Eyelids drooping after Botox: what to do?
Correction of age-related changes in appearance using botulinum toxin injections is one of the most popular and sought-after cosmetic procedures.
The effect after “beauty injections” is visible almost immediately. Recovery does not require extra effort and occurs quite quickly, which distinguishes the technique from any plastic surgery. Botox injections can be given an unlimited number of times. The cost of rejuvenation is affordable for every woman, there are no age restrictions, and there are few contraindications. This rejuvenating technology really has many advantages. Among the advantages is an extremely low percentage of complications, provided that the procedure is performed by a cosmetologist with extensive injection experience and high qualifications. However, the risk of undesirable consequences cannot be completely eliminated. They may appear due to the patient’s fault, due to the individual characteristics of the body, or due to poor quality of the procedure.
Ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox is one of the possible undesirable consequences of botulinum therapy. The complication is not dangerous, but unpleasant. Drooping eyelids cause a lot of inconvenience and negatively affect the appearance, negating the result of the correction. How to cope with the problem, is it possible to speed up recovery, and how to avoid this side effect?
Beauty injections done wrong
This happens when injections are performed by a cosmetologist without higher education and additional courses. Sometimes, in pursuit of profit, the procedure is performed by people without any medical education at all. Such would-be specialists do not know anatomy and inject all patients according to templates, forgetting that everyone has individual features of the structure of the face and body.
As a result, the drug is injected in the wrong place, and therefore does not work. Therefore, when choosing a clinic, you need to evaluate the cost of the service - too low a price should alert you.
After what procedures can ptosis of the upper eyelid appear?
Botulinum neurotoxin can migrate in tissues, but the distance over which it can “shift” does not exceed a few centimeters. Injections into the area of the orbicularis oris muscle cannot lead to the problem discussed in the publication. In order for ptosis of the upper eyelid to appear, the cosmetologist must influence areas of the face located in close proximity to this anatomical structure.
Ptosis of the upper eyelid occurs during rejuvenation:
- skin of the frontal zone (forehead);
- skin of the periorbital area (around the eyes);
- corners of the eyes (smoothing out crow's feet);
- between the eyebrows.
When correcting hyperkinetic wrinkles of the frontal zone and periorbital region, this unpleasant consequence occurs most often, but even in this case, no more than 1% of patients suffer from a side effect. If the procedure is performed by a qualified doctor with extensive injection experience, the risk tends to zero.
§1. frozen face
Usually it is only the forehead, but in medical practice there are people who look as if the only moving part of the face is the mouth. Hollywood, this is about you! We've all seen those expressionless faces. The result looks too robotic and unnatural. A frozen face is not always the result of a mistake; sometimes some women deliberately do it. But most would probably prefer to look more natural. Still, the goal of Botox treatment should be to eliminate wrinkles, and not any mobility or facial expressions. If you've had too much Botox and your face has lost movement, you just have to wait. Unfortunately, there is no quick fix for this problem. The next time you come back for Botox, take the time to choose a good esthetician who understands what you need.
Causes of ptosis
The principle of action of botulinum therapy is based on blocking facial muscles. Botulinum neurotoxin penetrates the endings of efferent motor neurons that control facial muscles. In these endings, Botox binds to a certain protein (SNAP-25), which plays an important role in the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Once this protein is blocked, nerve endings lose the ability to release acetylcholine; the muscle does not receive signals from the brain and, as a result, relaxes.
Ptosis develops when the efferent innervation of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid is completely or partially blocked. “Switching off” this muscle is not the goal of the procedure; it is a side effect or complication that develops when botulinum toxin diffusions too actively from the frontal zone or periorbital region.
What factors can lead to an aesthetic problem? The first reason is the patient’s failure to comply with the rules of the rehabilitation period. If in the first days after Botox injections a girl takes hot baths, blow-dries her hair, actively plays sports, visits a sauna, drinks alcohol or sunbathes in a solarium, the risk increases.
The above actions increase peripheral blood circulation. Blood flow in the facial muscles and integumentary tissues increases, the neurotoxin migrates over long distances and blocks the muscle that is responsible for raising the upper eyelid.
The second reason is a violation of the procedure technique, that is, a medical error. When performing injections, the cosmetologist must take into account many factors. What matters is the total dosage of Botox, the injection points of the drug and the distribution of the dose between these points. Equally important are parameters such as the depth of needle insertion and even the direction of the needle. If the needle is inserted at the wrong angle, the doctor may simply “miss” the target muscle and thereby provoke the development of a side effect.
The third group of reasons is not related to medical errors or undisciplined behavior of the patient in the first week after injections. The “culprits” of an aesthetic problem can be the individual characteristics of the body, including the degree of development of the network of blood and lymphatic vessels, the abundance of collaterals, the dynamics of venous return and lymph movement. Metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance, infection are also among the risk factors.
A separate group of risk factors for the development of side effects after Botox should include taking medications and dietary supplements. Be sure to tell your esthetician about all the products, both prescription drugs and dietary supplements, that you take. When botulinum therapy, special caution should be observed in relation to the following drugs:
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (heparin, aspirin cardio and others).
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers from the NSAID group (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, diclofenac and others).
- Antibiotics.
- Multivitamin complexes and B vitamins.
- Nutritional supplements.
Myth: Botox can cause you to lose or significantly impair your vision.
It is a myth. Botox cannot cause vision impairment because it is not injected into the optic nerve. But eyebrows can certainly “fall”. How are the muscles on the face different from the muscles on the body? The muscles on the body are attached to the bones at their “ends” and each one can be isolated and pumped up. And the muscles on the face are attached to the bone with one “end”, and “woven” into the skin with the other. It is impossible to isolate one muscle and pump it up. If we are talking about eyebrows, all the muscles located above will raise the eyebrows, and those below will lower them. To get the effect of fallen eyebrows, you need to administer an inadequate dose of the drug. Eyebrows can also become “skewed” when one becomes higher than the other - I see this all the time. The professionalism of the doctor is very important here. An experienced cosmetologist can adjust the height of the eyebrows. But to return “fallen” eyebrows to normal, you will need physical therapy. And this won’t be fixed quickly.
© Pexels.com
Symptoms and degrees of ptosis
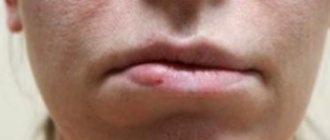
The main manifestation of ptosis is a drooping of the lower edge of the upper eyelid below the upper edge of the iris or pupil. Since the eyelid begins to partially block the pupil, the patient is forced to constantly lift his head to see something. The prolapse is often one-sided or unevenly expressed on the right and left sides. Hence, another sign is facial asymmetry.
There are 3 degrees of severity of ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox injections:
- 1st degree: the lower edge of the eyelid covers only the upper third of the pupil.
- 2nd degree: the lower edge covers half or two-thirds of the pupil.
- 3rd degree: the lower edge completely covers the pupil.
Eyebrows with eyelid ptosis may appear raised higher than usual, causing the face to take on a surprised expression. Some patients experience accompanying symptoms such as lacrimation or dryness of the mucous membrane of the eye, impaired accommodation, double vision, and blurred vision. All these problems are complications of botulinum therapy.
Botulinum toxin in cosmetology: desirable and side effects
Interest in botulinum toxin as a possible drug appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. The first to use botulinum toxin in medical practice was American ophthalmologist Alan Scott in the late 70s. He injected the purified toxin in microdoses into the orbital muscle of the eye to treat blepharospasm. He also studied the effect of the toxin on nystagmus (involuntary rhythmic movements of the eyeballs), hemifacial spasm (painless involuntary contraction of the facial muscles), spasmodic torticollis (improper head position caused by pathological tension of the neck muscles) and spastic diseases of the legs.
Since 1994, botulinum toxin has been used in cosmetology. In modern practice, drugs based on botulinum toxin are used to treat hyperactivity of striated muscles and sphincter muscles, hyperfunction of exocrine glands (exocrine glands), various spastic pain syndromes, and to relieve migraines. Several preparations containing BTA are used in aesthetic medicine.
In cosmetology, the toxin is used to smooth out existing facial wrinkles and prevent the appearance of new wrinkles.
When a medicinal product enters the human body, its effect on the body occurs. These effects are divided into desirable and side effects. Side effects of drugs are undesirable effects that are included in the spectrum of pharmacological activity of the drug, occur when the drug is used in therapeutic doses and are considered toxic. Side effects of drugs can be due to both the specific activity of the drugs and the peculiarities of the body's reaction to the drugs. In addition, during diagnostic or therapeutic measures, a pathological condition such as a complication may be added to the underlying disease.
Complications can arise if the doctor does not comply with the rules for performing the injection (dilution, accurate calculation of the administered dose, correct choice of injection points, direction of the needle and depth of injection), excessive diffusion of the drug into muscle groups close to the injection site, as well as if the patient behaves incorrectly or hides it from doctor the necessary information. It is also important to take into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient’s injected muscles, the degree of their activity and hypertrophy. The classification of complications after BTA injection can be presented as follows: associated with the active substance (botulinum toxin) or associated with the injection (the procedure itself, which violates the integrity of the skin).
Among the complications associated with the administration of the toxin are the following:
- an immediate allergic reaction associated with the introduction of a toxin develops during the first hours after the procedure. If you suddenly notice signs of an allergic reaction: red rash on the skin, itching; difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat - emergency measures should be taken immediately;
- flu-like symptoms. They develop very rarely and go away on their own within a few days;
- when a large amount of the drug is injected into various areas of the face, the effect of an amicable “mask-like” face may occur. Although this effect is not always a complication, since patients sometimes achieve exactly this;
- facial asymmetry can occur due to uneven relaxation of muscles on the right and left sides of the face (crooked smile);
- after injections into the eyebrow area, botulinum toxin can spread into the muscles of the upper eyelid, which leads to ptosis (the eye is half-closed by the upper eyelid, it can neither be opened nor closed completely, which, in turn, leads to dry eye and lacrimation). Ptosis can be either unilateral or bilateral. It has now been proven that botulinum toxin can spread through the needle trauma channel, so strictly intramuscular injection into the corrugator should be used, without reaching the periosteum with the needle. There are also patients with congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid, which is detected during a test: we ask the patient to lower his head and raise his eyes without raising his head. Normally, the eyelid should open the pupil completely. Otherwise, the patient must be denied the corrugator correction procedure;
- when injected into the orbicularis oculi muscle, the blinking process may become more rare, which leads to dry eye, dry keratoconjunctivitis, and the appearance of corneal erosions;
- if botulinum toxin gets into the orbital space - diplopia (double vision), ophthalmoplegia (paralysis of the eye muscles);
- when injected into the lower eyelid area, eyelid inversion may occur;
- short-term swelling of the eyelids;
- when injected into the neck area, difficulty swallowing and hoarseness of the voice may occur (with partial paralysis of the laryngeal muscles);
- with partial paralysis of the orbicularis oris muscle caused by the injection of botulinum toxin, articulation disorders are possible (difficulty in pronouncing the sounds “O” and “U”);
- when the drug is administered into the oro-buccal area, drooping of the corners of the lips is possible, which is expressed in the effect of a “tragic mask” and drooling, difficulty in eating.
Complications associated with injections:
- in the first days after BTA injections, inflammation, pain at the injection site, swelling, and redness may appear;
- Bruises and hemorrhages are possible immediately during the procedure. This, by the way, can increase the diffusion area of the drug.
Frequent injection of high doses of botulinum toxin into the extraocular muscles leads to drooping of the eyelids, their swelling and visual disturbances (double vision, photophobia). Eye irritation and dryness, watery eyes, and the ability to blink may also be impaired.
It is necessary to separate two conditions: when the patient cannot close his eyes and when the patient’s eyelids do not close. In the case where it is difficult for the patient to close his eyes, winking is the expected result and botulinum toxin injections are carried out into the outer part of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
While a violation of eyelid closure is already a complication, and in this case it is worth talking about either the wrong place of drug administration (the middle or inner part of the orbicularis oculi muscle), or about pathological individual diffusion of the drug. As a rule, such complications go away on their own within a few days (weeks).
It is necessary to inform your doctor about taking antibiotics: which ones, for how long, how long ago you finished taking them. Many systemic antibacterial drugs, such as macrolide drugs, can cause myopathy as a side effect. If, while taking antibacterial drugs, myopathy develops (usually unnoticeable in daily life) and BTA (a potent muscle relaxant) is additionally administered, then their actions synergize.
Treatment of myopathies resulting from the use of BTA should be aimed at increasing the formation of new synapses, which requires enhancing the trophism of the affected area. It is possible to use antiglaucoma drops of the alpha-adrenergic agonist class to enhance the tone of the Müller muscle (which has adrenergic innervation), the function of which is also to raise the eyelid. A good effect is observed with therapy with intramuscular injections as prescribed by a neurologist. A good therapeutic effect is observed against the background of physical procedures, such as fractional non-ablative treatment of the problem area.
The doctor must be aware of the use of such drugs and inject botulinum toxin no earlier than one month after taking the last tablet. Important information is the presence of pregnancy or lactation, during which the administration of BTA for cosmetic purposes is contraindicated.
With botulinum toxin therapy, there is a possibility of developing resistance. With primary resistance, there is no effect even with the first injection of the toxin; secondary resistance, which occurs after several successful injections, includes the formation of anti-botulinum toxin antibodies that neutralize the effect of the drug. Typically, the formation of antibodies to the hemagglutinin complex of botulinum toxin type A occurs in 3-10% of cases, in the period from 200 to 1100 days after the first administration of the toxin. The formation of antibodies is facilitated by the administration of the drug in high doses (more than 250 units), usually used in neurology, or booster injections (small doses at short intervals).
Since immunity to the toxin is unstable, if resistance develops, it is recommended to refrain from injections for at least a year or use other serological types of botulinum toxin (B, F). Botulinum toxin type B is currently being developed for patients who are not sensitive to botulinum toxin type A.
There are several hypotheses about the development of insensitivity to BTA. First: botulinum toxin preparations have a protein shell that can cause an immune reaction and the production of antibodies. This mechanism of insensitivity occurs in 1% of cases, although a reliable correlation between the level of antibodies and insensitivity has not yet been proven. Second: in men who served in special forces, a possible cause may be the previous administration of botulinum toxoid, which is part of a complex vaccine against anaerobic infections. Third: botulinum toxin is a zinc-dependent endoprotease. It has been noted that resistance is often observed in patients with zinc levels that deviate from the norm in one direction or another, but no special studies have been conducted on the effect of plasma zinc levels on the effectiveness of BTA.
It happens that the doctor and the patient fulfill all the conditions perfectly, but complications still develop. In general, adverse reactions after BTA injections develop during the first week and are transient. Rarely do they last for several months or longer.
Reference : Botulinum toxin (botulinum toxin, botulinum toxin) is a protein neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, obtained as a result of fine purification and subsequent lyophilization of the bacterial culture.
Make an appointment at the Department of Dermatovenereology, Mycology and Cosmetology
Treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid
The effect of botulinum toxin is limited in time: muscle activity is fully restored after a few months. The exact period of blocking neuromuscular conduction depends on individual characteristics, but on average, the result of Botox injections lasts from 4 to 6 months. The complication of drooping eyelids lasts about the same amount of time.
For obvious reasons, few are willing to wait patiently for the drug to wear off. The problem is that there are no specific methods for neutralizing the botulism neurotoxin, but you can speed up its elimination and restore facial activity with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and certain medications.
Among the physical procedures used for these purposes are galvanic currents, phonophoresis, electrophoresis, and lymphatic drainage massage. Manual facial massage can also lead to positive dynamics, but it should only be done by an experienced specialist. Medicines used include: nicotinic acid, drugs that improve blood microcirculation, B vitamins, and some eye drops.
Treatment of complications of botulinum therapy should be prescribed by an ophthalmologist, who will subsequently monitor the success of therapeutic measures.
You can learn more about botulinum therapy, as well as how to avoid complications of the anti-aging procedure, at a consultation with a cosmetologist at the Soho Clinic aesthetic medicine clinic (Moscow).
Incorrect dosages and medications
Most often, this situation occurs in small salons and private beauty salons, which, in pursuit of profit, use drugs in minimal dosages. Here, everyone is often injected with the same drug in the same dose, which is unacceptable.
There are softer and harder options for drugs based on botulinum toxin. The choice depends on how often the injections are given and at what previous dosage the injections were given. The dose also depends on age and skin characteristics.
The strength of the drug is influenced by the features of facial architectonics. For example, with a heavy forehead, low eyebrows, a large amount of skin on the upper and lower eyelids, a wide bridge of the nose, and a tendency to swelling, you need to increase the dose. But only an experienced cosmetologist knows how much to increase it. Therefore, Botox often does not work for such facial features.
“Botox parties” have become fashionable, for which doctors buy botulinum toxin in bulk and arrange a meeting for people who want to get injections. Such events are common in Western countries, especially in the United States.
Here's how a party usually works - a group of men and women of different ages mingle in a common area. Snacks are sometimes served. One after another they go into the room for 15 minutes. There, payment is taken and an informed consent agreement is signed. After this, injections are given and the participants rejoin the group. You can’t expect any miracles from such “wholesale cosmetology”.
Therefore, it is not worth doing Botox injections in questionable conditions, and especially at parties while abroad. The effect of such an event is low, and no one bears responsibility for the procedure.
Botox doesn't work - reasons
Effect of fillers on vision
In addition to Botox, so-called fillers are widely used in cosmetology - substances that fill certain areas of the face to make them more expressive, smooth the skin, and eliminate wrinkles.
According to the results of a study conducted by South Korean scientists, the introduction of certain fillers under the skin of the face can adversely affect the functioning of the visual system. For example, injections of autogenous fat (own fat tissue) can cause blockage of the vessels that provide blood supply to the retina. In severe cases, after such cosmetic procedures, occlusion of the central vein or retinal artery may occur, which leads to blindness quite quickly.
Effect of the procedure
To avoid swelling at the injection site, after the procedure, it is recommended to apply tampons with ice or a cooling solution. Sometimes, after a few minutes, slight redness may occur in the injection area. You should not touch the injection site for at least 12 hours. After the procedure, it is better to rest for a while.
The clinical effect of Botox injection can begin to appear in the range from 2 days to 2 weeks after the injection, which depends on the existing pathology. The dosage of the toxin is calculated in accordance with the volume of muscles that need complete relaxation. After the injection, long-term, persistent relaxation of facial muscles lasts 3-6 months. To achieve a lasting effect, it is usually recommended to perform 2-3 courses of injections, with an interval of 6-9 months. Possible side effects of the drug are always temporary and can be observed for no longer than 10-20 days. Their occurrence is due to partial penetration of the toxin into neighboring muscles. With repeated injections, an increase in the effect of the drug may be observed.
In parallel with the main treatment, this method allows you to restore facial symmetry in case of facial paresis and in the case of muscle aplasia.
Myth: You need to start getting Botox as early as possible.
Personally, as a specialist, I agree with this. Botulinum toxin in cosmetology has always been used for only one purpose - to wean the patient from frowning and wincing. Of course, we are not talking about sixteen-year-old girls, but after twenty-five years this habit is visible on the face. If left uncorrected for a long time, facial wrinkles become fixed by a fracture - it is much more difficult to remove. At the age of 50+ you can start injecting Botox, but the kinks will not go away. So botulinum toxin is a good prevention of wrinkle formation.