Normally, the mammary gland in men is not enlarged and contains only small amounts of fatty and glandular tissue. The underdevelopment of this organ in comparison with the female one is emphasized by the name itself - the mammary (rather than mammary) gland.
Gynecomastia is an unnatural enlargement of the male mammary gland (one or both) according to the female type. According to the degree of prevalence, diffuse (extensive) and nodular (partial) gynecomastia is distinguished. Breast enlargement can be moderate (up to 6 cm), medium (up to 10 cm) and severe (from 10 cm).
Characteristic symptoms of gynecomastia are:
- lumps or formations in the mammary glands, noticeable upon palpation;
- growth of the gland in size;
- pain in the breast area, increased sensitivity of the nipple;
- feeling of heaviness, bursting from the inside.
Important! Fluid discharge from the nipple, inflammation of the lymph nodes, changes in the color of the breast skin or nipple configuration may indicate the development of a breast tumor in a man! Be sure to consult a doctor if you notice these signs.
Causes of gynecomastia in childhood
The ICD-10 code (international code) for gynecomastia in men is No. 62. This group includes pathologies of the mammary glands that are not associated with childbirth. Depending on the reasons that provoked the disease, it is divided into pathological and physiological. The latter type of gynecomastia occurs more often in newborn girls and teenage boys. The main reason lies in hormonal imbalance, namely in the ratio of androgens and estrogens, and at the same time exceeding the permissible level of prolactin.
In infants
Situations where a baby has signs of gynecomastia occur quite often. The disease is common among this age group and can be considered a variant of the norm, since over time the pathology goes away on its own. Typically, the symptoms of such a disease in an infant gradually smooth out during the first month after birth, and then disappear completely. Such a manifestation can develop in a baby as a result of the mother’s hormonal background, which has left its mark on the child’s endocrine system.
In children and adolescents
Pathology can occur in children during puberty. The fact is that all people have both male (androgens) and female (estrogens) hormones. During puberty, the levels of these hormones fluctuate, sometimes significantly deviating from the norm, which causes the prevalence of one or another level.
Pubertal gynecomastia most often begins at 10-12 years of age and is at its peak around 13-14 years of age. Usually the disease begins to gradually regress at this time and disappears completely within a year and a half. Guys 17 years of age and older rarely encounter this problem.
In addition to hormonal imbalance, other diseases and abnormalities can also provoke the development of gynecomastia in boys:
- taking pharmacological drugs whose action is aimed at treating endocrine diseases, tuberculosis, depression;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the area of the ovaries and adrenal glands;
- unhealthy lifestyle, which includes the use of alcohol and drugs.
- liver and kidney diseases;
- injury to the mammary glands;
- autoimmune diseases;
- herpes zoster affecting the chest area;
- overweight, obesity caused by metabolic disorders.
If gynecomastia appears in a child under the age of one year, or at the stage of puberty, and then disappears on its own, then it is called physiological and does not require therapy. If the disease develops in adolescence and persists for two years, it is called a permanent sexual pathology and requires medical intervention.
Diagnosis of teenage gynecomastia
Diagnosing juvenile gynecomastia is not difficult. In most cases, an examination by a specialist is enough to make the correct diagnosis. Ultrasound can be an auxiliary diagnostic method.
The main task of the doctor is to exclude hormonal disorders, as well as genetic diseases, the symptom of which may be gynecomastia. If there are none, and gynecomastia is a manifestation of a hormonal imbalance noted during puberty or obesity in a teenager, treatment can only be surgical. Of course, such a young person needs to be oriented towards a healthy lifestyle, motivated to eat right and play sports. Often the first step on the path to physical rehabilitation is a surgical operation to get rid of female breasts.
Classification of the disease
Gynecomastia is divided in medicine into true and false. In the second case, the mammary glands increase in volume due to adipose tissue. This happens because the boy is overweight. And the true disease, in turn, is divided into categories: newborn, puberty and elderly. Depending on how severe the pathology is, three stages are distinguished:
- Initial gynecomastia. The enlargement of the glands in this case is almost invisible upon visual inspection.
- Second stage. In this case, the excessive volume is more pronounced. Now the child’s reproductive system also suffers, the number of sperm and libido decreases.
- The final, third stage. At this stage, the deformation is already irreversible. In the area of the mammary gland, the amount of connective and fibrous tissue predominates, which means that the problem can only be solved by surgical intervention.
According to localization in childhood, the disease is divided into unilateral and bilateral, when only one mammary gland enlarges (in the first case), or two at once (the second option). Most often, adolescents develop a bilateral, symmetrical appearance.
Differences between gynecomastia in girls and boys
The term “gynecomastia” refers to a pathological phenomenon in which benign growth of the mammary glands occurs specifically in men. It does not imply application to girls and women. The structure of the mammary glands in both sexes is very similar. These are sweat glands that have undergone significant changes in the process of evolution. They consist of glandular and adipose tissue. The structure of the breasts in men and women is identical, the only difference is in the degree of development.
With the onset of puberty, girls begin to actively grow their mammary glands, which is a physiological norm. In men, this phenomenon will be considered a pathology. Breast enlargement in girls should be called a disease only in isolated cases, when the volume increases significantly. The phenomenon also occurs as a result of the influence of sex hormones. But it happens that even with normal levels of androgens and estrogens, a girl’s breasts can become greatly enlarged. Therefore, modern medicine is trying to combat the use of the term gynecomastia in relation to women, considering the designation incorrect. In addition, during life, adipose tissue can accumulate inside the mammary glands in women, which will cause breast enlargement, but again cannot be considered a pathology. Therefore, most often doctors are inclined to call female breast enlargement hypertrophy, but not gynecomastia.
A change in the volume of the mammary glands in women can be called gynecomastia in two cases - if the increase occurs during the neonatal period, and in a situation where the volume of one breast exceeds four hundred cubic centimeters.
Causes of development and types of gynecomastia
Depending on the type of tissue, due to the growth of which the male breast increases, gynecomastia is divided into several types.
In the case of false gynecomastia (lipomastia), a man’s breasts acquire an atypical shape due to the growth of subcutaneous adipose tissue. And then the solution to the problem can be sports exercises, diet, liposuction for gynecomastia (removal of excess fatty tissue of the mammary gland).
However, sometimes a problem arises for other reasons and requires other solutions.
True gynecomastia is called unilateral or bilateral enlargement of the mammary gland due to the proliferation of glandular or connective tissue.
True gynecomastia is not always associated with alarming changes in the body. As a variant of the norm, it can accompany a man during three periods of his life ( so-called physiological gynecomastia ); this condition usually does not need correction and goes away without consequences.
Manifestations of physiological gynecomastia are associated with natural changes in the level of male sex hormones:
Gynecomastia in newborns is explained by the penetration of maternal sex hormones estrogen through the placenta into the boy’s body. Gynecomastia in adolescents (otherwise known as pubertal gynecomastia ) is caused by overactive production of gonadotropins during puberty; With the normalization of hormonal levels, the symptoms disappear. Gynecomastia in the elderly is associated with an age-related decrease in testosterone production and an increase in estrogen levels.
The term “pathological gynecomastia” is used when hypertrophy of the mammary glands is caused by various painful conditions that provoke the following hormonal imbalances in the male body:
- imbalance of estrogen and testosterone;
- an increase in the concentration of the hormone prolactin in the blood;
- metabolic disorders due to endocrine disorders;
- severe pathologies of non-endocrine nature;
- taking medications that affect hormonal levels;
- men taking anabolic steroids or androgens to increase muscle mass (gynecomastia in athletes);
- prolonged stress conditions, exhaustion of the body).
Mixed or combined gynecomastia is a pathology in which the mammary gland in a man becomes enlarged due to excessive growth of connective, glandular and adipose tissue.
In cases where the reasons for the development of pathology are unclear, the term “idiopathic gynecomastia” .
Symptoms and signs of pathology in different age categories
The disease manifests itself as a list of defining symptoms that can be used to identify the presence of a pathological process in the patient. In addition to enlargement of the mammary glands, when their volume can reach 10 and sometimes 15 cm, and the volume varies within 150 grams, the disease also manifests itself in other phenomena:
- In the area of the glands there are painful compactions of a homogeneous nature.
- Darkening of the areolas and nipples occurs, and excess pigmentation is acquired.
- The areolas increase in diameter, expand, and develop according to the female type.
- In some cases, the nipple can retract and become flat.
- The boy may complain of pain and heaviness in the chest.
- There may be clear or whitish discharge from the nipples.
In addition to the above, there are other signs, if present, you should immediately consult a doctor and get immediate treatment. These are unbearable pain in the chest, bloody discharge from the nipples, the formation of cracks in the areolas, damage to the skin, an increase in the volume of the axillary lymph nodes, and the formation of papules on the chest. Such signs may indicate the beginning of the development of carcinoma - a malignant tumor, which is extremely dangerous, so you need to consult a doctor immediately!
Diagnostic features
The doctor determines the presence of pathology through visual examination of the mammary glands and palpation. The boy's genitals can also be examined. Also mandatory studies for suspected gynecomastia are:
- Ultrasound of testicles and mammary glands;
- analysis of the patient’s blood for the content of hormones;
- X-rays of light;
- mammography, breast biopsy if there are lumps in it.
Only as a result of a full examination will the doctor be able to make the correct diagnosis and determine the direction of further treatment.
Treatment methods for gynecomastia in children
The method of treatment is determined based on the results obtained after the diagnosis. Therapy is selected by an endocrinologist or an endocrinologist-andrologist. The method of combating the disease depends on the degree of development of the pathology and other equally important aspects. If, as a result of the research, no dangerous deviations from the norm were identified, then moderate gynecomastia can not be treated, but only regularly monitored over the next six months. Most often, during this period the disease goes away on its own. In other cases, qualified treatment is required.
Surgical intervention
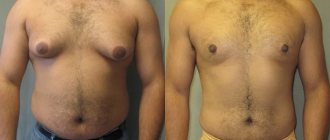
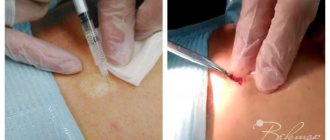
Obvious gynecomastia in young men, which does not go away on its own and is not amenable to conservative treatment within two years, requires surgical intervention. Surgical intervention in this case can be of three types, but always under general anesthesia and lasting about an hour each:
- Liposuction. It is carried out in the case of a false type of pathology arising as a result of obesity. During the process, the deep layers of tissue are not affected; you only need to reduce the volume of fat in the chest area.
- Mammoplasty. Consists of partial tissue removal. After such an operation, the mammary glands function normally.
- Mastectomy. This is the complete removal of breast tissue. It is used in extreme cases, but after such an operation the development of a true form of gynecomastia is completely excluded.
The type of surgical intervention is determined individually for each patient, and mostly depends on the degree of breast hypertrophy. In this case, you must completely trust the recommendations of an experienced medical specialist.
Drug treatment
If the disease persists for six months, the doctor prescribes treatment with pharmacological drugs. Typically these are medications whose action is aimed at suppressing the production of prolactin and stimulating the release of luteinizing hormone. Medicines should be used in accordance with the individual doctor’s recommendations for each patient. Under no circumstances should you try to set the dosage yourself, as this can only worsen the boy’s condition and provoke complications. Medicines are selected taking into account the level of hormones in the teenager’s body:
- "Thiamin bromide." Blocks aromatase, an enzyme that promotes the transition of testosterone to estrogen.
- "Bromocriptine" (and analogues). Stimulates dopamine receptors and also blocks the production of prolactin. The drug is suitable for patients with hyperprolactinemic type of teenage gynecomastia.
- "Testosterone". It is used in case of low testosterone levels in a boy’s body.
- "Clomiphene", "Takmosifen" and analogues. They are antiestrogenic drugs. They are used in case of excess estrogen in the male body.
In addition to the main treatment, doctors prescribe a course of taking vitamins A, B and E.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy (for example, electrophoresis) is prescribed as a stimulating technique that has a beneficial effect on increasing the activity of male sex hormone production in the area of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Physical training
Through physical activity in the early stages of gynecomastia, the patient can develop the production of male hormones. Also, regular activity will help bring your weight back to normal and get rid of extra pounds, if any. At home, it is recommended to perform push-ups, which will eliminate fat cells in the problem area and also help build muscle in the arms. You can also raise and lower your arms while lying down while holding dumbbells.
It will be an advantage if the classes are supervised by a trainer. A sports instructor will help develop an individual set of exercises that will be designed to solve the health problems of a particular patient and improve his well-being.
Changing the diet and quality of food
In the case of false gynecomastia, following a diet will help to effectively combat the problem, since reducing the caloric content of the diet will have a beneficial effect on the disease caused by excess body weight. Experts recommend starting to drink up to two liters of water a day, completely eliminating alcohol, and including slow carbohydrates in your daily menu, which are found in brown rice, cereals, and unleavened bread. You also need to eat protein foods in the form of cottage cheese, turkey, chicken, etc. Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet, reduce the amount of fried, flour and sweets.
In general, you need to calculate and consume no more than 2300-2500 kcal per day. A nutritionist will help you calculate the exact value. But it is important to understand that if with false gynecomastia the diet gives a good result, then with the true type of the disease a healthy diet will not be enough. The diet will help normalize the child’s psychological state and also strengthen his immune system, but the disease will need to be treated using other methods.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine can be a good help in treating the disease, but should not be used as the only method of combating pathology. Herbal medicine is permissible only after the approval of the attending physician.
According to reviews, thyme decoction works well as an anti-inflammatory agent. You need to take two tablespoons of dry raw materials, add 500 ml of water and simmer on low heat for five to seven minutes. This drug should be taken three times a day, 100 ml before eating.
You can also use herbal mixture with ginseng. To do this, you should prepare equal parts of licorice root, eleutherococcus, raspberry leaves and ginseng itself. Pour boiling water (400 ml) over a tablespoon of the crushed mixture and leave for three hours. Take two to three spoons of the prepared composition before meals.
News
18.11.2015
Pubertal gynecomastia in adolescents is associated with an increase in IGF-1 levels, but not a change in the ratio between estrogens and testosterone.
Pubertal gynecomastia is detected in adolescents during puberty in 50–70% of cases. Pubertal gynecomastia is believed to be associated with an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone production in favor of estrogen. However, such changes are very rarely found during examination in adolescents with this disease.
A team of authors from Denmark observed 106 adolescents aged 5.8 to 16.4 years as part of The COPENHAGEN Puberty Study from 2006 to 2014. The average age of the first examination was 9 years. Every 6 months, the anthropometric indicators of children, the dynamics of sexual development, as well as the levels of FSH, LH, testosterone, estradiol, sex-steroid binding globulin (SSB), inhibin B, anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH), insulin-like growth factor type 1 (IGF-1) were assessed. and IGF-1 binding protein (IGFBP).
Pubertal gynecomastia was detected in 52 out of 106 adolescents (49%). The average age at which this condition was diagnosed was 13 years; gynecomastia was most often detected at the stages of puberty G3 and G4. The average duration of persistence of gynecomastia was 1.9 years (1.1–2.6). According to the results of the study, boys with pubertal gynecomastia reached their peak growth rate at an earlier age than boys who did not have gynecomastia (13.5 years versus 13.9 years), they had significantly higher levels of IGF-1, estradiol, and free testosterone and FSH during puberty. However, no differences were found in the estradiol to testosterone ratio. It should be noted that the level of IGF-1 was within the reference interval in all examined children and corresponded to the stage of sexual development.
The authors note that IGF-1, together with estrogens, is a factor in the growth of breast tissue. In general, “there is no need to worry about gynecomastia in a pubescent boy. The main task of the doctor is to reassure the child and his family members and convince them that the condition is benign. However, it must be remembered that when examining adolescents and men with gynecomastia, endocrine causes of the development of this condition should be excluded.”
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/849975
Possible complications and consequences
Teenage gynecomastia usually goes away within the first two years after it occurs. This pathology only causes psychological discomfort in the boy. Young men with this problem are sometimes embarrassed to go to the swimming pool, gym, or use shared locker rooms.
But in some cases, the disease can cause serious problems in the socialization of a teenager. An increase in the volume of the mammary glands, which persists and develops for more than a year, can provoke fibrosis - scarring of tissue in the affected area. This significantly complicates drug therapy.
In extremely rare cases, gynecomastia can cause the development of carcinoma, a very serious disease. Therefore, if you experience severe chest pain, dark discharge from the nipples, or swelling, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Leave breasts to women and be men!
Adolescent gynecomastia is not only a medical, but also a social problem. Female breasts in a young man can be a serious obstacle to the formation of his personality as a man. Sports activities, equal relationships with peers, and communication with the opposite sex can be difficult or even impossible for boys with gynecomastia. We know examples when teenagers became withdrawn, preferred “communication with the computer” to social contacts, fell into depression, lost motivation to study, develop physically and become men.
In addition to psychological complexes and social maladjustment, such adolescents experience poor posture. In an effort to hide women's breasts, they stoop for many years, which leads to curvature of the spine. Some young men are forced to bandage their breasts with elastic bandages or cover their areolas with a plaster. There is no point in hoping that gynecomastia will go away over time. It is impossible to get rid of breasts with the help of medications.
Prevention of gynecomastia in children
Preventing the development of a disease is always easier than treating it. You can try to avoid gynecomastia by playing sports and monitoring your diet. There should be a diet, and it is advisable to choose healthy food with a high glycemic index. Also, patients who are prone to developing gynecomastia should regularly visit a doctor for preventive examinations. Alcohol, drugs and strong medications must be completely avoided.
Let's sum it up
Gynecomastia is common in boys of all ages. With proper treatment, the pathology does not pose a danger to the child, but parents need to take their son to the doctor in advance in order to begin to fight the disease at the initial stage. After 15 years of age, therapy becomes more difficult; surgical intervention may be required, so do not delay and make do with medications, physiotherapy and lifestyle adjustments.
If you or your loved ones have encountered the problem of gynecomastia, share your experience in the comments. Tell us which treatment was effective and how quickly you managed to get the desired result.