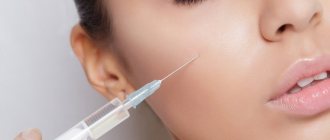
You do your best to take care of your skin, but there will always be times when things go wrong and you end up with a nasty problem. Redness around the nose is a skin problem that most often occurs in the winter when your skin is already dry or chapped, but it can also happen at other times of the year. In some cases, you can add a little extra concealer, but it's always best to identify the root cause of the problem and address it.
If you notice that the skin around your nose is red, know that this is happening for a reason. Your skin reacts to your diet, your environment, and your skin care routine in ways you cannot predict. Before you apply another layer of foundation or concealer, ask yourself why your skin is red and see if you can find a way to solve the problem.
In this article we will look at the topic of redness around the nose in more detail. We'll talk about what causes it and how to reduce redness. You'll also see our top picks for professional Yon-Ka Paris to reduce redness around the nose.
Common Herpes Symptoms
Foci of infection of the virus are usually located on the skin in the area of the red border of the lips, wings of the nose, corners of the mouth, and can also be located on the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose and chin. There are acute and chronic herpes. Herpetic lesions of the eyes are much less common than the nasolabial area.
Signs of acute herpes:
- redness, swelling, itching;
- the appearance of small bubbles with transparent contents, which can reach 1.5 cm in diameter;
- drying of the bubbles and the formation of a yellowish-gray crust or the formation of erosion with a bright red bottom;
- disturbance of general well-being, in some cases – increase in body temperature.
With the development of herpetic stomatitis, the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, gums and palate are affected. A “cold” in the eyes leads to inflammation in the eye area and to symptoms such as redness of the eyelids, increased lacrimation and changes in the sharpness of vision.
Herpes simplex rashes are almost always accompanied by burning, pain and a tingling sensation. If there are a lot of rashes, swelling of nearby tissues occurs. As a rule, it is quite difficult to quickly stop a relapse or get rid of symptoms, however, the whole process usually lasts no more than two weeks. If a secondary infection occurs, the duration of the disease may increase. With reduced immunity, relapses of herpes simplex can develop up to several times a month.
Herpes on the lips
SymptomsOf course, the most common cold is on the lips - those same painful blisters containing clear exudate. There is hyperemia, swelling, and tingling sensation. Gradually, the contents of the bubbles become more cloudy, they burst and in their place erosions, covered with a crust, form. | How to treatViferon Gel in the form of a strip up to 0.5 cm long is applied with a spatula or a cotton swab to a previously dried affected surface 3-5 times a day. The course of treatment will take 5-6 days. The gel is a colorless preparation, so it does not stain clothes, is invisible on the face and can be used simultaneously with decorative cosmetics. |
Simple Tips to Reduce Redness
The best treatment for redness around the nose is one that addresses the underlying cause. If you're experiencing redness and inflammation but you haven't yet identified the exact cause, you may still have some idea of what's going on.
To quickly reduce redness and inflammation, try one of these methods:
- For redness caused by skin irritation (windburn, sunburn, or dryness), apply a hypoallergenic, non-comedogenic moisturizer.
- For redness caused by acne, rosacea and other skin conditions, try a moisturizer designed to treat these specific conditions. Make sure it's suitable for your skin type so you don't make the situation worse.
If applying a topical moisturizer isn't enough to soothe inflamed and irritated skin, you may need to take it one step further. Talk to your doctor or dermatologist about your concerns and any additional symptoms you notice. Providing your doctor with as much information as possible is the only way to make an accurate diagnosis so your doctor can recommend the appropriate form of treatment.
Here are some additional tips you can try to reduce inflammation and redness:
- Use a humidifier at night to prevent your skin from becoming too dry while you sleep.
- Apply a cold compress to relieve inflammation around the nose.
- Apply some hydrocortisone to reduce swelling and redness.
- Use an LED lamp to treat redness caused by rosacea and dermatitis.
- Switch to tissue moisturizing if you are struggling with a cold or runny nose.
- Take a probiotic daily to combat harmful bacteria that may be affecting your skin.
- Try yoga or meditation to combat chronic stress.
If you're not sure what's causing the redness around your nose, you may need to try a few of our tips before you find a solution that works. In the meantime, don't use any harsh skin care products or heavy makeup, and avoid anything that isn't labeled as non-comedogenic (won't clog your pores).
Herpes in the nose
SymptomsHerpes inside the nose is also accompanied by the appearance of painful blisters, but if a herpes infection on the lips is usually easily identified, then when the nose is affected, a person at first may not be aware of the reasons for his discomfort. The wounds that form on the nasal mucosa may not be visible. | How to treatFor 5-6 days, apply Viferon Gel in the form of a 0.5 cm strip using a cotton swab. The procedure is repeated 3-5 times a day depending on the patient’s condition. |
Hives
Both compression and contact urticaria (Figure 3) are rare complications of PPE use. Compression urticaria occurs due to downward pressure from the mask and is characterized by the formation of blisters immediately or with a delay (4–6 hours) after the onset of compression. Wearing a well-fitting mask that is not too tight is recommended, or alternatively changing PPE frequently. Contact urticaria is an immediate reaction to an offending allergen such as latex or formaldehyde. It usually goes away within 24 hours after the trigger is removed. Regular use of antihistamines such as loratadine is the mainstay of treatment for inducible urticaria.
Figure 3. Urticaria
Herpes on the chin
SymptomsSometimes a herpetic infection can spread beyond the lips, nose and affect the skin of the chin. In this case, there is a risk of the formation of a continuous wound consisting of bubbles filled with liquid, which covers the entire nasolabial triangle. The development of complications can only be prevented with the help of timely antiviral therapy. | How to treatDuring treatment, Viferon ointment is applied in a thin layer to the lesions 3-4 times a day. The duration of the course of therapy is approximately 5-7 days. |
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) is the most common occupational dermatosis associated with mask wearing. ECD is a form of exogenous eczema caused by direct physical or chemical damage to the skin. Manifestations of RCD associated with pressure while wearing face masks are usually found over the cheeks and bridge of the nose. In this case, dermatitis is associated with prolonged mask wearing (> 6 hours), and its severity depends on the irritant and duration of exposure. Manifestations range from discrete, dry, scaly patches to swelling and vesicles, erosions, and ulcerations. People with atopic dermatitis who already have a skin barrier defect are particularly at risk of developing RCD. Restoring the skin barrier is key to treating RCD, and taking regular mask breaks (every hour for respirators) is one way to achieve this. For broken skin, a silicone-based dressing (a thin, all-purpose sponge dressing for wounds with little exudate) can be applied to protect the skin while maintaining the mask's seal.
Herpes on the eyes
SymptomsMost often, ophthalmoherpes affects the cornea, less often – the conjunctiva and inner membranes of the eye. It manifests itself as rashes, which can lead to the formation of ulcers and decreased sensitivity of the cornea. This may cause vision impairment. Depending on the form of the disease, inflammation of the cornea of the eye can be acute (with lacrimation, pain, photophobia) and practically asymptomatic. Sometimes there is damage to the posterior parts of the eyeball. The chronic form of recurrent herpes and the lack of adequate treatment can lead to blindness. | How to treatAccording to the instructions for medical use, VIFERON Gel/Ointment is not used for the treatment of herpes on the cornea, however, in severe cases, VIFERON Rectal Suppositories are used in a dosage of 1,000,000 IU for adults and 150,000 IU for children. |
Taking into account the above, we can conclude: for the treatment of herpes in the area of the nasolabial triangle and chin, the antiviral immunomodulatory drug VIFERON is used in the form of an ointment and gel.
Thanks to the hydrophobic base, the ointment is better absorbed on the skin, and the gel, since it has a hydrophilic base, is more suitable for application to mucous membranes. In case of eye damage, suppositories (candles) can be used to strengthen the immune system. When applied externally, the ointment and gel have an effect only in the affected area, so they can be used by expectant mothers from the first week of pregnancy and during breastfeeding. VIFERON is also approved for use in pediatrics: the gel can be used from the first days of a child’s life, and the ointment can be used in children older than one year.
The combined use of VIFERON Gel and VIFERON Suppositories stops the formation of a rash on the second day of therapy, reduces the number of rashes on the third day of therapy and reduces the risk of relapses.
What you need to know:
- Not all facial dermatoses associated with wearing personal protective equipment are so-called “maskne”.
- The most common cause of rashes is irritant contact dermatitis.
- Maintaining the skin barrier and taking regular breaks from wearing masks are important aspects of treatment in addition to standard medical protocol for monitoring skin conditions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic increase in the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) both in and outside of healthcare settings.
The term "maskne" has become increasingly popular during the pandemic, especially in the media, where it is used to describe certain types of facial dermatoses. People often purchase expensive but potentially ineffective medications to treat these conditions. In this article, the authors outline the most common causes of facial rash associated with wearing PPE and highlight key points to consider when assessing individuals with new or progressive facial dermatoses that they attribute to the use of facial PPE. In this article, “face PPE” refers to full face masks, visors, eye protection, surgical masks (surgical mask, FRSM type IIR), and respirators (e.g., FFP3, FFP2, and N95). Facial dermatoses associated with PPE are well described, but data on their prevalence are limited and descriptive terminology is often used instead of specific diagnoses. Based on the limited evidence available, mask-induced acne and irritant contact dermatitis are the most common dermatoses associated with mask wearing. During the COVID-19 pandemic, a prospective cross-sectional study of 833 healthcare workers in Thailand, including medical and non-medical workers, found that 54% reported adverse skin reactions to surgical and cloth masks.
As a rule, the patient develops a rash on the face or an exacerbation of an existing dermatosis, most pronounced in the area of the face covered by the mask. Ideally, such an examination should be carried out in person, but a video consultation is an acceptable alternative during a pandemic.
Key information to clarify regarding maskne:
- Local status, medical history, including family history of skin diseases, and a comprehensive medication history, including prescription, over-the-counter, and complementary medications.
- Temporal association with mask wearing: determine whether periods without wearing a mask provide relief and improve skin conditions, for example, allergic contact dermatitis should regress after a period without wearing a mask, whereas pimples (common acne), once present, may not react so quickly to the lack of a mask.
- Symptoms of itching, soreness and the appearance of pustules or papules.
- Duration of daily use of PPE.
- Ask if “mask rest” (periods of time when PPE is completely removed from the face) is allowed.
- Assess the impact on the patient's mood, work, and social life to determine severity and decide on further treatment. The impact of PPE-related dermatoses on the quality of life of healthcare workers can be significant.
The examination should focus on the morphology of the rash, the distribution and the presence of morphological elements of the rash on any areas other than the face.
Each condition described below may occur de novo or be aggravated by wearing facial PPE. An exacerbation usually occurs due to the formation of a warm, moist, occlusive environment around the face, facilitated by the use of a mask. Added to this is the friction effect of the material being held in place by the rubber band. General measures to prevent facial dermatoses associated with PPE are outlined below and are recommended for the treatment of all conditions listed below. Additional standard treatments for each dermatosis are discussed separately. When post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or scarring occurs, a more aggressive treatment approach is required to prevent permanent skin changes. At this stage, if there is no improvement, a referral to a specialist is necessary.
How does a cold become infected?
The source of HSV is a person with symptoms of disease or a virus carrier, who himself may not be aware of the presence of the herpes virus in his body. Most often, this virus is transmitted by contact; in rare cases, transfusion (through blood transfusion) transmission of the infection is also possible. Vertical (from mother to fetus) infection also occurs.
Experts say that in almost 50% of cases, infection occurs in early childhood. In this case, the source of infection is most often the child’s relatives, who periodically encounter the well-known “cold”.
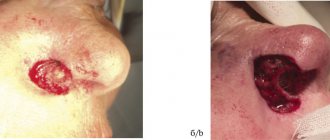
Seborrheic eczema
This type of dermatosis (Figure 2) affects approximately 1–3% of adults in the population and usually manifests at a young age. On examination, dermatitis with greasy yellow scales is often observed, affecting mainly the scalp, eyebrows, glabellar and nasolabial folds. Treatment includes regular use of antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole 2% shampoo, and/or short courses of topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone 1% ointment. As with atopic eczema, the warm, moist occlusive environment created by wearing a mask may predispose to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
Figure 2. Seborrheic eczema
When does the herpes simplex virus appear?
The activation of HSV and the appearance of a “cold” on the face is provoked by the following factors:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- the presence of chronic diseases of internal organs and their frequent relapses;
- poor nutrition;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- stress;
- harmful working conditions.
After initially suffering from herpes, it is possible to develop unstable immunity, which for some time will prevent the development of symptoms. But, unfortunately, a complete cure is almost impossible: one way or another, one day the virus will make itself known. In some cases, HSV becomes recurrent.
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Loading...
Take other surveys