The mammary gland is a distinctive feature of an entire zoological class - the class of mammals.
From the birth of a child to the later years of life, the mammary gland changes its appearance many times - starting with a small bud, it goes through its exciting heyday and ends its life in fading calm.
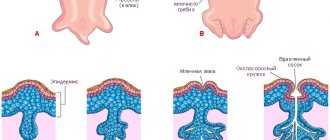
The mammary glands begin to form in the 6th week of intrauterine life. From the moment of birth until puberty, the ducts in the mammary glands lengthen and the nipples enlarge. During puberty, rapid lengthening and branching of the ducts, formation of glandular lobules, and changes in the morphological structure of the mammary gland occur. Connective tissue forms 2 zones: intercellular and interlobar (supporting lobes), subject to hormonal influences. After full puberty, the mammary gland stops developing until the second trimester of the first pregnancy. Thus, from puberty until the end of the first pregnancy, the epithelium of the mammary glands is immature, it is not able to respond to its own circulating progesterone, and this becomes a risk factor in the development of breast cancer.
The mammary gland is extremely dependent on the cyclical physiological processes of the body. In practice, the mammary gland is never at rest, regardless of the woman’s age. Constant variability in the structure of the mammary gland, sensitivity to sex hormones, thyroid hormones, dependence on sexual comfort and the state of the emotional status of a woman, lead to the frequent occurrence of dysplastic processes in this gland, which are most often combined with the term mastopathy or fibrocystic disease.
Mastopathy or fibrocystic disease is a general name for benign changes in the mammary glands, which differ greatly in anatomical features, clinical manifestations and the danger of malignancy, which forces us to consider mastopathy as a precancerous disease.
Causes of mastopathy
According to scientists, mastopathy is associated with an imbalance of hormones in the body, such as estrogen, progesterone and prolactin.
Normally, they determine biological changes in the mammary gland, as well as the reproductive organs of a woman in different phases of the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy, in the postpartum and menopausal periods. The production of the hormone in the wrong amount or at the wrong time contributes to the uneven growth of glandular or connective tissue.
This is the main, but not the only theory of the occurrence of the disease. The causes of mastopathy continue to be studied. Factors that increase the risk of its occurrence have already been established:
- chronic stress;
- overweight;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- bad habits;
- irregular sex;
- mastopathy in female relatives;
- lack of childbearing before age 30;
- stopping breastfeeding before three months or refusing it altogether;
- repeated termination of pregnancy;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- diseases of the genital organs and menstrual irregularities;
- early menopause;
- breast injury;
- endocrine disorders (hypo- or hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus);
- pathologies of the liver, gall bladder.
Why does fibrous mastopathy occur?
It is believed that hormonal imbalances in the body play a role primarily. Even in the last century, girls had their first period at about 17 years old, and at 40 menopause had already occurred. Today the boundaries have expanded - the lower one has dropped to 12-14 years, and the upper one has risen to about 50. A woman is in reproductive age longer; sex hormones, estrogens, remain active in her body longer. They, presumably, become the “culprits” for changes in the breast.
Other factors interfere with the hormonal effects. Modern women have become less likely to give birth, and more often refuse to breastfeed (often without good reason). Many have problems in the area of intimate health, chronic diseases and ignore them for a long time. Representatives of the fair sex in modern cities often experience stress, work long hours, and suffer from bad habits just like men. This is believed to increase the risk of mastopathy.
All of the above is mostly speculation. The causes of mastopathy and, in particular, the fibrous form, are not fully understood. Scientists continue to work in this direction.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Types and symptoms of mastopathy
Symptoms of the pathology depend on the form of the disease, each of which is characterized by its own changes in the mammary gland.
Doctors distinguish diffuse and nodular mastopathy. The first is characterized by changes in the entire organ and is of the following types:
- Adenosis. Proliferation of the glandular component – lobules. More common in young women and early pregnant women.
- Fibroadenomatosis. Fibrous mastopathy, which is characterized by a predominance of connective tissue.
- Cystic mastopathy. Cavities filled with fluid form in the thickness of the mammary gland.
Signs of the disease are manifested by the following symptoms:
- there is breast tenderness;
- the mammary glands become rough and swollen, and swelling is sometimes observed;
- when palpated under the fingers, compactions and gaps are determined;
- A clear liquid or dirty white colostrum is spontaneously released from the nipples, and when an infection occurs, it is green or dark brown.
The nodular form is characterized by the formation of compactions and cysts with clear boundaries.
The connective tissue is replaced by glandular tissue, the ducts of the organ are compressed and clogged. When palpating the mammary gland, elastic nodes of round or oval shape are determined. The pain can be radiating and spread to the armpit, shoulder and shoulder blade. With this type of mastopathy, they become constant and practically do not depend on the day of the cycle. Transparent, greenish-brown, white, and less often bloody discharge from the nipple, formed during pressure or randomly, is also characteristic. About 15% of women with mastopathy do not experience pain, although upon examination significant pathological changes are detected in the mammary gland. This is due to different thresholds of pain sensitivity and characteristics of the innervation of the organ in individual people.
How to treat fibrous mastopathy?
If diffuse mastopathy is diagnosed, treatment is usually not required. You just need to periodically visit a doctor and undergo examination. The mammologist can prescribe you hormonal and symptomatic medications.
Surgical interventions are used extremely rarely. But if a nodular form of mastopathy is diagnosed, surgery becomes almost inevitable.
Fibrous mastopathy is not a dangerous condition. But in order to distinguish it from more serious diseases, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination. Make an appointment with a mammologist at the International Clinic Medica24 by phone
Diagnosis of mastopathy
One of the most significant ways to timely detect breast diseases is self-examination.
It is recommended to do it monthly, on a certain day of the menstrual cycle, preferably on the 5th–6th day, when the breasts are relaxed and soft. The procedure also involves regular examination of the underwear, shape and skin of the organ in front of the mirror. It is more comfortable to palpate the mammary glands while standing during water procedures with soapy hands or in the room using cream or lotion. It is carried out with the pads of 3-4 fingers closed together, in a circular penetrating motion. An important part of the self-examination is to feel the organ while lying on your back, one by one in each square or in a spiral direction from the outside to the nipple. The arm of the same side must be extended along the body or placed under the head. Finally, the nipple is examined, after which it must be gently squeezed between the thumb and forefinger to ensure that there is no discharge.
Three specialists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of mastopathy: a gynecologist, a gynecologist-endocrinologist and a mammologist. To detect diffuse pathological changes in organ tissue, determine the shape, size, and number of formations, instrumental examination methods are used:
- X-ray examination of the mammary glands - mammography. The method is one of the most informative and specific; it involves taking a picture of the breast in two projections. Performed mainly in the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Ultrasound. Indicated for all women under 40 years of age, from 40 years of age mammography is required, and ultrasound is preferably once a year.
- Ductography. A contrast agent is injected into the mammary gland through the nipple and X-rays are taken. This is how the milk duct system is studied.
- Digital tomosynthesis. Recommended for equivocal mammography results. Layer-by-layer images of the mammary glands are reconstructed by a computer program into a three-dimensional image, which allows a more detailed examination of all the structures of the organ.
- MRI.
Note that all findings on ultrasound, mammography and/or MRI are assessed according to BI-RADS criteria - a scoring system for assessing the risk of breast cancer.
If cancer is suspected, the doctor prescribes a fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the mammary gland and a cytological examination of nipple discharge.
To determine the hormonal levels in the body during mastopathy, laboratory tests of sex hormones and instrumental examination of the organs of the endocrine system are carried out:
- blood test for prolactin, progesterone, estradiol, thyroid hormones, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones;
- determination of tumor markers for the mammary gland;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- radiography of the sella turcica;
- CT scan of the pituitary gland.
Symptoms and signs in women
Diagnosing mastopathy is quite easy.
Firstly, it can be detected independently by palpation of the chest. It is advisable to carry out palpation at least once a month. If you can feel heterogeneity in the breast, most likely the lump will be a sign of mammary gland mastopathy. In some women, this heterogeneity is accompanied by chest pain during menstruation, and sometimes engorgement of the mammary glands occurs during menstruation.
To confirm the diagnosis, you should consult a doctor. A mammologist and most gynecologists can professionally palpate the breasts and detect mastopathy. But for an accurate diagnosis, equipment is used: ultrasound to detect relatively large objects, as well as mammography. By the way, it is advisable for women who have relatives with breast cancer to have a mammogram annually for early diagnosis.
Treatment of mastopathy
First of all, patients with pathology of the mammary glands are recommended to change their lifestyle: physical activity, giving up bad habits, proper nutrition, and, if necessary, taking multivitamins.
Treatment of the diffuse form of the disease includes the use of medications and regular monitoring.
In case of nodular mastopathy, the nature of the node is determined, and an operation is performed to remove it. The amount of intervention depends on a number of reasons, primarily on the cells forming the node. Surgical treatment is also indicated if malignant degeneration is suspected based on biopsy data.
An integral component of the treatment of dyshormonal mastopathy is the use of gestagens, antiestrogens, prolactin secretion inhibitors, and androgens in various combinations. For thyroid dysfunction, synthetic analogues of thyroxine and iodine preparations are used. To relieve the symptoms of mastopathy, painkillers, anti-inflammatory, diuretics and other drugs are prescribed.
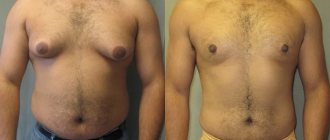
Breast lift or augmentation - what to choose?
Here are examples of common problems and ways to solve them:
- Lack of breast volume; there is no prolapse of the nipple-areola complex or it is observed to a slight extent (1-2 cm) - breast enlargement.
- Lack of breast volume; mild ptosis 1st degree - breast augmentation with periareolar lift;
- Lack of breast volume; ptosis 1 or 2 degrees - enlargement of the mammary glands with periareolar or vertical lift;
- Lack of breast volume; ptosis of the 3rd degree - breast endoprosthetics with anchor mastopexy;
- Sufficient volume of the mammary gland; ptosis 1,2,3 degrees - breast lift using an individually selected technique;
- Too large breast size (gigantomastia); ptosis 1,2,3 degrees - reduction mammoplasty using an individually selected technique;
- Tubular breasts, congenital or acquired asymmetry of the mammary glands - a combination of endoprosthesis, lift or reduction mammoplasty, depending on individual characteristics.
Thus, in order to correctly answer the question posed: “What is better, breast lift or breast augmentation?” - A face-to-face consultation with a plastic surgeon is required.
Prevention of mastopathy
Regular breast examination is the only correct way to detect cancer at an early stage, when the disease can be effectively treated.
Regular self-examination and annual instrumental examination - ultrasound of the mammary glands up to 40 years of age, or mammography and ultrasound of the mammary glands after 40 years of age - is the correct and necessary minimum examination of a modern woman. You also cannot ignore the signs of an infectious process. Fever, chills, weakness, purulent discharge from the nipples should be a reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician