Published: 09.27.2021 17:55:00 Updated: 09.27.2021
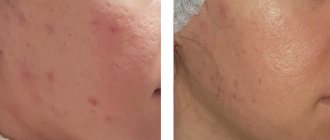
Eczema is a chronic or acute inflammatory skin disease of a non-infectious nature, characterized by frequent relapses in the form of a finely blistered rash with redness and itching. Symptoms appear under the influence of provoking factors and are caused by the body’s immunoallergic reaction. Depending on the form of pathology, manifestations may differ in location and nature. The disease is resistant to treatment, so secondary prevention of exacerbations and timely diagnosis in the early stages are extremely important.
Causes
A genetic predisposition to the occurrence of the disease has been proven. However, the causes of eczema are also considered:
- changes in the functioning of the immune system;
- allergies to household dust, medications, pollen, cleaning and detergents, washing powder;
- pathologies of the endocrine system organs - pituitary gland, adrenal glands, gonads;
- stress, neuropsychic disorders;
- chronic infectious process in the body - kidney damage, sore throat, otitis media, caries;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- hypovitaminosis.
External factors can provoke an exacerbation of the disease:
- influence of high or low temperatures;
- skin damage, friction;
- exposure to chemicals, including cosmetics or care products;
- food allergens and alcoholic beverages.
As a result, with eczema, allergic and autoimmune reactions develop, the body begins to produce antibodies - immunoglobulins to its own skin cells, which entails the development of inflammation, the appearance of blistering rashes and redness.
What can itchy skin mean?
Medical causes of itching and flaking can be divided into two large groups: the first is skin diseases themselves (eczema, seborrhea, psoriasis, etc.) and the second is diseases and pathologies of other organs and systems, including skin manifestations. A separate group includes mechanical damage to the skin, sunburn, bites, and skin reaction to the effects of artificial materials.
Skin itching and peeling can be caused by:
- Allergic reactions
- Neurological disorders
- The presence of parasites in the body
- Metabolic disorders that cause the sebaceous glands to malfunction
- Pathological conditions and diseases of internal organs and systems - for example, liver, gall bladder
Classification
The disease, depending on the severity of symptoms and duration, can have an acute, subacute or chronic course.
In the first case, bright manifestations are characteristic, lasting 1-2 months. As the process becomes chronic, periods of exacerbation of eczema are replaced by remissions, and the disease drags on for years. Eczema has a staged course:
- Erythematous stage. It manifests itself as redness of the skin, swelling and itching.
- Papular stage. The formation of small red nodules is characteristic.
- Vesicular stage. Small blisters with clear liquid inside appear on the skin, grouped mainly on the neck, palms, ankles, elbows and popliteal folds.
- During the weeping stage of eczema, the covers of the vesicles open and erosions form.
- Cortical stage. Eroded surfaces dry out and become crusty.
- Peeling stage. The crusts are peeled off and damaged tissues are restored. With chronic eczema, the skin becomes dry and rough, and pigmentation appears on it.
What are the symptoms of peeling and itching?
Itching is different from itching - of course, if you just have something itching, you shouldn’t immediately suspect the worst. First, you need to carefully examine the areas of the skin that bother you and listen to your condition. If you have a strong feeling that the cause is an allergy, under no circumstances should you postpone a visit to the doctor - severe forms of allergies can be accompanied by serious conditions, including Quincke's edema, from which you can die.
External causes (insect bites, sunburn, etc.) usually cause localized itching —one or more specific areas itch and hurt. As a rule, irritation is accompanied by characteristic redness and passes relatively quickly.
so-called prickly heat - irritation due to insufficient evaporation of sweat - also has characteristic manifestations. In order to cope with it, as a rule, it is enough to start carefully observing hygiene and wearing natural fabrics.
Itching and flaking that affect certain parts of the body (hands, areas under the knees, scalp under the hair) can signal scabies , ringworm or incipient psoriasis . Conditions in which exfoliated areas of the skin cause wounds and cracks are especially dangerous - since in this case an infection can occur and treatment will take much longer.
Blisters and sores, a rash in areas that itch are a signal of a possible infectious disease - for example, chicken pox or measles. With these diseases, the rash first appears in isolated areas and then quickly spreads throughout the body.
If the itching you experience has no obvious cause, covers the entire body and prevents you from sleeping, contact a specialist immediately. The sooner treatment is started, the faster you will be able to get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Itching all over the body is a very alarming signal. It is he who, as a rule, speaks about serious internal diseases, including, in particular, diabetes mellitus, tumors, leukemia, and hepatitis. It may subside for a while or be permanent - one way or another, the patient notes that the skin does not stop itching and peeling for a long time.
Symptoms and forms
The main symptoms of eczema are itching of varying intensity, burning, redness and swelling of the skin, and a rash in the form of blisters. Depending on the clinical picture, the following forms of the disease were identified:
- True. The affected areas without clear boundaries alternate with each relapse of the disease until the rash spreads throughout the body and the appearance of fever. The lesion is characterized by symmetry. During an exacerbation, a small rash appears on the skin in the form of red bubbles, reminiscent of bubbles when water boils. Later, erosions with weeping, yellowish crusts, and scratches form. Eczema is often complicated by the appearance of ulcers caused by infection.
- Seborrheic. The first manifestations of the disease occur on the scalp, moving to areas where the largest number of sebaceous glands is - behind the ears, on the chest, neck, between the shoulder blades, in the elbow and popliteal folds. The skin takes on a red tint, becomes swollen, yellowish-pink nodules, greasy yellowish scales and crusts appear on it.
- Microbial. An important role in the development of the disease is played by the skin barrier, which prevents the penetration of bacteria into the body. When its integrity is violated, in particular due to severe itching and scratching, microbes cause the appearance of foci of infectious inflammation. They are often localized around purulent wounds and in places of long-term pyoderma, have an irregular shape and asymmetrical location, and are clearly limited from healthy tissue by a border of exfoliating epidermis. In the center you can find purulent and serous crusts, under which there are oozing holes in the form of wells.
- Coin-shaped. Characteristic are clearly defined plaques up to 3 cm in diameter consisting of many nodules, vesicles, oozing and crusts. With ring-shaped forms, the density of the rash decreases in the central part. In the chronic course, the affected areas become dry, flaky, and the skin thickens.
- Varicose. Occurs with varicose veins, untimely treatment of varicose ulcers, trauma to varicose nodes. With this type of eczema, the skin on the legs, in the shin area, is predominantly affected. Severe itching is also noted.
- Sycosiform. Accompanies vulgar sycosis - inflammation of hair follicles of staphylococcal etiology. Lesions can be found not only on the scalp, but also on the upper lip, armpits, chin and pubis. The appearance of serous wells, intense itching and weeping is characteristic.
- Eczema of the nipples. Appears during breastfeeding due to trauma to the nipples and infection. The lesion is characterized by a symmetrical lesion with the formation of areas of redness, weeping, and in some cases cracks and blisters on the skin.
- Children's room. In children, the most common areas for eczema are the face, chest, chin, and buttocks. The first manifestations of the disease can be noticed 3-6 months after birth. The affected areas are symmetrical, the skin in them acquires a bright red color, is swollen, hot to the touch, has a shiny smooth surface, weeping, layered and milky crusts.
- Professional. The disease usually occurs in production workers and upon contact with chemical allergens or water. The lesions are located in areas of the skin affected by provoking factors. Symptoms are the same as with true eczema, with localization on the arms, legs, face and other parts of the body.
- Dyshidrotic eczema. The disease occurs with rashes in the form of small serous blisters.
Exfoliative keratolysis - symptoms and treatment
Exfoliative keratolysis is a focal symmetrical peeling of the skin on the palms, surfaces of the fingers and, less commonly, on the soles. The disease is characterized by dry skin and superficial blisters filled with air.
Exfoliative keratolysis is also called recurrent focal palmar desquamation, dry lamellar dyshidrosis and recurrent palmar desquamation.
The disease is widespread and often chronic, but benign. Exfoliative keratolysis is more common in children and adolescents, less common in adults. It is often mistaken for psoriasis, eczema or chronic contact dermatitis. In people with excessive sweating of the hands, the condition worsens in warm weather and may be associated with hyperhidrosis - increased sweating [1].
Previously, exfoliative keratolysis was called dyshidrotic eczema, and it was believed that the disease was caused by a malfunction of the sweat glands. This connection has already been refuted, but the term “dyshidrotic eczema” is still used [2].
Dyshidrotic eczema, also called pompholyx, may precede exfoliative keratolysis. This condition causes fluid-filled blisters and severe itching to form on the fingers, toes, palms, and soles [2]. The cause of dyshidrotic eczema is unknown, but many factors are likely to influence the development of the disease. In most cases, the cause and predisposing factor cannot be identified [17].
Causes of exfoliative keratolysis
It was assumed that ekfoliative keratolysis could be caused by a fungal infection, but further studies did not confirm this hypothesis.
Possible triggers for exfoliative keratolysis:
- friction and contact with water [3][6];
- Soaps, detergents and solvents: the chemicals they contain can cause cracks and blisters on your hands;
- allergies: food, air pollution and other substances can trigger skin allergies;
- stress: can not only cause, but also aggravate the course of the disease;
- hot climate: warm weather increases sweating, which can lead to flaking of the skin;
- exposure to salt water;
- dry skin.
Exfoliative keratolysis is not associated with a deficiency of any vitamin. There are familial cases of the disease, but the genetic role in the development of exfoliative keratolysis is not well understood [14].
Diagnostics
Eczema requires careful diagnosis, as its symptoms are similar to those of many other skin diseases. The doctor collects anamnesis and complaints, after which laboratory tests are prescribed:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood test (ALAT, AST, triglycerides, total protein, urea nitrogen, creatinine, total bilirubin, glucose);
- determination of the level of total IgE in blood serum using ELISA;
- allergy testing of blood serum to food, household antigens, plant pollen, animal hair and chemicals;
- in case of infection, a bacteriological study is carried out to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- detection of antibodies to parasitic pathogens.
In difficult cases, in the differential diagnosis of eczema from dermatitis or other diseases, a histological examination of the material taken during a skin biopsy is carried out. The occupational form of pathology is confirmed by skin tests with suspected irritants, allergy and immunological tests.
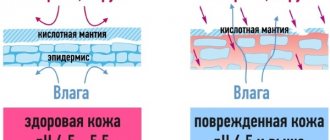
In addition to external factors, internal failures can also cause dry skin:
- water balance disturbance;
- lack of mineral elements;
- deficiency of vitamins A, E, C, D;
- hormonal imbalances;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe stress;
- allergic reactions;
- poor nutrition.
To clarify the cause of excessive dry skin, you should consult a doctor. And to prevent seasonal dryness of the skin of your hands and protect against winter frosts, you should not forget to drink enough plain water and properly care for your skin - use special restorative and protective creams.
Treatment
Treatment of eczema includes dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes and maximum limitation of provoking factors to prevent exacerbations.
The patient must avoid stress and emotional overload. Antihistamines are required. If the allergen is presumably localized in the intestines, then the use of enterosorbents may be recommended. Also indicated are diuretics in the presence of severe edema, antipruritic and sedative drugs, glucocorticoids to relieve inflammation, and antibiotics in case of bacterial infection. Remedies for eczema can be in the form of an ointment, used orally, or in injections for severe cases of the disease. Physiotherapeutic treatment using UV irradiation, magnetic therapy, and electrophoresis is also possible.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist