The concept of chloasma
Every year the number of patients with melasma and chloasma increases
Every year the number of patients seeking help from cosmetologists and dermatologists regarding the appearance of pigmentation on the face is increasing.
Experts pay special attention to this defect for the following reasons:
- skin cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin, can degenerate into an insidious malignant tumor;
- Benign hyperpigmentation does not affect health, but serves as a strong irritant that can lead to serious psychological personality disorders.
There is no precisely formulated concept of what chloasma is. It is one of the types of melanosis acquired during life, characterized by excessive pigmentation of limited areas of the skin due to excessive production of melanin pigment by cells.
The number of women suffering from this pathology is much higher than men. The age range of patients is 20 – 50 years.
The risk group includes people who have naturally dark skin that easily tans.
Causes of the disease
The disease manifests itself when melanocyte cells become hyperactive. These cells produce the pigment "Melanin". Hyperactivity is caused by various factors , including:
heredity;- excessive exposure to UV rays (if the patient spends a long time in the sun or often visits the solarium, she becomes prone to melasma; when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, melanocytes grow);
- hormonal disorder (the disease occurs when hormonal levels are disrupted);
- dysfunction of internal organs (pathology may be caused by diseases of the ovaries, liver and thyroid gland);
- taking medications (persons taking medications are more prone to this disease);
- dysfunction of the digestive organs, including the liver (hepatic chloasma occurs due to a lack of vitamins and microelements);
- frequent use of cosmetics (beauty products can cause not only allergies, but also melasma);
- Despite the above factors, doctors cannot determine the exact cause of melasma.
Difference between melasma and chloasma
Scientists from all countries cannot decide whether these two defects are synonyms of the same pathological process. Their opinions are divided and are based on the causes of each of these types of skin hyperpigmentation. It is on this basis that they are divided into 2 groups:
- chloasma is considered to be a disruption of the process of melanin formation in the body due to changes in hormonal balance, diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and genital organs;
- melasma is a general name for pigmented formations that most often appear on the face during age-related changes, as well as during pregnancy.
Considering the similarity of symptoms of these skin pathologies, as well as the same methods of treating them, doctors equate these diseases of the epidermis and are increasingly calling this condition one term - melasma.
Etiology and pathogenesis
An important etiological factor for melasma is heredity . In one study of 324 women with the condition, 48% reported having it in their immediate family. Melasma almost always occurs in identical twins, while it may not occur in fraternal siblings.
Another factor in the appearance of melasma is ultraviolet radiation of spectrum B (UVB, 290–320 nm) and spectrum A (UVA, 320–700 nm). It causes lipid peroxidation, promoting an increase in the number of reactive oxygen species, which stimulate melanocytes to actively synthesize pigment.
Melasma is caused by hormonal changes in the body. Moreover, this can be not only pregnancy, but also taking oral contraceptives. In nulliparous women, there is usually no significant increase in estrogen or melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) levels, but they do have an increase in the number of cellular estrogen receptors in the area of melasma lesions. In postmenopause, melasma can occur while taking drugs with progesterone (whereas it usually does not occur when estrogen is prescribed), which indicates a significant role of this hormone in the pathogenesis of the disease.
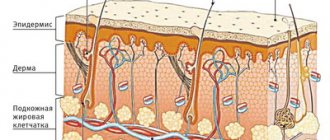
In general, the pathogenesis of melasma has not been well studied. It is noted that in this case, melanogenesis differs from tanning and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. In this case, epidermal-melanin units, mast cells and cytokines produced by fibroblasts and endothelium are involved in the process. Abnormalities that differ from other acquired pigmentation disorders occur in the upper layers of the dermis.
Clinical manifestations and forms of pathology
Melanosis, or in other words, skin hyperpigmentation, is characterized by the appearance of irregularly shaped brown spots that are flush with the skin surface and can merge with each other. They can affect both the face and body. On the face, such spots are most often localized in the forehead, cheeks, eyes, around the lips, and on the bridge of the nose.
These formations are not painful, do not peel, do not itch, do not cause a burning sensation and are not associated with inflammatory reactions.
There are 2 forms of melasma:
- solar, formed as a result of irradiation by sunlight;
- hepatic, associated with functional liver disorders.
According to the localization of pigment spots, there is the following classification:
- centrofacial, associated with the appearance of spots in the center of the forehead, on the nose, near the upper lip, in the chin area;
- molar, which is characterized by the formation of pigmentation on the cheeks and wings of the nose;
- mandibular (the second name is mandibular), with spots located in the area of the corners of the lower jaw (sometimes they can appear in the neck and chest).
Based on their level of prevalence, they are classified as:
- epidermal, having the appearance of surface formations of a dark brown color with clear boundaries. They respond well to treatment;
- dermal - light brown spots with unclear boundaries, usually difficult to remove;
- mixed (epidermal-dermal), representing heterogeneous pigmentation with more or less colored areas. In the case when the pigment is located in the epidermis, the treatment will be simple, if in the dermal layer it will be complex;
- asymptomatic (occur in dark-skinned races and are detected only with the help of a special medical lamp).
According to their clinical course they are divided into:
- passing (disappearing on its own without medical treatment);
- persistent (spots decrease during treatment, but the disease remains, slowing down in progression).
Only an experienced and qualified doctor is able to accurately determine the type of pigmentation and identify the true cause of its formation!
Types of age spots
Methods for diagnosing melasma
To study hyperpigmentation, a digital dermatoscope, a special Wood's lamp (a device that emits ultraviolet light in the long-wave spectrum), is used.
Regarding histological examination under Wood's lamp, three types of chloasma are distinguished:
· Epidermal - the lesion under a Wood's lamp becomes brighter and looks contrasting with respect to healthy areas of the skin. This reaction is associated with a high amount of melanin in the epidermis. As for treatment, this is a mild form of the disease that is treatable.
· Dermal - the lesion under a Wood's lamp does not stand out brightly from other areas. This process indicates the presence of pigment in the dermis, that is, melanin from the surface layer of the skin has moved with the help of macrophages into the dermis.
· Mixed - some areas are contrasted, while others are not. This reaction indicates both the superficial and deep location of the pigment. If treatment is started in time, the progression of the disease can be partially delayed.
Features of therapeutic treatment of chloasma/melasma
Therapeutic treatment of pathology should be carried out by a dermatologist. Initially, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound diagnosis of the genital organs, take hormonal tests, and obtain a gynecologist's opinion.
After this, the dermatologist must conduct tests for tumor markers to exclude the malignant nature of the pathology.
Therapeutic treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause - the individual factor that became the impetus for the appearance of pigmentation.
The standard correction scheme provides:
- complete abolition of hormonal contraceptives (provided that they were taken by the patient);
- a ban on taking medications, food and using cosmetics that have a photosensitizing effect;
- mandatory year-round use of sunscreen compounds;
- exclusion of independent use (without the prescription of a specialist) of products based on retinoids, alpha and beta hydroxy acids;
- the use of soft compositions for cleansing the skin with a neutral ph level;
- taking topical corticosteroids, which show positive results in the treatment of pigmentation directly related to inflammatory processes occurring in the skin. They should not be used during pregnancy;
- oral intake of special supplements that contain vitamin C, Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, oligomeric proanthocyanidins, condensed tannins, leukoanthocyanins, which have an antioxidant effect.
Melasma on the face
This disease refers to acquired pathologies of a benign nature and is characterized by a violation of pigmentation processes in the skin . Most often, such spots can be found on the face and neck.
The appearance of brown spots may indicate the presence of a pathology that needs to be treated
The color of the formations can vary from light brown to dark, in some cases even black. This depends on the amount of melanin produced: the more there is, the darker the spot. Many people do not know what skin melasma is, so they do not pay attention to the appearance of such spots. But if excess pigmentation affects most of the face and neck, you need to visit a doctor to find out the cause of this pathology and choose remedies to get rid of it.
Need to know. Most often, melasma spots appear on the face of women. This is due largely to the hormonal nature of the disease.
Types of melasma
There are several approaches to classifying this disease. If we consider skin melasma according to the location of the formations, we can distinguish the following types:
- Painting. Dark spots are localized on the cheeks and nose.
Spots on the cheeks and nose are not always freckles, so to eliminate such symptoms you should visit a dermatologist
- The central facial form affects the center of the face, that is, the forehead, chin, upper lip and nose.
The location of dark spots on most of the face causes psychological discomfort to patients
- Mandibular - spots appear on the lower jaw.
You can get rid of excessive pigmentation only with the help of modern treatment methods, which will be recommended by a specialist.
The nature of the course of the disease also varies:
- Transient melasma. The spots appear for a while and then disappear if the influence of the provoking factor stops.
- Persistent melasma is a form that does not disappear completely, but passes from a severe stage to a lighter one.
Histological characteristics divide melasma into the following forms:
- Epidermal. The amount of pigment increases in the epidermis. The spots are light in color.
- Dermal melasma leads to an increase in pigment in the deep and superficial layers of the dermis. The color of the spots is ashen or bluish-gray.
- The mixed form affects all layers of the skin. Such formations are most often colored brown.
If melasma is detected on the face, treatment will be prescribed only after the form of the disease and the degree of its manifestation have been established.
What triggers the development of melasma
Many people have heard about melasma, that this pathology is closely related to the period of pregnancy. Many pregnant women develop such dark spots on their faces. But after the birth of the child, the hormonal levels normalize, and the pathology disappears without any therapy.
Dermatologists can identify some other factors that provoke the development of the disease:
- Prevention from unwanted pregnancy using hormonal agents.
Long-term use of hormonal drugs is fraught not only with problems of the cardiovascular system, but also with the appearance of excessive pigmentation on the face
- Prolonged exposure to open sunlight without applying sunscreen.
- Excessive sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver.
- Hereditary predisposition to produce large amounts of melanin.
- Metabolic disorder caused by a lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Treatment with photosensitizing agents.
- Use of certain cosmetics.
We sometimes don’t even suspect that skin care products can provoke many skin pathologies.
- An increase in cells that are responsible for the production of melanin.
Important. Women with fair skin are more susceptible to developing melasma, so they need to use sunscreen when going outside.
How to recognize the disease
Melasma symptoms are as follows:
- Location of spots on the face and neck.
- The color of the formations is brown with different shades.
Melasma differs from birthmarks in its clear outline
- Clearly defined outlines.
- Most of all, increased pigmentation is found on unprotected areas of the body.
- Formations never appear on the mucous membranes.
- The resulting dark spots do not bother you with itching or peeling.
- In the summer, when the sun is most active, the spots become brighter.
Need to know. Before choosing a treatment method, melasma must be differentiated from pathologies that have similar symptoms.
Melasma may resemble:
- Xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Riehl's melanosis.
- Nevi.
- Lymphoma of the skin.
A Wood's lamp will help clarify the diagnosis; it will enable the doctor to accurately recognize melasma.
Defect removal using cosmetic procedures
Cosmetology and aesthetic medicine provide various methods and procedures that can effectively eliminate any type of benign pigmentation that occurs on the skin.
Some of them can inhibit melanin synthesis.
As an example, we can name cosmetic preparations that contain active ingredients such as arbutin, kojic, ascorbic and azelaic acids, hydroquinone, rucinol and others.
For this purpose, mesotherapy procedures are performed, as well as chemical skin peels (phytin, retinoic, pyruvic, azelaic, glycolic and others).
Popular hardware techniques aimed at ridding the skin of pigmentation include microdermabrasion, laser resurfacing or laser peeling.
The most effective type of laser in the fight against epidermal hyperpigmentation is the erbium laser.
For dermal melasma, it is recommended to choose a fractional method of treating the skin, which has a rejuvenating effect.
One of the best methods in the fight against various types of pigmentation, without compromising the integrity of the skin, are IPL or BBL photorejuvenation procedures.
Many readers are interested in the question of the effectiveness of the widely advertised Skinoren cream, which contains azelaic acid. It will be effective only for superficial – epidermal melasma. If the pigment is concentrated in the deep subcutaneous layers, this remedy will not bring any positive changes.
The choice of a specific correction technique depends on the depth of the pigment in the skin layer, the exact determination of which determines the degree of effectiveness of the treatment!
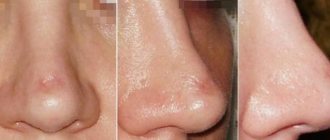
This is what chloasma looks like on the face
The use of folk remedies
To get rid of melasma faster, you can use traditional medicines. You should first consult your doctor .
- Vinegar. To treat facial skin, use a 1:1 solution of vinegar and water. Before using the product, you need to make sure that it will not cause allergies or burning. It is recommended to use apple cider vinegar instead of regular vinegar; it is not as caustic.
- Onion juice. It is mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio and applied to clean skin.
- Lemon juice. If you use undiluted lemon juice, your skin will turn red. To avoid such a reaction, it is necessary to dilute it with cool water.
Prevention of pathology
The main measure to prevent skin hyperpigmentation is to limit the time spent in direct sunlight and prohibit visiting the solarium.
A prerequisite for preventing the appearance of new age spots is the daily application of cosmetics to the face that contain sunscreen filters that eliminate the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation.
Remember that timely contact with a dermatologist at the first onset of symptoms of pigmentation guarantees quick and successful treatment!
Arbutin
Arbutin is found in natural substances such as cranberries, blueberries and bearberry leaves. Once in the body, it breaks down into glucose and hydroquinone, one of the most commonly used skin-lightening ingredients that prevent cells from producing melanin.
Alpha-arbutin, which is the preferred form of arbutin, is found in bearberry leaves. It is water soluble, works on all skin types, and is especially effective when combined with vitamin C. Since synthetic hydroquinone is only available by prescription, consider including products containing arbutin in your diet.