How is it formed
Every person from birth has a genetically determined skin color - the so-called permanent pigment.
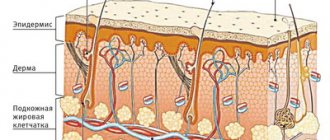
When exposed to external and internal factors, an additional one is produced, which can be either a temporary physiological phenomenon (natural tanning) or a pathological one, difficult to remove even with special lasers (lentigo, vitiligo, etc.). The formation mechanism itself occurs in the epidermal layer. Here are located keratinocytes - epidermal cells. Their life cycle is up to 60 days, so they are constantly updated. To protect young and vulnerable cellular structures from sun exposure, melanocytes exist. They belong to the nervous system and are called upon to produce melanin, which absorbs ultraviolet radiation.
If the body is healthy, there is no overdose of solar radiation, melanocytes will produce a sufficient amount of protection. However, if there are failures, the “protectors” begin to be distributed unevenly, which leads to the formation of hyperpigmented areas.
Red
If your face is constantly red, you should definitely consult a doctor - most likely the reason lies in high blood pressure.
But if the skin turns red only in places or from time to time, it’s not so bad. Probably, your blood vessels are located close to the surface of the skin, and the skin itself is too sensitive, so any unfavorable external or internal factor - cold weather, wind, lack of humidity or excitement - leads to redness of the face.
If this is your case, skin care should be gentle. Avoid harsh alcohol-based lotions - they dry out the skin, thereby reducing its natural protection. Avoid steam baths, contrast washes and facial massages - all this can injure blood vessels and lead to the appearance of additional redness and “stars”. Use unfamiliar cosmetics carefully - before applying a new cream to your face, try it on a small area of skin.
Article on the topic
Cuperosis: how to get rid of spider veins on the face
Causes of hyperpigmentation
An increase in melanin production can be associated both with physiological changes occurring in the body and as a result of pathologies. The most well-known factors influencing the occurrence of stains are:
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and adrenal glands;
- metabolic disorder;
- vitamin deficiency or hypervitaminosis;
- helminthic infestations;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- trauma or inflammatory processes;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- taking medications - antibiotics of the tetracycline group, gentamicins, erythromycins, as well as some NSAIDs, salicylic acid, antidepressants, diuretics, sleeping pills and sedatives, antihistamines, St. John's wort extract, etc.;
- heredity.
Changes can also appear due to prolonged stress. Since melanocytes belong to the nervous system, any fluctuations and unstable conditions lead to serious pigmentation disorders.
White
Previously, aristocratic pallor was held in high esteem.
In the Middle Ages, to achieve perfectly white skin, ladies drank vinegar, took small doses of arsenic, and used lead powder, which often caused poisoning and tumors. Question-answer What color should facial skin normally be?
Fortunately, times have changed - and pallor is no longer held in high esteem. But what to do if a healthy blush is in no hurry to appear on your cheeks?
First you need to determine the cause of excessive whiteness of the skin. This may be a low-calorie diet, a lack of certain microelements in the body, especially iron, which is why paleness is often characteristic of vegetarians.
Another reason: chronic lack of oxygen. Therefore, white, often even grayish or bluish skin tint is the lot of smokers.
Sometimes pallor can appear against the background of lung diseases, low blood pressure, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
If an unhealthy complexion is not the result of any disease, it is entirely within your power to change it.
Localization of spots
They can have different sizes, both with clear contours and blurry ones, merge together or not grow at all. Depending on the differential diagnosis and the type of hypermelanosis, they can be located both in certain areas and without specific boundaries, covering absolutely any area of the body.
On the face
One of the most common sites of localization of many hyperpigmentations. This is due to the fact that the skin here is thin enough so that negative factors can attack them faster. Among the common phenomena are freckles, which can decorate the face all year round and also appear and disappear after exposure to the sun. They are also localized over the entire surface or located pointwise in the area of the cheeks, eyes, and forehead.
Anti-age drugs
Bb Laboratories – Delicate oil for deep cleansing
Laennec – solution for injection
Bb Laboratories – Two-phase serum concentrate
Two-phase placental serum concentrate
On the body
Namely on the arms, shoulders, chest, back, groin area. For each individual disease, there are areas where pigment accumulation is observed. For example, senile hyperpigmentation is typically located on the hands, forearms, and upper back.
LIGHTENERS
If pigment spots appear on the skin at least once, it is necessary to use prophylactically drugs with the function of blocking melanogenesis. We carefully select lightening products for the summer; they should not contain aggressive ingredients.
For the summer, medications are needed that normalize and maintain the physiological norm of skin pigment production.
Serum "SkinBright" against age spots for the face DermaQuest is a brightening serum for the face that gives the skin an even tone and a “healthy glow”, while moisturizing and restoring. Used on the entire face, suitable for use in spring and summer.
Types and symptoms of age spots
Let's consider the most characteristic signs of hypermelanosis, as well as control methods that are relevant for each specific type of pathology.
Freckles
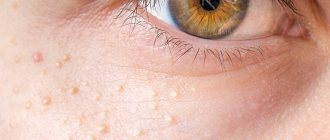
The most common type of melanin accumulation. They are mainly located on the face, in the cheek area. In advanced cases, they can completely cover the entire surface of the skin with small distances between the spots. And also have a round or oval shape, small diameter, clear contours.
Genetic predisposition plays a major role, so freckles can appear in childhood. People with red and blond hair are most susceptible to them. This is due to the need for high melanin production to protect the skin.
Freckles can be easily distinguished from other types of spots by the complete disappearance of pigmentation in cold weather, and the appearance of a whole scattering on the face with the arrival of warmth. Therefore, to combat them, creams with maximum sun filters are used throughout the year, as well as lightening cosmetics.
Melasma
Spots without clear boundaries and endings, varying in shade from bronze to dark brown. They have the ability to stretch, grow, and merge with each other into huge pigmented areas that occupy a large surface of the body. The main provoking factor is considered to be hormonal disorders caused by menopause, pregnancy, and the use of oral contraceptives. Treatments include peeling methods and procedures that promote cell renewal. When the root causes are eliminated, the stains quickly disappear.
Melasma
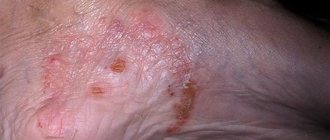
The second name is melanosis. It can be acquired or hereditary, manifests itself in the form of an accumulation of melanin with uneven but clear boundaries and localization in open areas of the body. May occur as a result of Addison's disease, hemochromatosis, due to sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, anthracene or acridine substances, diseases of the pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenal glands, syphilis, tuberculosis, malaria, treatment with hormones. Pigmentation is accompanied by redness, itching, peeling, and roughening of the skin.
To prevent progress, sunscreens are used, drug therapy is prescribed with steroid groups, retinoids, hydroacids, and vitamins B (1.6) and C are additionally used.
Becker's nevus
A characteristic defect in men, it is much less common in women. The first manifestations can be as early as 10 years of age. It is a hyperpigmented area protruding above the surface of the skin, on which dark long hairs grow. It occurs both as a result of genetic factors and can appear after sun exposure, changes in hormonal levels, in particular androgens. The location most often is the upper back and chest; it is not often found on the legs, groin, or head. It has a warty surface on which acne or comedones can be seen. Does not respond well to any cosmetic procedures or medications. An argon laser is used to minimize the aesthetic defect.
Secondary
Occurs at the site of mechanical damage. They can be either deep cuts, scratches, or acne, comedones, ulcers and other superficial causes that trigger the inflammatory process in the skin cells. There is an excess of melanin, resulting in staining. They are localized where the damage was and go away after the area returns to normal and the inflammation disappears. To speed up the lightening process, you can use special lightening creams or cosmetic procedures aimed at renewing the epidermal layer.
Age
As we age, the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation lead to increased melanin production in certain areas of the body. These are usually open areas that have been exposed to a lot of sunlight during their lifetime. With age, spots appear with a diameter of 1 to 5 cm, which are darker in color than the entire surface of the skin.
Berlocc's dermatitis
Refers to contact types of immune response to irritants. Usually due to contact with perfumes, colognes, and deodorants. It is located where the skin came into contact with the substance. Symptoms may include not only a change in the color of the dermal layer, but also itching, peeling, and swelling. It disappears quickly, just stop using perfume and in a few days everything will return to normal.
Chloasma
Large spots can merge into one large skin defect. They do not have a clear contour or boundaries and can grow and increase in size throughout life. Among the provoking factors are pregnancy and lactation, menopause, changes in hormonal levels due to diseases, stress, taking oral contraceptives, steroids, the use of hormone-containing ointments and some cosmetics.
Diagnostic measures
To treat anemia, it is necessary to determine its type and cause of development. The main diagnostic method for this disease is laboratory blood tests (general and biochemical).
Changes that are observed in the general blood test:
small red blood cells (microcytosis).
Changes that are observed in the biochemical blood test:
In addition, a visual examination of the patient and a detailed history is required. Among the most common symptoms are pale skin and mucous membranes, cracks in the corners of the mouth, a “glossy” tongue, and an enlarged spleen.
To effectively correct the condition, instrumental examination methods may also be required:
computed tomography of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum. colonoscopy. Ultrasound of the liver, spleen, kidneys, genitals. X-rays of light.
What causes pigment spots to appear on the face after sunbathing?
Most manifestations of hyperpigmentation occur after the negative effects of ultraviolet rays. Among those that immediately appear are freckles, various melasma and chloasma. There are also those that have a cumulative effect, for example, lentigo.
Also, if during the summer vacation there were inflammatory processes in open areas of the body, most likely after they heal, a change in shade can be clearly observed.
Prolonged exposure to the hot sun with the presence of existing tumors and increased pigmentation can be fraught with the degeneration of harmless spots into aggressive cancer - melanoma. Therefore, you should limit your tanning time and use special cosmetics for protection.
Age spots and peeling
Melanin accumulation occurs in the upper layers of the epidermis. In order to remove unaesthetic problems, products that stimulate the renewal of the dermis are used. The most effective peelings are: chemical, mechanical, laser. They promote the regeneration of epidermal cells, forcing keratinocytes to produce new ones as quickly as possible, which will not have a large accumulation of coloring pigment. When eliminating the root causes of hyperpigmentation, there is a chance that you will forget about various spots for a long time.
Causeless manifestations
It happens that people try to protect their skin, use special sunscreens, but hyperpigmented areas still appear. It's like it happens for no apparent reason. However, for melanocytes to malfunction, even a small but prolonged stress or temporary hormonal imbalance is enough.
It is also worth noting the cumulative negative effect of ultraviolet radiation, which can manifest itself over the years on areas of the body that received sunburn in early childhood. Therefore, only at first glance it seems that hypermelanosis arose without provoking factors. In fact, he has hidden reasons.
Liver pigment spots
Deterioration in the functionality of internal organs can also lead to the formation of aesthetic defects. The liver plays the role of a filter, retaining and processing all dangerous substances, and then removing them from the body. In cases where she fails to cope with her duties, slow but sure intoxication occurs, which is manifested not only by internal, but also by external pathologies.
Metabolic processes in tissues are disrupted, including the normal distribution of melanin; it accumulates in certain areas. Most often it appears on the face. The contours of such spots are not uniform, they do not have a clear boundary. The color can also vary from light to dark brown.
Post-infectious asthenia in children: selection of optimal therapy
Post-infectious asthenic syndrome
Doctors are well aware of the structure of the viruses that provoke this disease: 65–90% of it consists of influenza and parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses and respiratory syncytial virus.
In half of the cases (52%), pediatricians deal with a viral monoinfection; in 36%, an association of 2 (or more) viruses is detected.1 Each child experiences ARVI with varying degrees of severity. Not only the variety of pathogens affects, but also age, the state of the immune system, the presence of an unfavorable premorbid background (adenoids, allergies), and congenital pathologies.
Nevertheless, algorithms for the management of small patients with ARVI are well developed. In general pediatric practice, children are prescribed symptomatic antiviral therapy, and foci of chronic infection are sanitized.2 However, it often happens that catarrhal symptoms are replaced by a different clinical picture - asthenic syndrome, the manifestations of which - fatigue, weakness, irritability, tearfulness - are observed in 55‒ 64% of patients. 3.4
And this is understandable: the body spends a lot of strength and energy fighting a viral infection. Even with an increase in temperature of only one degree, the body’s need for energy increases by 13%.5 Drug load and viral intoxication play a role, which lead to changes in metabolism, deterioration of appetite (the body does not receive enough of the necessary substances responsible for energy production and recovery ), a decrease in the body's defenses.
And this is serious, because asthenic disorders significantly worsen the quality of life, complicate adaptation in preschool and school institutions, disrupt the learning process, and reduce communication activity.
Speaking about increased fatigue, two different concepts should be distinguished: “physiological fatigue”, which occurs in practically healthy people after physical or mental stress and always disappears after rest, and “asthenia” as feelings of weakness and fatigue that are not associated with any load, occur at rest and do not disappear after rest.5
It should be noted that experts consider the feeling of fatigue and tiredness as an incentive to stop activity, activity, any effort, etc. If we analyze this phenomenon from the standpoint of basic biological reactions: attack - flight and preservation - refusal, then asthenia can be considered as activation of the energy conservation system through refusal and cessation of both physical and mental activity. Reduced activity is a universal psychophysiological mechanism for preserving the vital activity of the system in the event of any threatening situation, which operates according to the principle: less activity - less energy need. Thus, asthenia is a general reaction of the body to any condition that threatens the depletion of energy resources.5
Post-infectious asthenic syndrome:
- occurs as a result of an infectious disease (ARVI, influenza, sore throat, etc.);
- the first symptoms appear 1–2 weeks after the infectious disease and persist for 1–2 months;
- prevail: general fatigue, fatigue, aggravated by physical activity, weakness, irritability, sleep disturbance, anxiety, tension, difficulty concentrating, emotional instability, touchiness, tearfulness, short temper, moodiness, impressionability, loss of appetite, sweating, feeling of heart failure , lack of air, lowering the threshold of tolerance to various irritants: loud sounds, bright light, vestibular stress.
The importance of asthenia after acute respiratory viral infections for clinical practice is indicated not only by numerous scientific studies, but also by the fact that in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, syndrome G93.3 is separately identified among other asthenic conditions - fatigue syndrome after a viral infection.6
Asthenic syndrome (chronic fatigue syndrome in English literature) has many faces. In the classification of this condition, post-infectious asthenic syndrome refers to classical secondary (or reactive) asthenia, which occurs in initially healthy individuals as a reaction to the stress of adaptation under stress, as well as during the period of convalescence (after the end of the disease process and continuing until the complete restoration of normal nutrition and functioning all organs) after infectious diseases. Children with reduced adaptive capabilities of the body are most susceptible to asthenic reactions.
The leading pathogenetic mechanism for the development of asthenia is associated with dysfunction of the reticular formation, which regulates the activity of the cortex and subcortical structures, also called the “energy center” of the central nervous system (CNS).3 Other mechanisms for the development of this syndrome include autointoxication with metabolic products, dysregulation of the production and use of energy resources at the cellular level. Metabolic disorders that occur during asthenia lead to hypoxia, acidosis, with subsequent disruption of the processes of formation and use of energy.3
Asthenia, without a doubt, poses a serious danger of increased exhaustion of the mental and physical functions of the body. In a real clinical picture, its mechanisms can manifest themselves not only as emotional and behavioral disorders (emotional lability, restlessness, anxiety, irritability, restlessness, internal tension, inability to relax, etc.), but also somatic manifestations - thermoregulation disorders, respiratory, gastrointestinal, vegetative or functional disorders (headaches, sweating, loss of appetite, heart failure, shortness of breath, sleep disturbances).4
It is noted that long-term asthenia can cause exacerbation of a chronic disease or reinfection. Therefore, this condition, regardless of the cause that caused it, requires correction. The tactics of managing patients with post-infectious asthenic syndrome involves an integrated approach, providing, first of all, a full recovery period and rational pharmacotherapy. Its goal should be to eliminate energy deficiency and hypoxia, cerebroprotection and normalize metabolism. However, the use of psychostimulants for the treatment of patients with post-infectious asthenia is undesirable.4
L-carnitine in complex therapy of asthenic syndrome
More than 100 years ago (1905), Russian scientists R. Krimberg and V.S. Gulevich isolated a vitamin-like substance, carnitine, from the muscle tissue of animals. Later it turned out that only the L-stereoisomer of carnitine (L-carnitine, levocarnitine) has biological activity. It took more than half a century to synthesize it. And another decade - to study the main functions of carnitine in the body: participation in bioenergy metabolism, binding and removal from tissues of organic acids - intermediate products of oxidative processes, etc. Such an important role of carnitine in the metabolism of fats, glucose, amino acids and energy formation made it possible to classify it as a essential substances.
Carnitine is found in all organs, especially in large quantities in tissues that require high energy supply - muscles, myocardium, brain, liver, kidneys. The need for carnitine is individual (on average 200-500 mg per day for an adult) and increases 4-20 times with mental, physical and emotional stress, diseases and functionally special conditions (stress, pregnancy, sports, etc.). Endogenous synthesis in an adult provides only about 10% of the body's need for carnitine and requires the participation of vitamins C, B3, B6, folic acid, iron, a number of amino acids and enzymes; with a deficiency of at least one of the components, carnitine deficiency develops with its diverse systemic manifestations. In young children, endogenous synthesis of L-carnitine is practically not carried out, which makes them more vulnerable to a deficiency of exogenous intake of carnitine from food (especially animal protein). A normal diet covers the need for carnitine by half, at best. All this necessitates the use of additional sources.7
As an important component of the cell's energy supply, L-carnitine affects many vital processes of the body, increases its endurance to stress - physical and intellectual, and its deficiency, accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of the substance in the blood serum and tissues, can lead to various disorders. Taking into account this, as well as the fact that the natural intake of this biological substance into the body and its endogenous synthesis (especially in infectious diseases) do not cover all needs, additional intake of L-carnitine preparations is necessary.7
This becomes especially obvious when considering the functions of L-carnitine. The main one is bioenergetic: L-carnitine ensures the transport of long-chain fatty acids from the cytoplasm through the inner membrane into the mitochondrial matrix, where the process of β-oxidation occurs with the subsequent formation of ATP, regulates the intensity of mitochondrial energy exchange by conjugation of the acyl radical and the release of CoA.7 The value of L has been proven. -carnitine for binding highly reactive organic acids (acetic, etc.), as well as participation in the process of glycolysis, the exchange of ketone bodies and choline.
L-carnitine has an antihypoxic, antioxidant effect, prevents degenerative damage to cells of the nervous system, helping to restore their integrity and functions.7
Preparations based on L-carnitine are produced in many countries around the world in various dosage forms for oral and parenteral administration. In Russia, since 2000, the drug L-carnitine Elcar® (INN: levocarnitine), developed by a domestic company, has been widely used.
The areas of application of levocarnitine and the unique combination of its therapeutic effects are reflected in the registered indications for use of the drug Elkar.8
The vitamin-like substance L-carnitine is involved in the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria, where they are used for energy production (ATP). Fat oxidation with the participation of L-carnitine provides up to 75% of intracellular energy. This is more than in the process of glucose oxidation.
L-carnitine, in addition to bioenergetics, performs a number of important metabolic functions:8
- enhances the detoxification process, removing excess organic acids and compounds foreign to the body from cells, preventing their death;
- has an antioxidant effect: removes free radicals from the cell, helps neutralize them;
- inhibits the formation of ketoacids and anaerobic glycolysis, reduces the degree of lactic acidosis;
- replenishes the alkaline reserve of the blood, helps restore autoregulation of cerebral hemodynamics and increase blood supply to the affected area;
- accelerates reparative processes in the lesion and has an anabolic effect.
Two decades of observations, numerous studies and clinical use of the drug Elkar® in the treatment of various diseases and pathological conditions in children and adults have shown high efficiency, safety and have opened up wide possibilities for its use in the treatment of patients in cardiology, endocrinology, neurology, gastroenterology, and sports medicine. In pediatrics, the drug is used for diseases and conditions accompanied by decreased appetite, decreased body weight, and exhaustion; in children with a variety of pathologies from birth (premature babies, children with weakened feeding reflexes, with malnutrition, hypotension and adynamia, who have suffered asphyxia and birth trauma); for diseases accompanied by a lack of carnitine or its increased loss; as part of complex therapy for a number of skin diseases, during intense sports training and, of course, during the period of convalescence after diseases, including acute respiratory viral infections.
Thus, in the study by S.O. Klyuchnikova (2005) in frequently ill children, in addition to immune pathology, identified cellular energy deficiency. To eliminate it, children with ENT pathology were prescribed energy-tropic drugs, including levocarnitine. Normalization of indicators of phagocytic activity of neutrophils, activity of energy exchange enzymes of blood leukocytes (SDH, LDH, GDPG, GDH) and restoration of enzymatic activity of lymphocytes (from 18 to 27%) led to a decrease in the incidence of ARVI in children after taking a course of energotropic therapy.9 At the same time, in In children with an imbalance of autonomic regulation, while taking complex therapy including the drug levocarnitine, an improvement in autonomic reactivity was noted in 100% of cases, which led to a decrease in complaints, normalization of sleep and appetite, and increased physical endurance.9
The authors of the study noted the absence of any side effects of the drug levocarnitine, even in children with a history of allergies and signs of central nervous system damage.10
Later, in a comparative placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effectiveness of Elkar® in the treatment of children with chronic bronchopulmonary diseases accompanied by hemodynamic disturbances in the pulmonary circulation system (chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, lung malformations, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, bronchial asthma), L. AND. Agapitov and Yu.M. Belozerov (2010)11,12 demonstrated the antioxidant properties of levocarnitine. After a course of treatment in children with chronic bronchopulmonary diseases who received Elcar for 4 weeks (50 mg/kg per day), maximum and total endothelium-dependent vasodilation increased (p 11.12
The effectiveness of levocarnitine (Elkar®) in children with bronchial asthma of physical exertion was assessed in studies by G.A. Novika (2009, 2012). Patients in the main group (with confirmed post-exert bronchospasm) received Elkar for 2 months; children in the comparison group did not receive the drug (both groups of patients were comparable in clinical and laboratory parameters). During dynamic observation, the indicators of external respiration and the size of the bronchial lumen in children of both groups did not change significantly, but in children of the main group, unlike the control group, tolerance to physical activity increased (p 13
The influence of Elkar on the state of autonomic regulation and increased resistance to stress is shown in the study of S.L. Morozova (2015). Thus, when assessing heart rate variability in children, normalization of the state of the autonomic nervous system and, as a consequence, increased adaptation were noted.2
Improved adaptation, as well as metabolism and energy supply to tissues when using Elkar®, but already in young athletes was proven by the study of L.A. Balykova et al.14,15 Children with stress cardiomyopathy took the drug for a course of 1.5 months at a therapeutic dose of 75-100 mg/kg/day, athletes without signs of heart damage - at a prophylactic dose of 30-50 mg/kg/day.
Taking levocarnitine (Elcar®) showed changes in the effector and immunoregulatory components of the innate and adaptive immunity. In the majority of young athletes, when taking Elcar®, the indicators of humoral immunity reached the norm, which, combined with an improvement in indicators of cellular immunity (an increase in the absolute number of neutrophils and their metabolic activity), contributed to an increase in the body's anti-infective resistance and a decrease in the incidence of ARVI. In addition, the treatment contributed to an increase in the level of physical performance, optimization of hemodynamics in the heart and a decrease in the level of biochemical, psychological and other markers of stress.14,15
Effects of the drug Elkar® during recovery from illness:
- improves metabolism and energy supply to tissues;
- promotes better absorption of proteins, vitamins and other nutrients from food;
- cleanses cells of toxins;
- helps strengthen the immune system;
- improves heart function.
Thus, the above research data, as well as many others not included in this review, indicate a combination of metabolic, neuroprotective and immunocorrective properties of levocarnitine and the effectiveness of the domestic drug based on it Elcar® (L-carnitine) in the treatment and prevention of a wide range of conditions and diseases accompanied by symptoms of asthenia, including after ARVI.
The use of Elkar can significantly improve the health of children by normalizing the mechanisms of autonomic regulation, stabilizing cellular energy exchange, which, in turn, contributes to an increase in their physical activity and improved immunity.
Literature:
Avezova G.S., Kosimova S.M. Frequently ill children: prevalence and risk factors // European Research. 2021, 5 (28), p. 79–80. 2. Morozov S.L. Frequently ill children. Modern view of a pediatrician // RMJ “Medical Review”. No. 8 (from 09.27), 2019, p. 7‒9. 3. Zakharova I.N., Mumladze E.B., Tvorogova T.M., Pshenichnikova I.I. Asthenic syndrome in pediatric practice // Medical Council. No. 16, 2021, p. 124‒130. 4. Nemkova S.A. Modern principles of treatment of post-infectious asthenic conditions in children // RMZh. No. 6, 2021, pp. 368‒372. 5. Kotova O.V., Akarachkova E.S. Asthenic syndrome in the practice of a neurologist and family doctor // RMZh. No. 13, 2021, p. 824‒829. 6. International classification of diseases, 10th revision. https://mkb10.su/. 7. Brin I.L., Neudakhin E.V., Dunaykin M.L. Carnitine in pediatrics: research and clinical practice. M.: Publishing House "Medpraktika-M", 2015, 112 p. 8. https://zdravmedinform.ru/grls/reg-lsr-006143-10.html. 9. Klyuchnikov S.O., Nakostenko T.N., Sukhorukov V.S. XII Russian National Congress “Man and Medicine”. Moscow, 2005, p. 409‒410. 10. Nakostenko T.N., Klyuchnikov S.O., Sukhorukov V.S. Correction of disturbances of autonomic homeostasis and intracellular energy exchange in frequently ill children // Bulletin of pediatric pharmacology and nutrition. No. 1, 2007, p. 25‒29. 11. Agapitov L.I., Belozerov Yu.M. The effectiveness of L-carnitine in the correction of endothelial dysfunction in children with chronic bronchopulmonary diseases and impaired pulmonary hemodynamics // Questions of practical pediatrics. No. 5 (4), 2010, p. 78‒81. 12. Agapitov L.I., Belozerov Yu.M., Mizernitsky Yu.L. Chronic pulmonary heart disease in children. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014, 152 p. 13. Novik G.A. Bronchial asthma of physical exertion and methods of its treatment // Attending physician. No. 6, 2012, p. 27‒34. 14. Balykova L.A., Ivyansky S.A., Soldatov Yu.O. et al. L-carnitine as a means of increasing adaptation and correcting dysfunctions of the body of adolescents during intense physical activity // Practical Medicine. No. 9 (85), 2014, p. 140‒146. 15. Balykova L.A. et al. Changes in the cardiovascular and immune systems in young athletes: positive effects of L-carnitine // Consilium Medicum. Pediatrics. No. 4, 2014, p. 20‒24.
Lentigo
The phenomenon is popularly known as “senile ripples.” Appears in older people in areas of the body that have been exposed to intense ultraviolet rays throughout their lives. The pigment usually appears on the arms from the hands to the top of the shoulders, upper back, décolleté, and face. It is distinguished by its small size, different diameters and chaotic arrangement of spots.
The first manifestations can be noticed after 40 years; they noticeably age the appearance, so many people at this stage turn to cosmetologists to eliminate the defect. During menopause, hormonal changes lead to an increase in the amount of pigment. Chemical, mechanical and laser peels are used for treatment. Cosmetics and whitening creams will not cope with the problem.
Cost of consultation for anemia?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1300 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1300 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1000 - 2500 rub. |
All our services and prices
Solarium - is it harmful?
It is also a mistake to think that sun tanning is harmful, and nothing will happen in specialized salons in a few minutes. On the beach, the skin gets a lot of heat, but this happens gradually. In the booths, a loading dose of ultraviolet radiation is given in a few minutes, which is difficult to obtain outdoors even in a whole day.
People with a fair skin type, with the presence of moles and nevi, freckles, existing aesthetic defects in the form of increased melanin production, need to get rid of the habit of visiting a solarium. The consequences can be expressed both in the progression of unsightly changes in the epidermal layer, and in their degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
Diagnostics
To accurately determine the type of hypermelanosis, as well as to identify effective means of control, you need to contact a dermatologist. At the initial visit, the doctor will collect the patient's medical history to determine the most likely internal and external factors that will indicate a certain type of disorder. He will examine the skin and also prescribe a number of tests:
- AOK and OAM;
- blood biochemistry;
- Wood's lamp tests;
- scraping;
- biopsy.
If a malignant neoplasm or fungal infection is suspected, referrals will be given for the last two procedures on the list. As a result, the specialist will be able to accurately determine the type of illness and prescribe therapeutic or cosmetic procedures.
Anti-age drugs
Bb Laboratories – Hyaluron-elastin-collagen extract
Laennec – solution for injection
Curacen Essence (20 fl x 2 ml)
Two-phase placental serum concentrate
Principles of classification of anemia
There are several types of classifications of anemia, based on a number of signs - the cause of the disease, the mechanism of its development, stages, symptoms and other parameters. The following groups are distinguished:
Sign up for an anemia screening
Make an appointment
How to fight
Among the modern and effective methods of struggle, it is worth highlighting:
- cosmetic preparations;
- laser peeling;
- phototherapy.
Depending on the variety, medications may be prescribed to address the underlying causes. However, to remove an aesthetic defect, it will be necessary to wait for the cell surface to renew itself, or to help it renew itself faster with the help of additional deep peeling and cosmetic photorejuvenation procedures.
Cosmetic preparations
Among the popular drugs that give noticeable results in the fight against hyperpigmentation are placental products with a high content of natural peptides, amino acids and hyaluronic acid, as well as vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Injection product Curacen (Curasen) and non-injection drug Curacen Essence (Curasen Essence) are the ideal choice of cosmetologists for triple action: brightening, moisturizing and eliminating wrinkles. You can also use specialized cosmetics from the Laennec Skincare brand - LNC. This line offers to transform the skin at the cellular level, eliminating and preventing hyperpigmentation.
Now you know about the main causes of pigmentation, as well as what causes the appearance of age spots on the face, and you can easily answer the question - what to do when pigments have already appeared. Dermatologists recommend not only limiting time spent on the beach and using sunscreen in summer, but also year-round use of skin protection from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. It is this that becomes the main catalyst, and in combination with internal disorders of the body can lead to serious changes in the epidermal layer.
Pale face
Paleness is a lightening of the skin, which is caused by a change in vascular tone in the skin or a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin and the content of red blood cells in the peripheral blood. Pale skin is not always a sign of disease. Sometimes this is an individual feature that is observed in people who spend little time in the fresh air. Therefore, it is worth assessing not only the pale skin color in general, but also the discoloration of the mucous membranes and the whiteness of the nails.
If there are pathologies in the human body, this can affect the quality of blood microcirculation in the skin. It begins to enter the skin in insufficient quantities and because of this, the complexion changes - it becomes pale. What does a pale face mean? And does it happen that such a skin tone is a normal human reaction to external stimuli?