Indications for surgery
Reduction plastic surgery often has medical rather than aesthetic indications.
This is due to the fact that large breasts shift the center of gravity, increasing the load on the spinal column and back muscles, which leads to worse posture and compression of the chest. The structure of mammary gland hypertrophy can be with a predominance of adipose or glandular tissue. Excessive growth of glandular tissue is associated with hormonal imbalance during puberty or pregnancy. Excessive formation of adipose tissue occurs with obesity and sudden changes in weight. In men, glandular tissue can also grow in the chest area or fatty tissue can be deposited due to endocrine diseases or the use of hormones by athletes. This pathology is called gynecomastia, and reduction plastic surgery can help get rid of it.
Based on the severity, breast hypertrophy is divided into several classes:
- Minor breast enlargement with excess weight not exceeding 200 g.
- Average hypertrophy with excess gland mass up to 500 g.
- Macromastia with excess weight from 500 to 1200 g.
- Gigantomastia, in which excess weight exceeds 1200 g.
Heavy breasts with drooping cause discomfort to a woman. It is uncomfortable to sleep with such mammary glands; it causes pain in the thoracic and cervical spine, causing curvature of the spinal column and osteochondrosis. Large breasts with ptosis cause diaper rash and maceration of the skin under the breasts. Hypertrophied glands are more often susceptible to mastopathy and mastitis.
Absolute medical indications for surgical intervention include:
- osteochondrosis and pain in the thoracic spine;
- mastopathy - benign neoplasms;
- rachiocampsis;
- circulatory and respiratory disorders caused by a large gland;
- chronic maceration of the skin in the submammary fold;
- functional neurological disorders.
Indirect indications include asymmetry of the mammary glands, severe ptosis due to large volume.
Contraindications for surgery
Reduction mammoplasty is not performed for the following diseases and conditions:
- Unbalanced diabetes mellitus;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Breast reduction surgery is not performed on girls under 18 years of age and is not recommended during the menstrual period. A relative contraindication may also be the tendency of the patient’s skin to form keloid scars, if she herself is not ready to have long, pronounced scars, and also does not agree with the decrease in nipple sensitivity. Breastfeeding after such an operation is impossible.
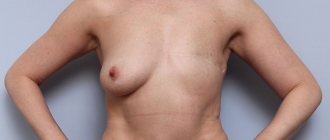
Result of breast reduction surgery
The changes are noticeable immediately, but the final result can be assessed after 6-8 months. The shape of the mammary glands becomes more natural and proportional. The nipple-areolar complex rises and takes its correct position. After 6-12 months, postoperative scars lighten and become almost invisible.
The sustainability of the result of reduction mammoplasty depends on compliance with restrictions during the rehabilitation period and the absence of sudden changes in weight. If these conditions are met, the new breast shape remains permanent.
See all photos
Technique of the operation
There are several techniques for reduction mammoplasty, each of which has its own disadvantages and certain advantages. The surgeon decides which one to use individually with each patient.
Periareolar
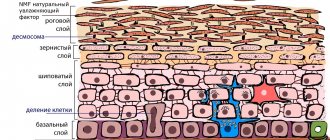
The incision is made around the circumference of the areola. Through periareolar access, excess tissue is removed and the size of the mammary glands is reduced. The tissues are sutured in layers. Due to the fact that the incision takes place at the border of the areola and the skin, the seam after the operation is almost invisible.
After surgery, compression garments or a bandage are also required. This technique is rarely used in reduction mammoplasty because it gives good results for relatively small breasts without significant ptosis, that is, drooping.
Vertical technique
The incision is made around the areola and down in a vertical direction to the inframammary fold, located directly under the mammary gland. The result is a figure-eight shaped incision. The skin flap inside the incision is removed, and the surgeon reduces the diameter of the areola.
In the second stage, fatty tissue and excess gland in the lower pole of the breast are removed. To reduce the volume of hematomas, homeostasis is controlled. For this, electric or laser knives are used, which thermally treat the edges of the wound.
The rest of the glandular tissue is lifted closer to the upper pole and sutured together. For better fixation, the gland is sometimes attached to the pectoral fascia. The nipple and areola are also moved closer to the center.
The incision is sutured in layers with absorbable threads using an intradermal cosmetic suture. The external seam is made with polypropylene threads that do not cause allergies. After four weeks, the surgeon removes them.
Sutures are placed around the circumference of the areola, then vertically down from the nipple to the inframammary fold. Sometimes after surgery several folds form along the seam. Usually they straighten out within two months after plastic surgery. Some of the advantages of this technique are the ability to change the position of the areola (it rises 1-4 cm higher), as well as the absence of a horizontal seam under the breast.
Immediately after mammoplasty, compression garments or a bandage are put on. During the healing period, it supports the mammary glands and reduces stress on the sutures.
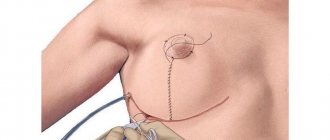
Anchor method
This is a classic breast reduction technique, in which the incision is made in the shape of an anchor: first along the areola, then vertically down, then along the inframammary fold. This operation consists of several stages:
- The incision is made according to the markings made before the operation. It outlines the border of the skin flap and the glandular tissue that is planned to be removed. It also determines where the nipple will be located.
- The nipple-areolar complex is moved higher, to the planned location, and fixed with sutures.
- After this, the excess gland is excised according to the markings.
- The remaining part of the glandular tissue is sewn together in layers with self-absorbing threads, and the breast is given a new shape.
- The edges of the skin are stitched with polypropylene threads. Cosmetic stitches are placed along the lower edge of the areola, vertically from the nipple down and in the fold under the breast.
- A bandage is put on to support the mammary glands during the recovery period.
Possible complications
- decreased sensitivity (skin, areola, nipples) in most cases is restored over time;
- hypertrophied scars (surgical excision is possible after six months);
- asymmetry of the mammary glands;
- deformation of the nipple-areola complex (manifests in the form of nipple retraction, flattening of the contour, dystopia, disturbances in the contour of the areola);
- deformation and drooping of the mammary glands due to stretching of the skin of the lower chest;
- loss of ability to breastfeed.
Preparation for surgery
The preparatory period consists of several stages, including consultation, examination, examination, tests and diagnostics.
Consultative appointment with a surgeon
At a consultation appointment, the surgeon collects an anamnesis, conducts an examination, during which he determines the size, individual characteristics of the mammary glands, the degree of ptosis, and the condition and ratio of glandular and adipose tissue, the presence of stretch marks.
The doctor finds out how much the patient wants to reduce her breasts, whether correction of the areolas is necessary, and whether the identified formations should be removed during surgery. A detailed history of all past and chronic diseases is collected to reduce the postoperative risk of complications.
The surgeon clarifies whether the woman is planning a child and whether she intends to breastfeed when she wants to do so. He recommends surgery after childbirth and lactation. If a patient is overweight and plans to lose weight, the surgeon advises her to do this before surgery.
Analyzes
Before the operation, you need to pass the required minimum tests:
- blood type, Rh factor;
- clinical blood test;
- blood for biochemical parameters;
- blood for glucose;
- coagulogram;
- blood for HIV (form 50);
- for syphilis (RW), for hepatitis B (HbsAg) and C (HCV);
- general urine analysis.
Examination and diagnosis
It is necessary to undergo a breast examination. Patients under 35 years of age are prescribed one MRI or ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, and after 35 years, two examinations and a mammogram. Women over 40 or with chronic diseases may need additional tests.
Mandatory fluorography (FLG) or chest x-ray, as well as an electrocardiogram with a conclusion. A physician's opinion on the possibility of surgery is required. Consultation with a mammologist and oncologist is required.
Still have questions? Ask them to a specialist
Plastic surgeon Vladimir Krugly will answer all your questions
Ask a Question
About the features of the operation
Reduction mammoplasty is performed under general anesthesia. The duration of the operation depends on the volume of surgery and ranges from 1.5 to 4 hours.
The choice of surgical technique is largely determined by the volume of tissue to be removed. For minor breast enlargement, the periareolar approach is used. For moderate hypertrophy, the vertical method is used. The anchor technique is used for macromastia, which is characterized by severe ptosis, so mastopexy, which lifts the breast, is performed simultaneously with reduction.
The markings are applied in advance, before breast reduction surgery. An incision is made along it, part of the glandular tissue, adipocytes, that is, fat cells, excess skin are removed, the nipple-areolar complex is pulled up, and the diameter of the areola is reduced, if necessary.
The tissues of the wound surface are closed in layers with sutures. A drain is installed to remove accumulated blood and serous fluid. The drainage tubes are removed the next day or a little later. After surgery, the patient is immediately put on compression garments.
Any reduction mammoplasty technique solves three main problems:
- removes excess gland tissue;
- raises the nipple-areolar complex;
- eliminates excess stretched skin.
Surgeries for gigantomastia are more difficult. Typically, this type of surgery involves a free transfer of the nipple-areolar complex. This way you can avoid complications. A new nipple can be formed in the right place from the skin, and then covered with tattooing.
Any plastic breast reduction can be combined not only with mastopexy, but also with the removal of benign tumors identified during examination.
How is breast reduction surgery performed?
Before starting surgery, the doctor makes markings. Next comes anesthesia - the anesthesiologist administers drugs through an intravenous catheter. The operation lasts 2.5-3 hours.
During the intervention, the surgeon excises the excess part of the gland and skin, while simultaneously shifting the nipple and areola to an aesthetically correct position, without disturbing trophism and innervation. After the operation, elastic micro-drainages are placed for 1-3 days. The surgeon applies intradermal sutures using high-quality suture material to form an even, invisible scar.
Advice from the surgeon in the postoperative period
After the operation, the patient remains in the hospital for one or two days and then switches to outpatient treatment. Swelling, hematomas, and decreased sensitivity of the nipples are the body’s natural reaction to surgery. Hematomas disappear after 2-4 weeks, the pain subsides after 5-7 days, nipple sensitivity is restored after a month.
In the first 4 days, it is recommended to take non-steroidal analgesics to reduce pain. Antibiotics are prescribed for a period of five to ten days to prevent mastitis and suppuration of sutures. The seams are treated with antiseptic ointment. To relieve tension on the seams, in addition to compression garments, a silicone patch is used. When the seams tighten and lighten and become soft, you can use a special gel.
Compression garments help reduce swelling and prevent seams from coming apart. You need to wear it for at least 6 weeks. After 5 days it can be removed for a short time, for example, to take a shower. The water should be warm. Hot baths and saunas are excluded for two months.
During this entire period of rehabilitation, injuries and pressure on the chest should be avoided. For the first month, it is recommended to sleep on your back. Physical exercise and heavy physical activity are prohibited during the entire recovery period.
Physiotherapeutic procedures that improve metabolic processes, stimulate lymphatic drainage and shorten the rehabilitation period give good results. Magnetic therapy has proven itself well.
The first results are visible after two to three months, but complete recovery will take a year.
Rehabilitation after breast reduction
If there are no complications, after 1-3 days the patient’s drainage is removed and she leaves the clinic. The recovery period depends on the volume and complexity of the plastic surgery. For at least a month, you must wear compression garments and come on the appointed days for follow-up examinations and dressings.
At the beginning of the rehabilitation period, you may experience pain, discomfort, swelling, and bruises. They pass on average after 5-6 days, after which the woman returns to normal daily life, with the exception of the pool, sauna, and increased physical activity for 4-6 weeks.