Reasons and types of changes
The mechanism of skin changes has not been sufficiently studied in medicine. It is believed that the appearance of formations has a hereditary predisposition. There are also several provoking factors:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- radiation, x-ray exposure;
- constant injuries in the same area;
- viral infection;
- exposure to carcinogens;
- insect bites;
- non-healing ulcers;
- metastases in cancer;
- chronic decreased immunity.
Based on the nature and degree of risk to humans, the following are distinguished:
- benign changes;
- malignant formations;
- precancerous (conditionally not dangerous, but they can degenerate into oncology at any time).
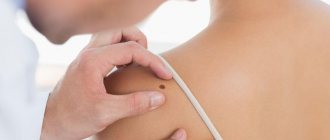
Are all moles dangerous?
As a rule, people are more concerned about convex formations; people usually do not pay much attention to flat spots of dark color. However, it is precisely these - flat borderline acquired nevi that look like black and brown spots - that should cause caution. Especially in cases where they change in size, increasing or decreasing. The color can range from light brown to black. Irregular in shape with uneven pigmentation, such nevi should be considered dysplastic - formations that can degenerate into melanoma.
Benign changes
This group of neoplasms is not life-threatening. This is a cosmetic defect that can be tolerated or removed. If the formation is located on the body, where it constantly rubs against clothes or is injured by jewelry, you should consult a doctor. To avoid degeneration into a cancerous tumor, it should be excised. Another risk factor is sun exposure. It is better not to expose areas where there are changes to ultraviolet radiation.
The most common benign changes are:
- Seborrheic warts appear in older people, more often on the head, face, and closed parts of the body. It is a round or oval plaque. Color ranges from black to yellow-brown. The average size is from 5 to 40 mm.
- Pigmented nevus is a spot (sometimes plaque) from brown to almost black. Nevi are often covered with hairs.
- Dermatofibroma is a hemispherical subcutaneous nodule. Most often it forms on the legs, closer to the feet, as well as in places of insect bites and areas that are constantly injured. They appear scattered or in single dense nodes that are pigmented compared to healthy skin.
- Angioma is a neoplasm consisting of altered vascular walls. It has an uneven shape, a reddish or cherry tint. Most often appears on the face and abdomen. A type of cavernous hemangioma is a blue-red soft nodule.
- Lipoma is a fatty subcutaneous tumor that is a soft ball, on which small lobules can sometimes be felt.
Skin neoplasms
Malignant skin tumors account for 7-10% of all malignant tumors. It affects both sexes, but older people are more susceptible. They differ from benign tumors in that dermal cells are difficult to differentiate already at the initial stages of the disease, they do not perform their functions, are capable of affecting nearby organs and tissues and metastasizing through the blood and lymphatic vessels, causing tumors throughout the body.
Melanoma is the most malignant of all skin tumors; the presence of congenital and acquired pigment spots increases the risk of melanoma, since it arises from melantocytes - pigment cells of the skin. Middle-aged and old women with blond hair and blue eyes are most susceptible to melanoma. The neoplasm on the skin is localized mainly on the lower and upper extremities; the pathogenesis of malignancy of moles and age spots is not fully understood, but their traumatization, attempts to remove moles and spots with aggressive chemicals, cuts and insolation contribute to malignancy.
The main symptoms that indicate malignancy of such neoplasms on the skin as age spots and moles are changes in the pigmentation of the nevus, a sharp increase in size, frequent bleeding and ulceration. That is, any previously nonspecific manifestations of a mole indicate its degeneration. And, despite its small size, the tumor quickly spreads to neighboring areas in the form of satellite nodules and metastasizes first to regional lymph nodes, and then to internal organs. Trauma can lead to premature degeneration into cancer, since even a biopsy for cytological examination is carried out in the presence of erosions and ulcers, so as not to intensify the oncological process.
Epitheliomas
are called all skin neoplasms from epithelial cells and are diagnosed in 50-60% of all skin cancers. Epitheliomas occur in areas not affected by other skin tumors. Initially, a small nodule of pinkish-yellow shades is observed, which grows over many years, but its size is not significant - up to 1-1.5 cm in diameter, so it goes unnoticed. The activation of the process is indicated by the presence of a yellowish-gray crust, which eventually covers the epithelioma. A ridge around a skin tumor consisting of cartilaginous compactions with a shiny sheen is an unfavorable diagnostic sign. Subsequently, ulceration and bleeding are observed, the tumor quickly metastasizes to regional lymph nodes and other organs.
Kaposi's sarcoma
or angioreticulosis is more common in patients with AIDS, but the classic form of sarcoma and skin neoplasms in patients with immunodeficiencies are clinically and histologically identical. Men are more susceptible to this type of malignant skin tumor; Kaposi's sarcoma is localized mainly in the lower extremities. Initially, violet, less often lilac, spots appear without clear outlines; later, against this background, dense round nodules of a bluish-brown color with a diameter of up to 2 cm appear. The nodules are prone to fusion and ulceration; in patients with HIV infection, the disease takes on an aggressive character, sometimes with fulminant damage lymph nodes and metastasis throughout the body.
How to distinguish dangerous skin changes
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. It is difficult to determine by eye whether there is a risk of cancerous changes. But there are a number of points that should be wary:
- the formation changes its color and shape, grows, and the number of affected areas increases;
- the affected area itches, becomes inflamed, and bleeds;
- the pigment spot has uneven edges and a diameter of more than 6 mm;
- general malaise, low-grade fever, loss of appetite;
- relatives have been diagnosed with cancer.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Typically, benign and malignant skin tumors begin as a small area of skin change: the appearance of growths, crusts, and round formations. In addition, any moles or nevi that change their size, shape, or color are dangerous. In these cases, if there are any changes in the epithelium and underlying tissues, targeted diagnosis of skin tumors is needed. It is performed by a dermatologist, and if there are signs of melanoma or another type of cancer, by a dermato-oncologist. The doctor will ask you in detail about the complaints, evaluate what the skin growths look like, clarify growth dynamics, color changes, additional complaints (itching, pain, ulcers, bleeding).
If a tumor is suspected, the doctor will perform a biopsy of the suspicious element, which will accurately determine the nature of the tumor.
Which doctor should I contact?
The first step is a consultation with a dermatologist. An experienced specialist will only need a visual inspection to eliminate the danger. Additionally, laboratory testing is carried out. Methods used to remove skin lesions:
- surgical excision;
- burning with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy);
- laser exposure
- electrocoagulation – exposure to high-frequency currents;
- removal using a radio knife.
The choice of method will depend on the size of the formations, their number, location, shape (convex or recessed), and general condition of the body. After surgery, the removed tissue is sent for histology to finally exclude or confirm oncology.
The medical appointment is conducted by an experienced dermatologist. The clinic has its own laboratory, where they will conduct the necessary studies to clarify the diagnosis. If the prognosis is favorable, the skin lesion will be removed.
Diagnosis of squamous cell skin cancer
The diagnosis of squamous cell skin cancer is established on the basis of clinical and laboratory data with mandatory morphological examination (cytological and histological). Histological diagnosis has its own difficulties in the early stages of development of squamous cell carcinoma and in the case of an undifferentiated variant. It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with various diseases. But histological examination is crucial when diagnosing squamous cell skin cancer.
Get a treatment program
Surgery
| Code | Name of service | Price |
| 1101 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method for 1 unit. | 650 rub. |
| 1102 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 5 units. | 2500 rub. |
| 1103 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 10 units. | 4000 rub |
| 1104 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 20 units. | 5000 rub |
| 1105 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 30 units. | 6000 rub |
| 1106 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 40 units. | 7000 rub. |
| 1107 | Removal of benign formations (up to 5 mm in diameter) of the skin using a laser or radio wave method up to 50 units. | 7500 rub. |
Reasons for the development of basal cell carcinoma
Among the main causes of the development of the disease, exposure to ultraviolet radiation for a long time should be noted. As a rule, exposed skin areas are most often affected. The disease can also be triggered by contact with carcinogens of chemical origin (soot, tar, tar, arsenic, etc.), and ionizing radiation. In addition, the likelihood of developing the disease is influenced by immunosuppression, exposure to retroviruses, and genetic predisposition plays an important role.
Treatment and prevention of neoplasms
special measures to prevent the occurrence of cancer . But as a preventive measure for the disease, if there are a large number of moles, they need to be removed. Given their genetic predisposition, these people need to be in the sun less often, use protective lotions and creams, exclude from the diet foods that can cause cancer, and avoid contact with aggressive substances. The stage of tumor progression is primarily determined by ultrasound and phototomography diagnostics, and sometimes by additional examinations.
As a rule, surgical intervention is used as a treatment for neoplasms , in which the infected tissue is removed while healthy tissue is captured. With laser removal, the relapse rate is much lower. For benign neoplasms, methods of radio waves, cryodestruction and electrocoagulation are used. If the tumor is inoperable, then chemotherapy and radiation are used.
If a tumor on the skin is initially malignant, then doctors usually make an unfavorable prognosis, since it creates deep metastases in various organs , despite the fact that this manifests itself only slightly on the body. The probability of death of the patient is high. With timely intervention, a precancerous tumor or benign formation can be completely treated, excluding relapses.
If you have any kind of growth on your skin, be sure to see a dermatologist . Then, when you receive an accurate diagnosis, you and your doctor can discuss methods to combat the formation. Protect yourself and your skin from adverse weather conditions, and especially protect yourself from negative ultraviolet radiation!
What are the advantages of the radio wave method compared to other removal methods?
The radio wave method for removing skin tumors is the most non-traumatic procedure, which is based on the use of high-frequency waves (radio waves) on the Surgitron apparatus, USA. This method is used even if it is necessary to remove an element located in a hard-to-reach place (oral mucosa, eyelids).
The advantages of the radio wave method include:
- complete absence of pain during the procedure;
- no bleeding after removal;
- no trace remains at the site of removal;
- no risk of secondary infection;
- healthy areas remain untouched;
- fast healing process;
- The method is universal - you can remove warts, papillomas and moles.
One of the important differences between radiosurgery and laser and other destructive techniques is the possibility of performing a histological examination of removed tissue when using the radio wave method of removal.
What does PDT mean and where is it used?
Photodynamic therapy is a method of treating malignant tumors that has appeared not so long ago. When tissue is exposed to a certain wavelength of light, cells with an accumulated special substance (photosensitizer) are destroyed.
This technique is used for superficial skin tumors; it is especially effective in cases where, as a result of the localization of the tumor, it is difficult to use other treatment methods (for example, for tumors located in the corner of the eye, on the auricle, etc.). The PDT method is also used when the lesion is extensive or resistant to previously administered therapy.
What is the difference when choosing a photosensitizer?
When choosing a drug, a number of criteria are used:
- A fairly high accumulation gradient between the neoplasm and healthy tissue - 10:1 to 15:1 (Photofrin II (USA) and Photogem (Russia) - from 3:1 to 4:1)
- Achieving optimal concentration after 2-2.5 hours (Photogem and Photofrin - 24-30 hours)
- When excitation of a photodynamic reaction with a wavelength of 661 nm, a greater effect can be achieved (photogem and photofrin - 630 nm)
- Rapid removal of the photosensitizer from the patient's body. 96% of the drug is eliminated after 24 hours, 98% after 48 hours. With rapid elimination, the likelihood of developing side phototoxic effects is minimal (removal of Photofrin and Photogem lasts 4-6 weeks)
- A wide therapeutic interval (with an average therapeutic dose of 0.8 mg/kg it reaches LD-158 mg/kg), as a result of which the likelihood of side effects in case of an accidental overdose of the drug is excluded.
- There is virtually no risk of unwanted effects.
Are there methods for preventing basal cell carcinoma?
To reduce the likelihood of developing a basal cell tumor, there are fairly simple recommendations. Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and take precautions when working with carcinogenic substances. An important role in the prevention of basal cell carcinoma is played by timely detection of the pathological focus. Any existing redness on the skin or long-term non-healing damage should cause alarm. If warning signs appear, you should visit an oncologist. In addition, dermatoses can be a sign of trouble; their appearance often indicates the presence of an internal tumor.
Types of photosensitizers
A photosensitizer is a component of the photodynamic reaction that increases the sensitivity of tissue to light. Today, many substances with photosensitizing characteristics have been developed. The main classes include:
- Derivatives of δ-aminolevulinic acid (precursor of the endogenous photosensitizer protoporphyrin IX) Alasens
- Photogem
- Visudin
- Tukad (WST11, TOOKAD)
- Photoditazine
- Thiosens
What methods exist for treating basal cell carcinoma?
Treatment tactics are influenced by clinical manifestations, size, and localization of the tumor. In addition, when choosing an appropriate treatment method, the patient’s age and concomitant pathologies are taken into account. Methods for treating basal cell carcinoma are very diverse; today, radiation and photodynamic therapy (PDT), cryotherapy, laser therapy and radio wave treatment, as well as medication, have proven themselves well. The goal of all techniques is destruction of the lesion. But the most radical method can be called excision of the tumor and PDT. Of course, treatment for basal cell carcinoma should be started without delay, because in advanced cases it is much more difficult to get rid of the disease.