with porous skin, the formation of numerous comedones is possible, not only on the face, but also on other areas of the skin - on the back, on the shoulders, etc. This situation requires special measures to clean the skin; it is better to consult a specialist for advice.
Closed comedones
White subcutaneous plugs - closed comedones - are also quite common. A closed comedon is a flesh-colored or white bump on the skin that slightly protrudes above the surface of the skin. It may be barely noticeable, only felt as some unevenness if you run your hand over the skin. Inflammation and any painful phenomena are not observed.
Milia
Milium (whitehead) is a dense superficial cyst of the sebaceous gland. having the appearance of a small white grain. These are painless, non-inflamed whitish nodules, 0.5-3 mm in size, containing thick sebum and keratin. They are usually observed on the so-called T-zones of the face, as well as on the cheeks, eyelids, and less often on the torso and genitals.
Papules
Papula nodules - usually called pimples - are a more severe case. Papules are dense, sharply defined pimples with a diameter of 1–3 mm, slightly rising above the dermis. They do not have a purulent head. Papules are usually formed from closed comedones. If the papule has formed from an open comedon, a dark plug and an enlarged mouth of the hair follicle can be seen. They can be both inflammatory and non-inflammatory in nature. If inflammation occurs, scars may remain, so papules must be treated. It should be said that papules can be a symptom of some serious diseases, such as chickenpox, measles, syphilis, smallpox, anthrax, lichen planus. Therefore, if numerous rashes appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Pustules
Pustula pustules are small balls, at the very top of which there is a white spot (purulent head). Around the pustule there is usually painful redness - inflammation. Pustules can be very painful. This epidermal lesion occurs not only on the face, but also on different areas of the body. In principle, these rashes are not dangerous, but treatment is required, since the pustules are infectious in nature. And antiseptic treatment is needed, and in severe cases, antibiotic treatment.
Nodules and cysts
In more serious cases, deep subcutaneous compactions are observed - nodes and cysts. Nodes are deep subcutaneous compactions with a diameter of more than 5 mm, red or bluish-purple in color, painful on palpation. After their healing, scars may remain (of various types - atrophic, hypertrophic, keloid). Cysts are nodes that have degenerated due to inflammatory processes, usually very painful, and have a reddish-bluish color.
Purulent capsules
If there is an inflammatory process in the deep tissues for a long time and the resulting infiltrate is not removed, a dense, voluminous capsule may form, inside which contains pus or sebum. Experts call this formation a cyst.
Scars and pigmentation
Also, with acne, scars can be observed (consequences of healed rashes), as well as spots of varying sizes on the skin (post-inflammatory pigmentation).
Symptoms
The red rash is caused by excess sebum production that clogs the pores. It will become a breeding ground for microorganisms, and the skin on the nose, cheeks, chin and neck is often affected, and in rare cases on the back and genitals. After the rash, traces may remain, which cannot be quickly removed in all cases.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
A subcutaneous red rash can appear at virtually any time. During their formation, a slight compaction is felt under the skin. When a pimple matures, a small bump of white, yellow or red color appears on the top layer of the skin. If you press it, the patient will experience painful discomfort. The inflammatory process is concentrated in different areas.
The red rash initially measures 0.2 cm in size. As inflammation develops, a pustule with pus forms inside the skin. It is a non-flesh-colored neoplasm protruding above the skin. Since these pustules are located under the skin, they are very difficult to eliminate.
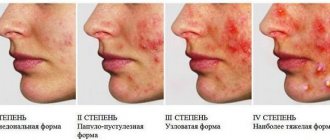
Acne grades
Clinical forms of acne are divided into non-inflammatory and inflammatory. Non-inflammatory forms of acne are open and closed comedones, milia. Inflammatory forms are superficial papules and pustules; nodules and cysts, as well as deep indurative, conglobate acne; complicated abscess, phlegmonous, fulminant, acne-keloid, scarring.
The severity of the disease, according to the classification proposed by the American Academy of Dermatology, is assessed as follows:
- 1st degree - the presence of comedones and single papules;
- 2nd degree - papular rash and a small number of pustules;
- 3rd degree - papules, pustules and from 3 to 5 nodes;
- 4th degree - a pronounced inflammatory reaction in the deep layers of the dermis with the formation of multiple painful nodes and cysts.
However, the most convenient, frequently used and more understandable to patients, is the following classification of Acne, proposed in 2000 (G Plewig MA Kligman):
- Grade 1 (mild) - less than 10 comedones and papulopustules in a limited area of skin.
- Grade 2 (moderate, average) - up to 20 comedones and 25 papulopustules on two or more areas of the skin.
- 3rd degree (severe) - many comedones (over 21), many papulopustules (over 26), conglobal and indurative elements, widespread form and severe psychosocial disorders.
Causes of acne
Acne is almost always the result of a number of causes. However, they can be divided into two large groups - internal (endogenous) and external (exogenous).
Endogenous (internal) causes of acne are associated with disturbances or abnormalities in the functioning of the patient's body.
Exogenous (external) causes are various external influences on the skin that can cause acne.
In each specific case, the cause may be either individual single factors or a combination of various endogenous and exogenous factors. A thorough examination, which we always conduct in our clinic, will help determine the exact cause or set of causes.
Homemade masks
Advertised products used by cosmetologists in salons cannot always help achieve the desired effect. Every girl can get rid of red pimples on her own. Simply taking proper care of your skin is enough. After performing water procedures in the morning, you need to wipe your face with a disinfectant tonic lotion.
Cosmetologists advise home treatment with anti-inflammatory masks. These are special formulations based on simple ingredients. So, different types of clay are suitable:
- Black clay is perfect for any skin type. You should mix two tablespoons of dry powder with a small portion of mint and string decoction. Mix everything until the consistency of a thick paste. Apply the mixture to your face. You should let the mask dry completely. Everything is washed off with warm water;
- If you have oily skin, you can prepare a preparation from green and white clay at home. You should mix one tablespoon at a time. of both products, add five drops of grape seed essential oil and a little non-carbonated mineral water;
- Sensitive skin is best treated with a white clay mask. It is recommended to dilute it with a medicinal infusion of chamomile;
- acne on the epidermis will go away if you apply a composition of blue clay to it. A couple of tablespoons of the substance should be mixed with water and a teaspoon of bodyaga powder. Apply the resulting mixture to your face, wait until it dries and rinse.
Endogenous causes of acne
Among the endogenous causes, it is first of all worth highlighting the physiological changes that naturally occur in the body and can trigger the appearance of acne. This is primarily a change in hormonal levels:
- in adolescence, when hormones have not yet established themselves,
- during pregnancy or after an abortion,
- before menstruation.
Some pathologies of internal organs may also be accompanied by acne. Thus, acne is possible in some diseases: ovarian dysfunction in polycystic disease, diseases of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands, etc. Rashes are also observed in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as an imbalance of intestinal microflora, gastritis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, disorders of the gallbladder, constipation, leading to intoxication of the body.
In men, when actively playing sports and taking anabolic steroids and sports nutrition to improve muscle relief, various types of acne may sometimes appear.
Very often, acne is a consequence of stress. Even a single stress leads to the release of hormones, which can lead to disruptions in the endocrine system and, as a result, cause acne. Chronic stress leads to a constant increased release of hormones and decreased immunity, which opens the way to many infections, including inflammatory forms of acne.
Viral diseases are another cause of skin rashes. Not only the acute phase of herpes, but also carriage of the herpetic group of viruses reduces immunity, and as a result, the body cannot cope with the disruption of the microbial flora. Bacteria flourish on the skin, and acne becomes chronic.
Hyperkeratosis - thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin, blockage of pores aggravates acne.
Areas of rashes and their connection with diseases of internal organs
There is a classification of acne zones - the Zakharyin-Ged zone - which, like a geographical map, makes it possible to understand where the malfunction of the body occurred. This classification correlates acne areas and human internal organs.
Zakharyin-Ged zones are limited areas of the skin (zones) in which, in diseases of the internal organs, reflected pain often appears, as well as changes in sensitivity in the form of pain and temperature hyperesthesia.
Exogenous causes of acne
Among the exogenous (external) causes of acne, it is first of all worth noting the incorrect and indiscriminate use of various cosmetics, especially foundations and correctors. Acne is also caused by improper daily care and excessive interest in cosmetic aesthetic procedures. These are, for example, cleansing, which CANNOT be done if there are inflammatory elements on the skin.
And squeezing anything in the area of the nasolabial triangle and the bridge of the nose is generally dangerous - this can lead to inflammation of the meninges and meningitis.
Another provoking factor is excessive insolation. The skin in the sun and in the solarium seems to dry out, but compensatory this leads to increased sebum secretion, clogged pores and worsening acne. In addition, the sun is a great immunosuppressant.
Excessive friction of the skin, frequent washing, rubbing with lotions, “cleanliness” syndrome - all this also leads to increased acne, because The protective layer of the skin with its “own” microbes, which play a huge role in the epidermal barrier, is washed away. Microcracks form on dry skin - entry points for infection. Contact with certain chemical compounds worsens acne.
Acne hormones and their role
It has long been known that Acne is a hormone-dependent disease, that is, one of the factors in the appearance of acne is hormonal imbalance. The provoking hormones are usually testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1, somatomedin C). Their overproduction leads to excessive work of the sebaceous glands and even changes in the composition and quality of sebum.
But these hormones are not the only ones that cause acne. Disruption of the hormonal balance of the pituitary gland, cerebral cortex, ovaries, adrenal glands and thyroid gland can also lead to acne. Therefore, we must remember that in addition to a dermatologist, you need to contact endocrinologists if any abnormalities are detected in blood tests.
Exacerbation of acne 5-7 days before the onset of menstruation is explained by an increase in the level of steroid hormones and a change in the hydration of the follicle epithelium.
The appearance of skin rashes may also occur after taking or stopping certain contraceptive medications.
During stress, the adrenal glands produce more androgens, which causes overactive sebaceous glands and a decline in immunity - as a result, acne flourishes. Nevertheless, quite often gynecologists prescribe contraceptives to young girls with absolutely normal hormonal background. It is not reasonable for gynecologists to prescribe external (topical) therapy for acne without consulting a dermatologist.
Acne treatment is a complex process
So, we see that acne can also be an independent disease, caused, for example, by improper care (usually mild forms of acne). But much more often, acne is a symptom of disorders in the body. That is why symptomatic treatment with external drugs, even if it leads to temporary improvements, often does not give lasting results, because it does not eliminate the cause of the disease. As a result, acne becomes more severe.
Patients often come to our clinic with complex, advanced, severe forms that require serious comprehensive treatment. And our methods make it possible to overcome the disease even in difficult cases - of course, with strict adherence to the recommendations of our specialists.
Acne treatment is often more than just treating acne. This is the treatment of the whole organism, bringing order and harmony to the work of its various organs and systems. And this requires a comprehensive examination and identification of all possible causes of the disease, and careful adherence to all doctor’s recommendations.
For more information about acne treatment in our clinic, see here
Ophthalmic rosacea –
In this form of rosacea, patients' eyes have a puffy or bloodshot appearance. Patients complain of a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, burning, tingling, dryness, itching, photosensitivity, blurred vision, telangiectasia of the eyelid margins, erythema around the eyes, blepharitis, recurrent conjunctivitis, iritis... With this form, a decrease in visual acuity may also occur, for example, due to corneal keratitis.
With ophthalmic rosacea, many patients mistakenly treat their eyes on their own, mistaking the onset of the disease for symptoms of an allergic reaction. As a result, patients most often end up seeing an ophthalmologist with moderate to severe forms of the disease.
Treatment regimens for ophthalmic rosacea –
| Expressiveness | Treatment |
| Mild course - redness of the conjunctiva of the eyelids and dysfunction of the meibomian glands. |
|
| Moderate course - redness of the conjunctiva of the eyelids, telangiectasia of the edges of the eyelids or conjunctiva of the eyeball, erythema around the eyes, impaired secretion of tear fluid, initial forms of corneal damage. | In addition to the above:
|
| Severe course - severe inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyelids and eyeball, resistant to treatment; episcleritis, iritis or keratitis in addition to corneal damage and visual impairment. | In addition to the above:
|