- Normalization of lactation
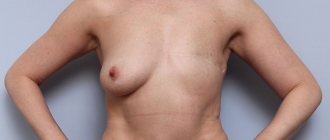
Breast asymmetry is a condition in which one female breast is larger than the other. Sometimes this becomes a big problem, in some cases it is a symptom of pathology. That is why every woman should know why one breast is smaller than the other. From this article you will learn the main reasons for different sizes or shapes of the mammary glands, methods for correcting asymmetry and answers to the most concerning questions.
When asymmetry is normal
In general, the body of any person is asymmetrical, and its paired parts are not exactly the same. This is absolutely normal. Visually noticeable asymmetry of the mammary glands in the fair sex is observed quite often.
So in what cases is breast asymmetry considered normal? It should not cause concern if the difference is insignificant or noticeable only upon detailed study. As a rule, normal asymmetry does not exceed 0.5 sizes. In this case, no other alarming signs or abnormalities should be observed.
If the differences are more noticeable and reach 1 size or more, and the woman notices other symptoms that worry her, this is no longer normal. In this case, you should consult a doctor, find out the causes of asymmetrical mammary glands, and, if necessary, correct them and eliminate the causes and related problems.
Breast asymmetry surgery
If disproportion of the mammary glands causes physical or psychological discomfort to a woman, it is worth seeking the help of plastic surgeons. In case of breast asymmetry, the operation is aimed at restoring the harmonious, natural and attractive shape of the main symbol of female beauty.
To solve this problem, reduction mammoplasty (reducing the size of a hypertrophied gland) or endoprosthetics (breast augmentation with implants) can be used. In case of tubular asymmetry of the breast, the operation is aimed primarily at restoring the shape of the mammary gland.
You can learn more about the possibilities of modern aesthetic medicine at a consultation with a plastic surgeon at the SOHO CLINIC. Make an appointment with a specialist and receive qualified answers to all your questions.
Types of asymmetry
Depending on external signs, breast asymmetry is divided into several groups:
- Hyperplasia of one of the mammary glands. The second has a normal shape and size.
- Bilateral hyperplasia with asymmetry. In this case, two breasts enlarge at once, but unevenly.
- Unilateral hypoplasia. One mammary gland is underdeveloped, and the second is normal.
- Asymmetrical bilateral hypoplasia, in which both breasts are underdeveloped and unequal.
- Hypoplasia combined with hyperplasia. In this condition, one breast is pathologically enlarged, while the other is not formed.
- Hypoplasia, combined with underdevelopment of the muscles and sometimes the chest. In this case, not only the breasts are underdeveloped, but also the sternum.
If we take the difference in size as the basis for the classification, we can distinguish three degrees of asymmetry:
- Mild or insignificant. The differences in shape and size are almost invisible, noticeable only upon closer examination.
- Average. The difference in volume is noticeable, reaching 30%.
- Heavy, pronounced. One mammary gland is 50% larger than the other.
Degree of severity and types of asymmetry
There are three types of severity of asymmetry:
- A slight difference between the right and left breasts (within the same size) is a slight disproportion.
- The disproportion is 1/3 of the size - average severity.
- The left or right breast is twice the size of the other - severe asymmetry.
For mild imbalances, vacuum massage and physical exercises are recommended to help strengthen the chest muscles. The use of such methods gives a short-term effect, which soon disappears.
Characteristic symptoms
Asymmetrical breasts vary in size in most cases. But the difference can also be observed in shape and structure. So, one mammary gland may be more elongated (the so-called tubular), and the second – rounded. Sometimes unilateral ptosis is observed - prolapse.
Other situations are also possible, for example, when one nipple is larger than the other, or the areola of one breast is larger or smaller. Sometimes the chest looks in different directions.
All the signs described above relate directly to external, aesthetic defects. But if the causes of breast asymmetry are serious, accompanying unpleasant or alarming symptoms may be observed: soreness, swelling, hardening or discomfort in the mammary glands, abnormal discharge from the nipples, menstrual irregularities, problems with conceiving and bearing a child.
If one breast is significantly and very noticeably larger than the other, then a girl or woman may have severe complexes, experience discomfort when in public places, become withdrawn and face problems when building relationships with the opposite sex. And all this can provoke neuroses and depression.
Contraindications for surgery
Mammoplasty is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- pregnancy (during pregnancy all types of surgical interventions on the mammary glands are prohibited, except for the treatment of cancer),
- diabetes mellitus,
- lactation,
- blood diseases with bleeding disorders,
- diseases of the thyroid gland,
- lung diseases,
- cardiovascular diseases,
- tumor processes in the mammary gland.
Mammoplasty cannot be performed from the first to the fifth day of the menstrual cycle. The operation is performed with caution if there is a tendency to form keloid scars.
Why can breasts become asymmetrical?
Why is the left breast larger than the right or, conversely, smaller? There are many reasons, and they can be divided into two types: congenital, which arose during the formation of the fetus in the mother’s womb, and acquired, which developed after the birth of the girl.
Congenital factors include the following:
- Genetic disorders, hereditary diseases. These are various congenital syndromes, and they are often accompanied not only by asymmetry of the mammary glands, but also by other pathologies, for example, deformities of the chest and other parts of the body.
- Fetal injuries. A developing child may be subject to mechanical stress, for example, when the expectant mother falls or receives strong blows to the stomach.
- Defects and anomalies of intrauterine development of the fetus. They occur for various reasons, for example, due to defects in the female egg or male sperm.
Acquired reasons are much more common, and they are worth talking about in more detail.
Puberty disorders
Normally, breasts begin to form in girls from the age of 9-13 years, develop fully around 17-20 years, and finally complete their formation after childbirth and lactation. During puberty, certain changes occur in the body, and they are not always uniform. If a teenage girl has growing breasts of different sizes, this is almost always the norm: as she gets older, the problem disappears, and the mammary glands become approximately the same.
But the process of puberty does not always follow a normal, physiologically correct scenario. Thus, breasts can begin to grow much earlier (at 3-6 years) without the appearance of other sexual characteristics such as menstruation, changes in body proportions and hair growth in the armpits and pubic area. In this case, fatty and glandular tissues begin to form prematurely in the mammary glands.
Another scenario is hormonal imbalance during puberty. The female hormones progesterone and estrogens are responsible for the growth of the mammary glands. The latter are responsible for creating the normal cellular structure of tissues. And progesterone promotes the proper formation of milk ducts and alveoli. If the levels of these hormones deviate from the norm, then one mammary gland may appear significantly larger than the other.
Hormonal imbalances
If one breast is larger than the other, the reason may lie in hormonal imbalances that can occur in the body of girls and women at different periods of life:
- after pregnancy and childbirth;
- after abortion or surgical curettage of the uterus;
- during menopause or menopause;
- after suffering severe stress or nervous shock;
- against the background of sudden climate changes.
Good to know!
With hormonal imbalances, irregularities in the menstrual cycle (delays, early periods or complete absence of critical days), discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen and mammary glands are also observed.
Gynecological diseases
With gynecological diseases, the concentrations of female hormones almost always change, and disorders develop, including those affecting the breasts. Such diseases include endometriosis, endometritis, polycystic ovary syndrome, uterine fibroids and other pathologies.
Breast surgeries
It is not uncommon for the left breast to be larger than the right (or vice versa) after breast surgery. Moreover, such surgical interventions can be performed for both medical and aesthetic reasons. In the first case, tumors are usually removed. If the tumor is excised along with the surrounding tissue, the mammary gland will inevitably become smaller. And after a mastectomy (radical removal), the asymmetry will be completely obvious.
Sometimes asymmetry develops as a consequence of plastic surgery, if the surgical technique was violated, the doctor made a mistake, or the patient did not follow the recommendations given by the doctor. Thus, after augmentation surgery, the endoprosthesis may move or a complication such as capsular contracture (an individual reaction of the body to a foreign body) may occur in only one breast, which can affect the appearance of the mammary gland. It is also possible to develop complications in the form of infection and hematomas.
Childbirth and lactation
Different breasts often become a problem during pregnancy or after childbirth, during breastfeeding. During the gestation period, the mammary glands change: the number of alveoli increases, the milk ducts begin to fill. And sometimes such processes in two breasts proceed unevenly.
One breast is larger than the other during breastfeeding (that is, during feeding) very often. Lactation can change the bust, because during this period milk production starts. And in one mammary gland its amount may be greater. Then she will be larger.
Often, excessive filling of one mammary gland is provoked by the nursing mother herself, who makes mistakes. The volume of breast milk directly depends on the stimulation of the nipple: the more the baby sucks on a particular breast, the more food comes to him. Therefore, if a mother often, or even more so constantly, feeds with only one mammary gland, then it will be larger in size. The difference can also be observed due to mastitis (inflammation of tissues) due to improper attachment or incomplete emptying.
Good to know!
Usually after the end of lactation the situation returns to normal, but sometimes the difference remains and is obvious.
Mastopathy
Mastopathy, also called fibrocystic disease, is characterized by pathological growths of mammary gland tissue against the background of a decrease in the amount of progesterone and an increase in the concentration of estrogen. With this disease, which occurs quite often, discomfort, swelling of the mammary glands, pain, and sometimes even discharge from the nipples are observed.
Neoplasms
Unfortunately, sometimes different breast sizes are associated with neoplasms, which can be either benign or malignant. In the first case, cysts (cavities filled with liquid content) or fibroadenomas are detected - fibrous nodes, accumulations of connective cells. With such neoplasms, discomfort, bloating, and sometimes pain are felt. Also, nodes and cysts can be felt during palpation.
Malignant neoplasms are cancerous tumors that may not make themselves felt in the early stages, but as they grow, they compress surrounding tissues and can metastasize.
Injuries
The cause of asymmetry of the mammary glands is sometimes due to injuries, even those received in childhood, when the breasts had not yet begun to form or were just at the stage of maturation. But injury in adulthood can also provoke a change in the shape or size of one mammary gland due to severe damage, as well as scarring and proliferation of connective tissue.
Physical activity
Even physical activity can affect breast size, albeit slightly. So, if a girl has one pectoral muscle working more actively and intensely, then it will be more voluminous. Therefore, the mammary gland will begin to protrude above the level of the chest more strongly.
Indications for surgery
Most of the methods for treating breast asymmetry are surgical treatment. These treatment methods have certain limitations, the decision is made in each case individually. Surgery to correct breast asymmetry is recommended for women with moderate to severe disproportion. The indication for surgery is a violation of the shape of the breast, when one breast has a different shape from the shape of the other breast.
Differences may include the following characteristics:
- Asymmetry in the projection and volume of the chest cavity.
- Discrepancy between the nipple and areola, the difference in their sizes. If there is asymmetry of the nipple areola, the size of the areola is changed. If one nipple is different in shape and larger than the other, the surgeon performs a nipple reduction, correcting not only its size, but also its shape.
- Asymmetry of the fold located under the breast.
- Sagging of the mammary glands, differences in shape or size.
Very often such pathologies have a genetic cause. If only one breast is of normal size, and the second is underdeveloped, then the defect is corrected using a silicone endoprosthesis. If one mammary gland is greatly enlarged and the other is of normal size, the surgeon performs a reduction of the enlarged mammary gland. If one breast is hypertrophied and the other is hypotrophic (this pathology most often refers to genetic disorders), the surgeon performs bilateral mammoplasty.
In case of breast ptosis, when the prolapse of one gland is greater than the other, the surgeon performs a lift through an incision in the alveolar area. This type of lift is performed when the breast size is small.
When there is hypertrophy of one breast and prolapse of the second gland, a lift and reduction mammoplasty is performed on the hypertrophied gland. Breasts of different sizes that have asymmetrical ptosis are corrected using mastopexy. If the breast size is small, the surgeon can enlarge both breasts using implants of different sizes or enlarge the smaller breast.
The small size of one mammary gland and the tubular (elongated) shape of the other gland are eliminated by installing an endoprosthesis under the tissue of a small mammary gland. The hypertrophied tubular shape of the breast is corrected by mammoplasty. The tubular shape of both glands is corrected without the use of endoprostheses.
Diagnostics
If one breast has become noticeably larger than the other, you should make an appointment with a doctor. First, visit a mammologist, who should conduct an initial examination with palpation, and if abnormalities are detected, prescribe additional diagnostic procedures: ultrasound, mammography, in some cases histological examination, MRI or CT (for high risks of cancer).
Based on the results of the examination, the mammologist can recommend an appointment with specialized specialists: gynecologist, oncologist, endocrinologist, geneticist, surgeon.
How to avoid implant displacement after surgery?
You should be careful when choosing a surgeon. A qualified, experienced specialist will select the correct endoprostheses and plastic surgery method based on the characteristics of each patient.
Compliance with all the surgeon’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period will allow the woman to avoid a number of problems and complications, one of which is different breasts after mammoplasty. The patient will recover as quickly as possible and return to her usual lifestyle, enjoying the beauty of her bust.
It is important to understand that plastic surgery will correct initially very pronounced breast asymmetry, but may not completely eliminate it. When talking about disproportions, what is taken into account is not the size of the breast, but the distance from the nipple to the inframammary fold and the armpit. Often, for an ideal result, it is necessary to remove excess skin, which will increase the number of scars, which the patient is unlikely to agree to. Therefore, after mammoplasty, the presence of slight asymmetry is acceptable.
Methods for correcting asymmetry
What to do when one breast is larger than the other? There are no general recommendations or universal methods for eliminating asymmetry. But in most cases, different sizes can be equalized, making the bust more attractive and symmetrical. The main methods of correction are discussed below.
Normalization of lactation
When one breast is larger than the other during breastfeeding, it is quite easy to solve the problem. It is enough to establish lactation:
- Apply your baby to the breast correctly.
- Feed your baby more often from the smaller breast. Then more breast milk will flow into her, and the bust size will even out.
- To prevent cracked nipples, pre-moisten them with a few drops of milk.
- Change breasts, do not feed one several times in a row.
Advice!
If one breast is larger than the other during breastfeeding, and the woman cannot cope with the problem, then it makes sense to get the help of a lactation consultant who will tell you how to do everything correctly.
Correctly selected underwear
A special bra will not eliminate it, but it will mask the defect. It may have removable foam or silicone inserts: by removing one of them, you can visually reduce the size of your breasts, which are larger. There are also specialized underwear for sale for women who have had a mastectomy. And if you wish, you can order a custom-tailored bra.
Drug therapy
When one breast has enlarged due to hormonal imbalances, medical conservative treatment is possible. A gynecologist prescribes hormone-based medications. But such drugs are prescribed only after a thorough assessment of hormonal levels. Their release forms, dosage regimens and exact dosages are selected strictly individually. When hormonal levels return to normal, different breasts will most likely become symmetrical.
Lipofilling
Lipofilling is the introduction of your own fat tissue into the mammary gland, which is borrowed from the most voluminous parts of the body. The fat undergoes preliminary cleaning and preparation and is injected into the bust with special instruments. But with this method it is possible to enlarge the breasts by a maximum of 1-1.5 sizes in one procedure. It is worth remembering that when losing weight, breasts with lipofilling will also shrink.
Mammoplasty
If one breast is very clearly larger than the other, and this is not corrected by conservative methods, causing psychological and physical discomfort in the woman, then plastic surgery becomes the only way out and the right solution. During the operation, asymmetry is eliminated and the bust is given the desired shape.
But what kind of surgery is performed when the breasts are different? There are different types of mammoplasty, and only the surgeon must decide what is suitable in a particular case. The doctor makes a decision in favor of using one or another technique, paying attention to important factors:
- presence/absence of contraindications;
- severity of asymmetry;
- features of the breast structure;
- the presence of ptosis and its severity (how much lower one breast is than the other);
- related problems;
- the need to increase or, conversely, reduce the bust;
- the wishes of the woman herself.
Below we discuss the main mammoplasty techniques that are used to correct an asymmetrical bust. To ask questions and pre-determine the appropriate option, you can simply call or contact other contacts, come to the clinic for a personal consultation, or find the information you are interested in on the website (sometimes online chat is available). In the same way, you can find out more about all the center’s services, prices and promotions.
Endoprosthetics
Endoprosthetics is the augmentation of the female breast with prostheses. Implants are made from biocompatible and safe materials. The shell of modern implants is made of medical silicone for long-term implantation. The same silicone is mainly used as a filler. In rare cases, implants filled with saline or biogel are used.
If one breast is larger than the other, then an implant can only be installed in the smaller breast. But surgeons usually recommend bilateral correction. The doctor carefully and personally selects different endoprostheses, choosing the optimal size, shape (round or drop-shaped) and profile (projection). As a result of a correctly performed operation, the bust will look as symmetrical as possible for each case.
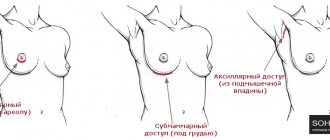
Installation of endoprostheses is carried out by three methods: periareolar (with an incision along the contour of the areola), submammary (under the breast, in the fold) and axillary (in the armpit area). The first method is mainly used for small implants and a sufficient areola size. Submammary access is considered the safest; the scar is located in the submammary fold and over time becomes almost invisible. With axillary access, the endoscopic method of installation is most often used. The scar is located in the natural fold of the armpit.
Reduction mammoplasty
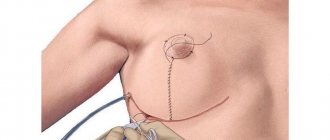
When one breast is very much larger than the other, the doctor may suggest reduction mammoplasty, that is, reduction with excision of excess tissue. Access is formed either vertically from the nipple to the inframammary fold, or using the anchor method along the contour of the areola from below, then down vertically and along the line of the inframammary fold. An incision around the areola is made extremely rarely if only minor amounts of tissue need to be removed. The surgeon excises excess skin and soft tissue, then fixes the edges of the skin and applies sutures.
Mastopexy
If one breast is lower than the other and there is obvious ptosis, then it is advisable to perform a mastopexy, that is, a lift. It involves removing excess skin and giving it an attractive shape.
With slight prolapse, a periareolar approach is formed around the areola. If the ptosis is severe, then other techniques are applicable - vertical (the suture runs from the areola to the fold) or anchor with incisions along the lower edge of the nipple-areolar complex, vertically to the inframammary fold and along the line of this fold. At the same time, the doctor will be able to correct the nipple and areola if they are deformed or stretched.
Asymmetry after mammoplasty: why it happens and what to do
When deciding on breast surgery, every woman expects to eventually become the owner of a luxurious bust. But sometimes things don’t go according to plan and the result turns out to be completely different from what was originally intended.
Breast asymmetry after mammoplasty is a specific consequence of the operation, in which the glands look different in shape, volume or level of areola. Subtle differences are considered a variant of the norm. More significant ones are considered as a complication; it may be caused by a surgeon’s error or violation of the doctor’s recommendations during the recovery period. To correct a pronounced defect, repeated intervention is often necessary.
What changes should not be considered a cause for concern, and in what cases should you contact a surgeon, says Ilya Vyacheslavovich Sergeev, a permanent expert at TecRussia.ru, a leading Russian specialist in breast plastic surgery:
↑ What is asymmetry and why does it occur?
Many patients begin to suspect something is wrong and become nervous in the first days after the intervention. But, as a rule, the alarm turns out to be premature. The final conclusion can be made no earlier than 1.5-2 months after the operation, when swelling and hematomas go away: they can greatly distort the result, making it difficult to adequately assess the volume and shape of the breast.
Sergeev Ilya Vyacheslavovich Plastic surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, leading specialist in breast plastic surgery at the DoctorPlastic clinic
There are no perfectly symmetrical people, and slight differences in the size and position of the mammary glands are absolutely normal. Both before and after plastic surgery. But if we are talking about asymmetry, which is calculated in centimeters and at the same time causes serious aesthetic discomfort, it makes sense to correct it.
The first step when working with such patients is the surgeon takes measurements, recording:
- width of the base of the gland;
- the distance from the areola to the inframammary fold and to the manubrium of the sternum separately;
- the interval from the center of the sternum to the nipple of each gland.
When obvious deviations are identified, it is important to determine the cause of their occurrence. The most common options:
- Displacement of the implant due to errors during surgery (for example, if the surgeon creates an excessively spacious pocket), ill-chosen shape or size (implants with a volume of more than 500 ml are more often displaced), non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period (early refusal of compression garments or irregular use). wearing, sleeping on the stomach, excessive physical activity), mechanical influences, etc.
- Seroma. This is a pathological formation that occurs as a result of the accumulation of serous fluid - lymph - in the area where the implant is placed. It usually develops in the first 10–15 days after plastic surgery. The reason is damage to the vascular walls, which is inevitable during extensive interventions. Provoking factors are injuries to the lymph nodes due to violation of the surgical technique, excessive compression of tissues, which occurs when installing large endoprostheses, and violation of the schedule for wearing compression garments. It can reach quite large sizes and be accompanied by additional symptoms: discoloration of the skin, local hyperemia, pain on palpation.
- Capsular contracture. Immediately after completion of the operation, a shell of fibrous tissue begins to form around the endoprosthesis; normally, its thickness does not exceed tenths of a millimeter. But under the influence of pathological factors, the walls of the capsule can thicken and become denser due to the deposition of calcifications. Dense fibrous tissue puts pressure on the implant, leading to its displacement and deformation.
- Rupture of the endoprosthesis shell. This complication is extremely rare and can be caused by mechanical trauma to the chest, a factory defect of the endoprosthesis, or accidental damage during invasive medical procedures.
↑ How to eliminate asymmetry
Once the exact cause of the deformity is determined, the surgeon will offer options for eliminating it.
Repeated operation.
It is often possible to restore the breasts to a harmonious and attractive appearance only with the help of another surgical intervention. If the patient’s condition does not cause concern, and the problem is purely aesthetic in nature, for example, the cause of asymmetry was the displacement of the implant due to increased physical activity, the operation is prescribed as planned. It is recommended to maintain an interval of at least six months between the two procedures. During this time, the final result will be formed, which will make it possible to clearly determine the volume of the upcoming correction.
In the event that a change in the size or location of the gland provokes a seroma or rupture of the thoracic endoprosthesis, emergency surgical assistance may be required after examination. The doctor determines the scope of intervention based on the causes and scale of the problem.
- In case of pathological thickening of the capsule walls, the operation is performed using one of the following methods: capsulotomy - involves dissection of the fibrous cavity to reduce pressure on the endoprosthesis, or capsulectomy - the shell is partially or completely removed, which is often combined with replacing the implant or its transfer to another area, as well as with a lift fabrics.
- Lymph accumulation usually does not require implant replacement: during surgery, the seroma cavity is cleared of its contents mechanically, using a syringe, or drainage is installed, which ensures gradual removal of tissue fluid. The surgeon's manipulations during aspiration must be as precise and careful as possible, since there is a high probability of touching and damaging the thin wall of the endoprosthesis.
- If there is displacement due to an overstretched pocket, a full-fledged operation is performed with or without implant replacement. At the same time, the surgeon usually performs a T-lift. The overstretched cavity is released, then sutured to the required size and the endoprosthesis is reinstalled.
- A rupture of the implant shell is also an indication for its replacement. As a rule, such situations do not threaten health, so the operation is carried out as planned.
During repeated surgery, the surgeon should pay special attention to selecting a new endoprosthesis and determining its placement location, taking into account the factors that provoked the complication after the previous operation. It is important to clearly establish in which zone the implant is located, assess the condition of the tissues, and take into account the presence of scars or adhesions. For this, the patient is prescribed additional tests: mammography, radiography. If possible, the incision is made along the old seam.
Non-surgical correction.
In some cases, you can try to eliminate asymmetry without using a scalpel. For example, for small seromas, it is possible to prescribe drug therapy, which includes taking broad-spectrum antibiotics (Ofloxacin, Ceftriaxone), glucocorticoids (Diprospan), NSAIDs (Meloxicam). After treatment, the cavity disappears and no longer puts pressure on the implant, as a result of which it can move into place on its own.
It is also possible to do without surgical intervention if the implants have moved slightly upward due to early refusal of compression hosiery. In this case, the doctor applies a special bandage to the glands, which presses on the upper part of the chest, helping to return the endoprostheses to the desired position.
↑ How to avoid asymmetry: general recommendations
This complication is easier to prevent than to treat. To minimize the risk, it is important to contact a reliable clinic, a plastic surgeon whose experience and competence you do not doubt. But even after a successful operation, the likelihood of developing asymmetry remains. You can avoid adverse consequences if you strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and rehabilitation rules, in particular:
- Wear well-chosen compression stockings, strictly according to the schedule determined by the surgeon. As a rule, the shapewear is not removed at all for the first week, then worn during the day for about 1 month. These periods may be extended depending on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Carry out regular treatment of sutures, monitor their condition, and if symptoms such as severe hyperemia, pain, discharge of ichor or pus appear, immediately consult a doctor.
- Do not raise your hands for 8–10 days. Sleeping on your stomach or side is allowed only three weeks after plastic surgery.
- Avoid sharp bends and turns for at least a month; for the same period, exclude heavy lifting and active physical activity. Strength and contact sports may remain banned for up to six months.
When operations are contraindicated
All operations described above have general contraindications:
- any neoplasms;
- ARVI;
- other severe infections;
- diabetes;
- foci of dermatological diseases, inflammation or ulcers on the chest;
- blood clotting disorders;
- mastopathy;
- pregnancy;
- minor age;
- acute general inflammatory processes;
- tendency to keloid scars;
- severe mental disorders;
- lactation and the six-month period after its complete completion;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
How to prepare for mammoplasty
Preparation for surgery requires, first of all, a comprehensive examination, including ultrasound examination of both mammary glands, ECG and fluorography, sometimes CT or MRI, and radiography. Blood tests are taken for coagulation (coagulogram), for syphilis, HIV and hepatitis, for group and Rh factor, for biochemistry, as well as general urine and blood tests. Sometimes consultations with specialized specialists are required: cardiologist, endocrinologist, phlebologist, oncologist, mammologist.
Preparation involves the following rules:
- refusal to take medications that affect blood clotting (two weeks before mammoplasty);
- quitting smoking, alcohol and junk food a week before the surgery date;
- taking a bath/shower the day before plastic surgery;
- stopping the consumption of food and liquids 9-12 hours before the start of the intervention.
Rehabilitation
Operations in clinics and plastic surgery centers are performed under general anesthesia. After completion of the plastic surgery, the woman is transferred first to the intensive care ward and then to the general ward. She remains in the hospital for a day, and then, if there are no complications or worsening of her condition, she is sent home. In the first days, dressings and treatment of sutures are carried out.
For a speedy recovery, you need to follow the rules:
- take antibiotics and painkillers as prescribed by your doctor;
- do not raise your arms or wave them for a month;
- sleep exclusively on your back for a month;
- wear compression garments constantly for 2-3 months and another year during physical activity;
- do not go to beaches, baths/saunas, or public bodies of water for two months;
- resume normal training no earlier than three months later, avoiding stress on the upper shoulder girdle;
- visit a surgeon for routine examinations.
The rehabilitation period depends on the complexity of the operation, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, and compliance with medical prescriptions. Pain may persist for the first few days, swelling may persist for one to two weeks. The first effect should be assessed after complete healing of the sutures and formation of scars - after 1.5-3 months. The final result will be visible in 8-12 months.
Complications, according to reviews and comments from patients, develop infrequently. But suppuration and dehiscence of sutures, hematomas, tissue infections, seromas, sepsis, migration (displacement) of prostheses, capsular contracture, etc. are possible. In some situations, repeated surgical interventions are necessary.
Progress of the procedure
Mammoplasty consists of the following stages:
- Marking future manipulations.
- Surgical work with adipose and glandular tissue.
- Change according to plan.
- Stitching.
After this, the patient is transferred to another ward, where she recovers from anesthesia under the supervision of a specialist. Next, the patient is sent to the hospital for a couple of days.
Rehabilitation
After the operation, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for 1-2 days. The stitches are removed after two weeks. During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to avoid sports and wear compression garments.
Beautiful female breasts are wonderful! And every girl deserves this. We are making a dream that seemed impossible for several decades into reality. Sign up for an initial consultation with our doctor by phone. A plastic surgeon will answer all your questions and tell you more about what results can be achieved in your case.