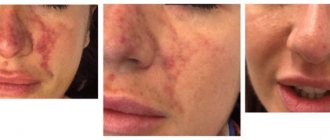
As practice shows, even those who carefully follow the rules of oral care and regularly take preventive measures to keep it clean and safe are not immune from periodontal diseases. High-quality brushing of teeth, rinsing the mouth, competent selection of toothpaste and brush, the use of cleansing floss, taking vitamin and mineral supplements and complexes certainly significantly reduce, but do not eliminate, the risk of infection and the development of a pathological process in the periodontium.
What is bioreparation and what makes Gialripayer unique?
Bioreparation is one of the methods of rejuvenation, which involves stimulating the natural processes of regeneration of skin tissue through injections of certain drugs. Before the synthesis of Hyalrepayer, amino acids, vitamins, hyaluronic acid, and trace elements were used for this procedure. These agents were administered alternately, so the course of injections could be quite long.
Scientific scientists had a goal - to synthesize a drug that would not only deliver the necessary substances to cells, but also force them to rejuvenate on their own. And such a product was created - the first complex long-acting bioremediate "Hyalripayer". What is his secret?
The basis of Hyalripayer was a modified hyaluronic acid molecule, to which molecules of a different kind were “sewn” in a certain way - vitamins, amino acids, peptides. Thus, there is no need to separately introduce the necessary substances - they are all combined into one stable complex.
By the way, about stability. The change in hyaluronic acid occurs using the solid-phase modification method. This method “hides” HA molecules from hyaluronidase, the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of this substance.
A regular HA molecule breaks down after 72 hours; the modified complex can remain in the skin for up to 3 weeks. The components of the bioreparant Hyalrepayer gradually split off from their carrier and not only nourish the cells, but also trigger natural regeneration processes. That is why the use of Hyalrepayer causes a more pronounced and long-lasting effect of bioreparation.
If trouble has already happened: what to do?
First of all, do not self-medicate and do not hope that “it will go away on its own,” but contact a competent specialist as quickly as possible. The periodontist will conduct an examination, ask in detail about the symptoms and manifestations, and then prescribe the most adequate and effective treatment.
One of the innovative methods for restoring damaged tissue in dentistry today is the bioreparation technique through the use of the drug “Dental Hyalripayer”. The main component in it is hyaluronic acid, which has already gained an impeccable reputation in cosmetic surgery and ophthalmology. It has a powerful regenerating effect, allowing you to restore the integrity and functionality of damaged tissue in a short time. The drug also contains various vitamins, microelements and amino acids that promote natural tissue restoration and renewal.
Depending on the complexity and severity of the disease, the dentist will prescribe the drug in one of the following ways:
- applications;
- dental mouthguards;
- microinjections.
Advantages of bioreparant Hyalripayer
If you compare Gialrepayer with other products that are used for facial mesotherapy or biorevitalization, you can see certain advantages of Gialrepayer:
- The complexity of this drug allows you to solve not just one aesthetic problem, but several at once.
- Additional components are attached to hyaluronic acid not using chemicals, but on a Bridgman anvil using high pressure and shear deformations. This method allows you to deliver only the necessary substances to cells.
- The HA molecule is modified, which allows it to act not for 72 hours, but for about 3 weeks.
- One drug molecule consists of several different substances that act complexly and simultaneously.
Bioreparation Hyalripayer
Hyalrepair-02 / Hyalrepair-02
In addition to hyaluronic acid, it contains vitamin C and amino acids (glycine, proline, lysine). Used to moisturize, rejuvenate and lift the skin. Indicated for dry, flabby, thin skin. The course consists of 3 procedures with an interval of 3 weeks, after which maintenance procedures are performed once every 2 months.
Hyalrepair-04 / Hyalrepair-04
Contains hyaluronic acid, vitamin C and amino acids (cysteine and glutathione). It is used to moisturize, rejuvenate and lift the skin, and also treats skin prone to pigmentation, dull skin, and rosacea well. The recommended course is 3 procedures with an interval of 3 weeks, then maintenance procedures once every 2 months.
Hyalrepair-08 / Hyalrepair-08
It contains vitamin C and L-carnitine, as well as hyaluronic acid. It is used for dehydrated and sagging skin, skin with local fat deposits on the skin of the face and body (cheeks, double chin, arms, inner thighs, abdomen, and so on). The recommended course is 3 procedures with an interval of 3 weeks. Then, for lasting results, maintenance procedures are recommended - once every 2 months.
Description of the Gialripayer product line
There are two lines of the drug Hyalripayer in the world - one solves the problem of bioreparation, the second - mesolifting.
The line of bioreparation products is intended for clients of middle and older age groups and has the following effects:
- activates the regeneration of dermal cells, replenishes reserves of useful and nutritious substances;
- correction of visible signs of photoaging and biological withering of the skin occurs;
- help eliminate not one, but several aesthetic problems;
- contribute to a longer and more pronounced rejuvenation effect.
Below are those modifications of Hyalripayer that are used as bioremedies.
Gialripayer-02
Available in the form of a 1.5 ml syringe.
The product contains: hyaluronic acid (14 mg/ml) with added lysine, proline, ascorbic acid and glycine.
Indications for use of this Hyalripayer:
- reduction of involutional changes in the skin;
- additional hydration;
- increased skin tone on the abdomen, shoulders and thighs;
- leveling of scar changes;
- preparing the skin for aggressive influences: laser rejuvenation, acid peels, plastic surgery.
The bioreparant Hyalripayer activates the synthesis of elastin and collagen fibers, and also provides the skin with the substances necessary for this process.
Gialripayer-04
The release form is similar to the previous drug.
Molecule structure: hyaluronic acid (14 mg/ml), ascorbic acid, glutathione, cysteine.
This Hyalrepayer is used to eliminate any damage to the skin, as well as for the purpose of:
- improvement of tone;
- combating facial wrinkles;
- improving complexion;
- reducing the severity of hyperpigmentation;
- treatment of rosacea.
Hyalripayer stimulates the formation of elastin and collagen and has an antioxidant effect.
Gialripayer-08
Available in the form of a 1.5 ml injection syringe.
Ingredients: 14 mg/ml hyaluronic acid, L-carnitine and vitamin C.
Application of Gialripayer:
- for the correction of involutional changes in the skin;
- with a combination of age-related skin changes and excess fat deposits on the face or torso;
- to combat excess fat in the cheeks and chin;
- in order to increase the tone of the skin after liposuction and as a complement to the course of anti-cellulite therapy.
The drugs used for mesolifting differ from bioremedies in the form of release, volume, composition and amount of hyaluronic acid in 1 ml of solution. They are intended for clients with pronounced age-related skin changes, as well as for young clients suffering from acne.
Gialripayer-06M
Available in 5 ml bottles.
The product consists of hyaluronic acid 2 mg/ml, vitamin C and raboflavin.
This Hyalrepayer is used for:
- combating the decrease in firmness and elasticity of skin tissues, which are combined with inflammatory processes;
- acne treatment;
- reducing the severity of atrophic scars;
- additional hydration.
Gialripayer-07M
5 ml bottles contain a complex of substances: 2 mg/ml hyaluronic acid, ascorbic acid, cysteine, valine and glycine.
Gialripayer is used in the following cases:
- sensitive, flaky and irritation-prone skin;
- sluggish, flabby, dehydrated skin;
- the presence of wrinkles of varying degrees of depth;
- scarring.
This drug can be used together with peeling, laser resurfacing, and even in combination with plastic surgery.
Gialripayer-08M
5 ml bottles.
Ingredients: 2 mg/ml hyaluronic acid, ascorbic acid, L-carnitine.
Indications for Gialripayer:
- fat deposits in the correction area, which go along with biological aging of the skin;
- fat in the chin area;
- excess lipid tissue around the joints;
- cellulite treatment;
- violation of skin turgor and elasticity after removal of fat deposits.
Gialripayer-10M
5 ml bottles containing the following complex of substances: HA – 2 mg/ml, vitamin C, glutathione and cysteine.
It is applied for:
- eliminating signs of biological aging;
- acne therapy;
- restoration of tone and elasticity of the skin.
Hyaluronic acid preparations in the treatment of osteoarthritis: focus on Chondroreparant Hyalripayer
Chondroreparants are a new class of drugs based on hyaluronic acid salts modified with low molecular weight bioactive compounds. The article discusses the production technology of the drugs Chondroreparant® Gialripayer®, and also presents the results of studies of their effectiveness and safety in various etiological forms of osteoarthritis.
Rice. 1. Mechanism of action of the formulas Chondroreparant Gialripayer
Rice. 2. Histological examination of tissues of experimental animal models before and after the introduction of the gel Chondroreparant Gialripayer-10 (staining with hematoxylin and eosin, magnification × 200): A – model of traumatic cartilage damage, B – model of non-adjuvant arterial cartilage
Rice. 3. Histological study of the reaction of connective tissue of animals to the introduction of modified HA formulas: A – the third day after subdermal administration of HA gel modified with ascorbyl phosphate (staining with hematoxylin and eosin, UV × 200); B –
Rice. 4. Cultures of cell lines of the morphotype of fibroblasts and endothelial cells (micrographs, Nikon Eclipse TE200-U, Hoffman contrast): A – endothelial cells of the EA.hy926 line, B – fibroblasts of the FRSN line
Rice. 5. Dependence of the number of EA.hy926 cells in the synthesis phase on the concentration of native HA and Hyalripayer-02 when exposed to cells for 48 hours
Rice. 6. Dependence of the number of fibroblasts in the synthesis phase on the concentration of native HA and Gialripayer-02 when exposed to cells for 24 and 48 hours
Rice. 7. Summary data on the severity of pain according to the modified VAS and stabilometry during therapy with the drug Gialripayer-02 in the group of professional athletes
Rice. 8. Decrease in the area of central motion on the coordinate axis during stabilometry in the sixth month of observation in the group of professional athletes
Rice. 9. Symmetrical distribution of step phases during podometric study at the sixth month of observation in the group of professional athletes
Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) leads in its prevalence among other rheumatic diseases. It is considered as a chronic progressive disease of synovial joints affecting primarily hyaline cartilage and subchondral bone as a result of the influence of a complex of biomechanical, biochemical, microcirculatory and/or genetic factors [1]. The pathogenesis of OA is based on an imbalance between anabolic and catabolic processes in joint tissues, especially in hyaline cartilage, the main springboard of pathological changes. In recent years, the theory that reduced blood flow in the subchondral bone is involved in the pathogenesis of hyaline cartilage destruction has also been discussed.
The true prevalence of OA is difficult to assess, since there is no parallelism between clinical symptoms and data from radiography of joints, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound methods, as well as macro- and microscopic indicators obtained during arthroscopy or biopsy of the synovium. Thus, many patients with X-ray positivity do not experience clinical manifestations of the disease. On the contrary, with a pronounced clinical picture, X-ray negativity may be observed. According to recent epidemiological studies, the prevalence of symptomatic OA of the knee joint in the population is approximately 10%, and that of the hip is 5–7% [2]. At the same time, there is a tendency towards a further increase in the prevalence of OA due to increased life expectancy and an increase in the percentage of obese people aged 60 years and older.
In OA, the load-bearing (knee and hip) joints are primarily affected, which significantly worsens the quality of life of patients and represents a serious socio-economic problem [3]. Despite the fact that the disease does not directly affect life prognosis, it is one of the main causes of premature loss of ability to work and disability, second only to coronary heart disease. The World Health Organization report on the social impact of musculoskeletal diseases indicates that knee OA is the fourth leading cause of disability in women and eighth in men [4].
The involvement of all the structures that make up the joint, which can be considered as an independent organ, leads to various mechanisms of pain, one of the leading symptoms of this disease. Thus, damage to the subchondral bone contributes to the development of pain through the occurrence of intraosseous hypertension and microfractures, formed osteophytes lead to trauma to the sensory nerves, and damage to the periarticular muscles is accompanied by their spasm. However, the leading role in the origin of pain and progressive chronicity of the disease belongs to inflammation, which is of paramount importance in the development and progression of OA [5].
Individualized therapy for OA is largely determined by its phenotype or its heterogeneity. The following disease phenotypes are distinguished:
- primary (idiopathic) and secondary OA;
- localization: gonarthrosis, coxarthrosis, osteoarthrosis of the joints of the hands, polyosteoarthrosis, etc.;
- nature of progression;
- the main cause (or causes) of pain;
- presence, severity and localization of inflammation (synovitis, periarthritis);
- comorbidity;
- the presence and severity of functional deficiency, determination of its leading cause.
Treatment of a patient with OA is a complex task and includes a set of measures consisting of a physical rehabilitation program (limiting load, stabilizing the affected joint, correcting orthopedic disorders) and prescribing medications aimed at reducing pain and slowing down structural damage in the joint tissues.
Great importance in therapy is given to influencing the metabolism of cartilage tissue in order to restore the balance between the load and the reparative capabilities of chondrocytes. For this purpose, slow-acting symptom-modifying or chondroprotective (chondroactive) drugs are used.
Application of hyaluronans in arthrology
Hyaluronic acid (HA) salts have been widely used in clinical practice since the early 1980s. last century. The therapeutic activity of GCs has been proven in many randomized controlled studies.
Currently, this compound is included in the list of drugs recommended by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR), and the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) (level evidence 1b) [6–8].
HA forms the axis of a giant proteoglycan molecule, which, together with collagen, is the main biopolymer of connective tissue in general and articular cartilage in particular. Proteoglycan is a supermolecule consisting of aggrecan subunits and a linear sulfated polymer HA [9, 10]. In linear form, HA is secreted by the synovial membrane into the joint cavity, where it is the main type of macromolecule. It is HA that is responsible for the unique viscoelastic properties of normal synovial fluid, which without HA is a simple plasma dialysate. In vivo
the polysaccharide is constantly located on the surface of the articular cartilage and synovial membrane, acting as a lubricant and absorber of mechanical stress. This property is extremely important, since mechanical stress promotes not only the production of metalloproteinases, one of the main molecules responsible for cartilage degeneration, but also the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. In addition, HA is an obligate component for chondrocytes in the synthesis of hyaline cartilage proteoglycans.
In the synovial fluid of an intact joint, a high concentration of hyaluronan with a large molecular weight (2–4 mg/ml) provides mechanical protection to cartilage cells. The gradual loss of full synthetic function by fibroblasts and, as a consequence, a decrease in the molecular weight and concentration of hyaluronan in the synovial fluid are one of the leading links in the pathogenesis of OA. The introduction of high-molecular-weight HA in high concentration into the joint cavity helps restore the viscoelastic properties of the synovial fluid. The newly formed HA restores joint homeostasis.
The potential ability of hyaluronan to influence the metabolism of cartilage tissue allows it to be classified as a means of pathogenetic therapy for OA [9].
The anti-inflammatory potential of GC is realized through a decrease in the level of prostaglandins, primarily PGE2, weakening the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α), suppression of the synthesis of metalloproteinases with simultaneous stimulation of the synthesis of tissue inhibitors of these endopeptidases. In addition, hyaluronan reduces the formation of nitric oxide and suppresses the expression of the cytokine RANTES (Regulated on Activation Normal T-Expressed and Secreted).
Chondroreparant® Hyalrepayer®. Drug formula
Employees of the International Research Center for Innovative Technologies "MARTINEX" and the Institute of Synthetic Polymer Materials named after. N.S. Enikolopova have developed a series of unique formulas with the patented composition Gialripayer. The line of drugs Chondroreparant Gialripayer has undergone preclinical and first clinical studies.
Reparants are a new class of drugs based on HA of biosynthetic origin, modified with low molecular weight compounds. When creating them, the method of solid-phase reaction mixing was used. A solid-state method for cross-linking and modifying (stabilizing) HA salts was developed in 2007 by Russian scientists [10, 11]. This technology makes it possible to obtain stable drugs based on mechanopolymers.
During solid-phase stabilization (mechanosynthesis) of HA, chemical agents with polymerizing properties are not used, which ensures good tolerability and high safety of the drugs. Modified HA with “stitched” low-molecular compounds is not recognized by tissue hyaluronidases, as a result of which its effectiveness increases due to the slowdown of enzymatic biodegradation in tissues.
The chondroreparant Gialripayer promotes the formation of a local depot of active elements with targeted delivery and prolonged action (up to three weeks) and, as a result, the launch of cascade mechanisms of connective tissue repair.
Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 contains highly purified modified HA, magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, L-proline, L-lysine and glycine. L-proline is a proteinogenic amino acid. It is involved in collagen synthesis and has antioxidant properties. L-lysine hydrochloride also has proteinogenic properties and stimulates the formation of collagen and elastin. Glycine is involved in collagen synthesis and improves regeneration processes (Fig. 1). In addition to modified HA, the composition of Chondroreparant Gialripayer-10 includes zinc, sodium ascorbyl phosphate, L-cysteine, L-glutathione, that is, a triad of active antioxidants with extracellular and intracellular synergistic activity.
A study of the effectiveness and tolerability of new gel preparations from the Chondroreparant Gialripayer line was carried out both on laboratory animals and in patients with OA.
Analysis of the results of preclinical studies
in vivo study
Using male Wistar rats, we began to study and evaluate the reparative properties of drugs under conditions closest to the conditions of their practical use, in order to be able to extrapolate the results to the human body (Roszdravnadzor accreditation certificate dated 02/18/2011). This study involved modeling the pathology of the knee joint, namely inflammation and injury, followed by treatment with Gialripayer-02 and Gyalripayer-10 (intra-articular administration) and analyzing their effect on reparative processes in cartilage.
Two different experimental pathologies of the knee joint in different groups of animals were obtained by simulating trauma (a LifeScan lancet was used to draw blood) and an inflammatory process (0.02 ml of a sterile 1.5% solution of lyophilized Escherichia coli
in saline). The treatment regimen for models of two types of pathology included double injection into the joint cavity with a three-day interval of Gialripayer-02 or Gyalripayer-10. Animals in the control group were administered native HA. Some animals were removed from the experiment at the stage of formation of pathological changes in the joints for histological confirmation of the fact of modeling. The second series of excretion was carried out on the seventh day after the course of injections, followed by a morphological study of hyaline cartilage samples [12].
Histological examination of the joint injury model showed that the damage affected the superficial and intermediate layers of cartilage. There is no clear delineation of the layers of hyaline cartilage; signs of destruction of chondrocytes, dystrophic and necrobiotic changes are observed. Dystrophic changes prevail over inflammatory ones. Inflammation is predominantly productive in nature (Fig. 2A). When studying a model of joint inflammation, inflammatory and post-inflammatory changes prevail over dystrophic and necrobiotic ones. The zone of destruction (ulceration of cartilage), sharp congestion of blood vessels and congestion in the lymphatic vessels are clearly defined. In places of dead chondrocytes there are swollen bundles of collagen fibers; in some places the bundles are so swollen that they turn into an eosinophilic mass resembling fibrinoid foci (Fig. 2B).
The authors found that Gialrepayer-02 and Gialrepayer-10 have a pronounced reparative effect: they accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue from full-thickness defects in both types of pathological process. At the same time, in the control group, pronounced tissue changes remained. Thus, after treatment of the injury model with the drug Hyalripayer-10, histological examination showed complete restoration of the cartilage surface, polarity and row of chondrocytes. Clear, medium-sized cell nuclei, constricted microvasculature vessels, loose connective tissue with small vessels, vascular spasm, and absence of fibrosis are visualized (Fig. 2B). Morphologically, the result of treatment of the arthritis model is expressed in the almost complete restoration of cartilage integrity, focal proliferation of chondrocytes, formation and restoration of cartilage polarity and rowing. A compact intercellular substance with greater basophilicity, vascular spasm, and intact bone beams without degenerative changes are also detected (Fig. 2D).
A more significant reparation effect when using Hyalripayer-10 can be explained by its antioxidant effect. This fact is confirmed by data that oxidative stress is involved in the destruction of cartilage tissue and a decrease in its reparative potential. At the same time, during a preliminary assessment of the effect of the studied drugs on an intact joint without modeling, it was morphologically shown that the drug does not cause pathological processes in healthy tissues. After its introduction, the structural organization of the joint remains intact, connective tissue dysplasia and disruption of hyaline cartilage trophism are not observed [12, 13].
Another series of studies assessed the effects of native HA and its modified formulations on biological tissue and cell lines.
When administered subdermally to animals, a uniform distribution of all studied drugs was observed with penetration into the subcutaneous fatty tissue and connective tissue. The tissue response to damage and drug administration was accompanied by moderate neutrophil infiltration, dynamically changing to lymphocytic-macrophage infiltration. Morphologically, fibroblast proliferation and the formation of new capillaries were noted already on the third day. These processes turned out to be most pronounced when introducing gels based on modified HA. Thus, a histological study of the reaction of the connective tissue of animals on the third day after subdermal injection of HA gel modified with ascorbyl phosphate compared with the introduction of native HA gel showed increased proliferation of fibroblasts and new formation of capillaries (Fig. 3A). When performing electron microscopy of tissue fragments taken on the third day after intradermal injection of HA gel modified with ascorbyl phosphate and glutathione, fibroblasts with pronounced hyperplasia of the endoplasmic reticulum were visualized, near which newly formed collagen fibrils were detected (Fig. 3B), as well as newly formed capillaries without pathological changes ( Fig. 3D).
On day 14, the gel with immobilized HA was detected in the form of small fragments in adipose tissue or hyperplastic lymph nodes and macrophages, indicating active phagocytosis. Resorption of native HA was observed starting from the third day, and of the modified formula – no earlier than 14–21 days. Thus, a histological study showed that on the 14th day after subdermal administration of the drug Gialripayer-02, the gel had a fine-fibrillar, fine-grained and small-vacuolar structure with the inclusion of lymphocytes, macrophages and giant multinucleated cells (Fig. 3B).
Thus, the results of the study confirmed the ability of modified HA preparations to activate fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis and neoangiogenesis, as well as resist rapid biodegradation, the duration of which for these preparations is several times higher than that of native HA [14].
A cytological study was carried out on cultures of fibroblasts and endothelial cells of the effect of the Gialripayer-02 material on metabolic activity and distribution over the phases of the cell cycle. This comparative study shows the effect of native HA and the drug Gialripayer-02 on various cell cultures (Fig. 4A, B).
Incubation of a monolayer of endothelial and fibroblastoid cells with the drug Gialripayer-02 did not cause cytodestruction, while their mitotic activity slightly increased. Analysis of the metabolic activity of cells of the endothelial cell line EA.hy926 indicated that both drugs primarily cause an increase in the metabolic activity of cells, and not their proliferation. Evaluation of the effect of drugs on the cell cycle of endothelial cells, carried out on the basis of flow cytometry data, indicated the absence of significant changes (Fig. 5).
On the contrary, Gialripayer-02 stimulated the metabolism of the fibroblast line FRSN - this effect was recorded at relatively low concentrations. At the same time, there was a tendency towards the accumulation of fibroblasts in the S phase during incubation with both drugs, which was more pronounced when incubated with Gialripayer-02. This result indirectly confirms the reparative activity of the components in the composition of the drug under study (Fig. 6).
In addition, Gialripayer-02 demonstrated relatively low cytotoxicity against endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Stimulation of proliferation was detected only in relation to fibroblasts, as evidenced by a change in the distribution of cells across the phases of the cell cycle with a shift towards the synthesis phase, mainly when exposed to Gialripayer-02 [15].
Analysis of clinical trial results
Recently, great importance in the development and clinical presentation of OA has been given to disorders of joint biomechanics [16, 17]. Peculiarities of biomechanical characteristics are associated with the intensity of pain, limitation of joint mobility and the rate of progression of OA. These assessment methods have become widely used due to the revealed fact that there is no complete correlation between the severity of radiological signs of OA, its clinical manifestations and real functional disorders in the joint and periarticular structures.
Together with the Department of Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine of the Russian National Research Medical University. N.I. Pirogov carried out a clinical and instrumental assessment of the use of a drug for intra-articular administration - Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 for secondary OA of the knee joints in highly qualified athletes (masters of sports, world championship medalists) involved in wrestling [18]. Chronic trauma (overload) of the knee joints in this population often leads to the development of traumatic OA.
The study group included 10 wrestlers with an average experience in sports of ≥ 10 years and aged ≤ 35 years. All participants were diagnosed with stage II secondary patellofemoral gonarthrosis. The intensity of pain in the knee joint is not lower than 40 mm on a standard visual analogue scale (VAS). The course of treatment included three intra-articular injections of the study drug, 2 ml every two weeks.
To evaluate the results, in addition to the standard examination, including x-ray examination and, if indicated, magnetic resonance imaging, a combined diagnostic plan was also used:
- subjective pain assessment using a modified VAS;
- assessment of proprioceptive function of the lower extremities using computer stabilometry;
- assessment of the roll phase uniformity function during a step - podometry;
- assessment of tremor amplitude and speed-angular characteristics of flexion/extension in the knee joint - biomechanical study.
This diagnostic program allowed researchers to identify and evaluate adaptation and compensatory processes in the musculoskeletal system.
The severity of pain was determined, including after sports activity. For this purpose, we used the VAS adopted in domestic and international studies for OA, with the addition of pain assessment immediately after sports activity. The verbal rating scale developed by the department staff included an assessment on a five-point scale of the severity of pain at rest, with palpation, movement, “starting” pain, pain after sports activity, as well as night pain during the week. The maximum total score on this scale is 30.
The dynamics of biomechanics and proprioception indicators were analyzed. To assess biomechanical disorders, computer stabilometry was used in American and European stances using the ProKin B hardware and software complex (TecnoBody, Italy). To obtain more accurate results and determine the Romberg coefficient, an accelerometric sensor was used. It was used to compare the projection of the spinous processes of the Th-section of the spine with the projection of the general center of pressure (GCP). Using this complex, stabilometric indicators such as the average position of the central motion in the frontal and sagittal planes, the velocity of the central motion, and the area of the statokinesiogram were recorded and analyzed. The proprioception parameter Romberg coefficient (QR) was calculated based on the obtained areas of the statokinesiogram with eyes closed and open (SZG / SOG).
The uniformity of the rolling phase of the feet during a step was assessed during podometry using a Winpod barometric platform (Medicapteurs, France) with a step length of 2 m. When the software of the device analyzed the force of foot pressure on the platform, the results were displayed in the form of podometric curves.
The tremor amplitude and speed-angular characteristics of flexion and extension in the knee joint were determined using a Motion Analysis wireless inertial sensor system (TecnoBody, Italy).
The last two research methods made it possible to diagnose changes in support and gait phases on the affected side with high sensitivity, as well as monitor the dynamics of the patients’ condition during treatment.
The dynamics of clinical and biomechanical parameters were analyzed one month from the start of treatment (before the last injection), as well as three and six months after the last injection of the drug.
At the beginning of the study, significant impairments of proprioception were revealed in all patients: the area of support was increased, the velocity of central motion was increased, and the Romberg coefficient was increased. 80% of athletes spared the limb on the affected side of the knee joint when standing and walking. After a month of therapy and three months after its completion, an improvement in the support function of the injured limb and proprioceptive function was observed (the Romberg coefficient was initially 210 units, after three months it was 150). This was accompanied by a significant decrease in pain intensity and leveling of clinical manifestations of synovitis. Six months after the end of treatment, there was no pain, a statistically significant improvement in proprioceptive function, and normalization of biomechanical parameters (Fig. 7–9).
Significant positive dynamics in the manifestations of gonarthrosis both after two injections of the drug and after six months of observation confirmed the presence of the basic effect of Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02. Therefore, the gel material under study can be classified as a slow-acting chondroactive drug. In addition, the study demonstrated the longevity of the treatment effects. The safety of Gialripayer-02 was similar to the safety of drugs based on HA salts for intra-articular administration [18].
At the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a clinical study was conducted on the effectiveness and tolerability of intra-articular administration of the drugs Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gialripayer-10 in patients with OA of the knee and hip joints.
At baseline, all participants had intense joint pain (more than 40 mm on VAS) and impaired function of the affected joints. The latter was determined using the WOMAC index (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index).
The therapeutic significance of the drugs was established based on the assessment of the general health status of patients and doctors. A significant reduction in pain in the target joint was recorded on the third to fifth day after administration of the drug. However, in most patients it was completely relieved. In addition, a significant increase in range of motion was observed (unpublished data). More than 80% of patients noted an improvement or significant improvement in their condition during therapy, which was consistent with the doctors’ assessment.
Thus, the results of clinical studies allow us to characterize the therapeutic activity of the line of drugs Chondroreparant Gialripayer as follows:
- reduce the intensity of pain in the target joint for a period of six to 12 months;
- have an analgesic effect by improving the viscoelastic properties of synovial fluid and protecting pain receptors in joint tissues;
- have an anti-inflammatory effect and help resolve the symptoms of inflammation in the synovium and periarticular soft tissues without affecting cyclooxygenases (COX);
- activate the formation of collagen and elastin due to the action of proteinogenic amino acids;
- have a reparative effect on hyaline cartilage and other joint structures by stimulating the synthetic activity of cells.
In addition, their use reduces the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Repeated courses of administration reduce the risk of endoprosthetics.
Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gialripayer-10 are well tolerated and highly safe. Thus, adverse events occurred in approximately 5% of patients, were transient in nature and did not require discontinuation of the drug or any medical intervention.
It is known that GC metabolites, under conditions of a pronounced inflammatory process, have pro-inflammatory activity and are capable of initiating an exacerbation. Therefore, before starting treatment of patients with OA with Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gyalripayer-10, it is necessary to assess the possible presence and severity of the inflammatory process in the tissues and, if necessary, prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy.
Indications for intra-articular use of the drugs Chondroreparant Gialripayer in syringes are primary and secondary OA of the knee joints without manifestations of secondary (reactive) arthritis, as well as OA of other localizations, post-traumatic lesions of the joints (meniscopathy, injuries of intra-articular ligaments, surgical intervention on the joints). The course of treatment involves three to five intra-articular injections. The frequency of administration is once every two weeks. Repeated courses are carried out depending on the clinical picture of the disease and the effectiveness of the previous course.
Another form of release of the drugs Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gialripayer-10 - in 5.0 ml bottles can also be used for periarticular use for periarthritis, tendonitis, enthesopathies. According to the manufacturer's recommendation, these drugs can be used extra-articularly for degenerative diseases of the spine (intervertebral osteochondrosis, spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis). A course of local injection therapy also involves three to five injections at intervals of two weeks. Repetition of courses - according to indications.
Place of GC drugs in ESCEO recommendations
Currently, a large number of international and national recommendations for the treatment of OA have been proposed. Of greatest interest are the recommendations of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO) from 2014 [7]. ESCEO was the first to propose a detailed algorithm for patient management, which will allow doctors of various specialties to navigate the numerous methods of treating OA and choose a rational treatment regimen depending on the stage of the disease. The ESCEO guidelines list the knee joint as the most common and most significant anatomical location of OA.
In addition to the general principles of patient management: education, weight loss, aerobic exercise, the developed algorithm includes four multimodal steps.
Step 1. Exercise therapy and the use of slow-acting symptom-modifying drugs such as glucosamine sulfate or chondroitin sulfate. These two drugs are the only slow-acting symptom-modifying drugs that the study team recommends based on strong clinical evidence. Topical NSAIDs may be used for additional pain relief.
Step 2. Prescription of oral selective or non-selective NSAIDs to patients with severe clinical manifestations, including pain and symptoms of persistent inflammation in the joint tissues. Oral NSAIDs should be used in short courses due to the potential for serious adverse events, and the prescription of non-selective or COX-2-selective NSAIDs is determined by the presence of associated gastrointestinal, cardiovascular or renal risks. If there are clear symptoms of secondary synovitis or periarthritis, intra-articular administration of prolonged glucocorticosteroids is recommended. These drugs promote progressive degeneration of articular cartilage, so they can be injected no more than three times a year into one joint. The use of GCs is also recommended at this stage, especially in patients refractory to NSAIDs and slow-acting symptom-modifying drugs, as well as crystalline corticosteroids. GCs and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the joint and only for justified indications. Therapy with these drugs is clinically different: the rapidity of development of the therapeutic effect is more pronounced with intra-articular corticosteroids, but it is less durable compared to GCs. In the latter case, the effect lasts from six to 12 months after a three to five week course of therapy.
The list of treatment tools for steps 3 and 4 includes central and/or opioid analgesics, the prescription of which is justified by the need to manage persistent pain in the preterminal and terminal stages of the disease.
In each specific case, the choice of rational therapy for OA is based on a comparison of the effectiveness and safety of interventions, analysis of predictors of response to therapy, rates of radiological progression, the presence of comorbidity, analysis of prognostic parameters, psychological factors, pain mechanisms, level of socialization of the patient, determining the balance between risk and benefit and availability of drugs. When determining injection tactics for the treatment of gonarthrosis, the presence of local (excess weight, unfavorable mechanical factors, high physical activity) and general (age, concomitant diseases, polymedication) risk factors, the severity of algo-functional manifestations in the joint, the presence of signs of inflammation, as well as the localization and degree of structural damage. Conservative treatment of gonarthrosis is aimed at reducing pain and inflammation, as well as slowing down the degradation of cartilage.
Conclusion
Solid-phase modification of HA is a way to stabilize it, that is, without the use of liquid-phase chemical polymerization. In this case, non-covalent bonds of hyaluronate with amino acids and ascorbyl phosphate are formed.
The drugs obtained using this technology in syringes for intra-articular administration - Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gialripayer-10 - are used to temporarily replenish the viscoelastic properties of synovial fluid. Modification of the spatial structure of the components makes it difficult for hyaluronidases to “recognize” the modified HA. Due to this, the duration of action of the drug increases. Chondroreparant Gialripayer-02 and Gialripayer-10 promote rapid activation of antioxidant and reparative processes.
Indications for the use of drugs are primary and secondary OA. Chondroreparant Gialripayer can be used both as monotherapy and in combination with symptomatic fast- and slow-acting drugs, including NSAIDs, glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate.
For a more complete assessment of the symptomatic and basal effects of these drugs, as well as their tolerability, including in combination with other treatment methods, their study should be continued in a model of primary OA with the participation of a sufficient number of patients with different phenotypes of the disease.
Contraindications and side effects
The following body conditions can be considered contraindications to the administration of Hyalripayer:
- disorders in the blood coagulation system;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- the presence of malignant or benign tumors;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- chronic diseases of any system of the human body, in the acute stage;
- allergy to any of the components of this product.
During or after bioreparation, the following complications may occur:
- hyperemia in the injection area;
- swelling of the subcutaneous tissue;
- feeling of itching;
- hematoma in the injection area;
- pain;
- change in skin color.
Questions and answers
Frequently asked questions:
What is the difference between the release form of Gialripayer in syringes and in vials?
The syringe contains only 1.5 ml of the drug, and the bottle contains 5 ml. In addition, these products differ in the concentration of hyaluronic acid in 1 ml of “Hyalripayer”: the solution in the syringe contains 14 mg of HA, the solution in the bottle – 2 mg. Also, preparations for bioreparation contain a larger number of components and remain in the dermis longer (up to 3 weeks).
What is the duration of the course of Gialripayer procedures and what is the interval between them?
If drugs from the “bioreparant” series are used, then the course of procedures consists of 3 injection sessions, which are carried out once every 3 weeks. When using mesolifting products, the drug is administered more often - once a week.
What procedures can the use of Hyalripayer be combined with?
Experts recommend combining the administration of the drug with various types of chemical peeling. If you want to use other methods of rejuvenation, contact a cosmetologist no earlier than 2 weeks after completing the bioreparation course.
The bioreparation procedure using Hyalripayer can be seen in the video:
HYALRIPAYER 10 Chondroreparant 5 ml bottle 0.8% 1 pc
HYALRIPAYER-10 (chondroreparant) 5ml
Compound
Zinc hyaluronate and copolymer of hyaluronic acid with sodium ascorbyl phosphate - 8 mg/ml, L-cysteine - 1 mg/ml, L-glutathione - 3 mg/ml, sodium chloride, phosphate buffer, water for injection.
Description
HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) is a transparent, colorless, slightly gel-like substance, supplied in a glass bottle. Contains a unique form of highly purified modified hyaluronic acid obtained by bacterial fermentation, with the addition of a copolymer of hyaluronic acid with sodium ascorbyl phosphate, L-cysteine and L-glutathione.
Mechanism of action
The condition of fascia and tendons, viscoelastic properties, protective and trophic functions are largely determined by the concentration of specific proteoglycan in them - hyaluronic acid, vitamin C and amino acids, which ensure a dynamic balance between the biosynthesis and catabolism of collagen and elastin. Immobilization of joints is accompanied by morphofunctional changes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system. Excessive physical activity, trauma, hypoxia, impaired microcirculation and tissue metabolism lead to excessive fusion of the tendon with surrounding tissues, degenerative disorders with increased formation of covalent bonds between collagen molecules, with the formation of tendogenic and myogenic contracture and their transformation into fibrous (scar) tissue with serous - fibrous and chronic fibrous tendinitis. Elevated levels of homocysteine and dimethylarginine in the fascial tissue matrix form chronic aseptic inflammation, which leads to ruptures and other damage to tendon bundles, loose tissue, nerves, lymphatic and blood vessels. One of the causes of microcirculation pathology is disruption of the functioning of redox systems. With an increase in the formation of reactive oxygen species, ischemia (hypoxia) develops, which is especially noticeable in myofascial tissues containing a branched capillary network. HYALRIPAIER®-10 (chondroreparant) is a bioactive composition of modified hyaluronic acid with ascorbic acid, L-glutathione and L-cysteine, involved in redox processes and the regulation of the initial synthesis of collagen and elastin. Creates a complex depot and allows for targeted delivery of microdoses of active ingredients directly to the area of damaged connective tissue structures. In all types of connective tissues and cells, glutathione, cysteine and ascorbic acid, as antioxidants, inhibit the development of pathologies caused by toxic metabolites and xenobiotics.
The action of HYALRIPIER®-10 (chondroreparant) is based on the biological stimulation of natural metabolic processes in relation to muscle-tendon elements, thereby improving the physiological and rheological status of the system of trophic connections and systems of growth regulation and cytodifferentiation. The structural modification of hyaluronic acid in HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) determines a prolonged reconstructive effect on damaged tissue due to injury or degenerative processes. Maintaining the optimal state of the intercellular matrix of cartilage and the tendon-ligament apparatus also depends on the balance of synthesis and degradation of this glycosaminoglycan. Vitamin C, which is part of the material, is involved in the stabilization of the triple helix of collagen and the formation of covalent bonds between collagen molecules during the formation of collagen fibrils. Ascorbic acid reduces the formation of excess urates during dystrophic calcification of connective tissue. Intracellular L-glutathione inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators. L-cysteine, being a donor of sulfhydryl groups, directly takes part in the binding of free radicals, as a result of which free radical oxidation reactions are interrupted, protecting the information center of the cell. Zinc controls the synthesis and breakdown of many neurotransmitters, reducing the physical ability to feel pain. It accelerates wound healing due to its participation in the formation of phagocytes and increased activity of macrophages, which helps cleanse necrotic tissue elements, activates enzymes responsible for collagen synthesis, and attracts fibroblast cells to the affected area. Extremely important for antibacterial immunity. Replenishes the deficiency of hyaluronic acid, while activating enzymes - matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), which are capable of breaking down almost all components of the extracellular matrix of connective tissues.
Indications for use
HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) is used in sports medicine, rheumatology, traumatology, orthopedics and maxillofacial surgery. Periarticular, intramuscular and perineural administration is allowed.
Applicable:
1. As part of complex therapy for:
– periarthritis, tendonitis, stenosing tendovaginitis (de Quervain’s disease), bursitis, enthesitis;
– radicular syndromes, spinal stenosis, to eliminate fibrotic changes in muscles (proliferative myositis), ligaments, fascial restrictions (proliferative fasciitis), periarticular algic zones, myofascial trigger points and tunnel syndromes;
– subfascial hypertension syndrome, tendinopathy, enthesopathy;
– spondyloarthrosis and facet syndrome, fixing ligamentosis (Forestier’s disease), with ankylosation of the articular processes (Bechterew’s disease);
– degenerative-dystrophic condition of the ligamentous apparatus, connective tissue and cartilaginous structures;
– periarthritis in remission.
2. During the period of rehabilitation after injuries and surgical interventions.
Contraindications
1. Hypersensitivity to the components of the material.
2. A history of autoimmune diseases or undergoing autoimmune therapy.
3. Pathological bleeding (endogenous or caused by the use of anticoagulants). 4. Infectious (septic) inflammatory process in the joint or periarticular tissues, a general infectious disease.
5. Presence of signs of active skin disease or skin infection in the immediate vicinity of the injection site
6. Pregnancy and lactation.
Precautionary measures
When treating the skin before injection, you should not use disinfectants containing quaternary ammonium salts. Before administration, the material must be warmed to room temperature. Patients should be warned in advance about the restriction in drinking alcoholic beverages during the entire course of treatment with HYALRIPAYER® -10 (chondrorepa - rant). The action of ethanol leads to an increase in a large number of free radicals and disrupts metabolic processes in the cell. After injection of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant), the patient is advised to avoid excessive physical activity for several days.
It is not allowed to administer HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) in the same syringe with an anesthetic and other pharmacological drugs.
Mode of application
The dosage and depth of injection of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) into the projection of the area of damage to the ligamentous apparatus or tendon canals, as well as the selection of the injection needle, is determined individually by a specialist. Depending on the anatomical and physiological characteristics and condition of the soft tissues, multiple injections of 0.2-0.5 ml of solution are recommended once every 14 days for 6-8 weeks. A repeat course is carried out after 6-12 months. Several areas can be treated at the same time.
Attention! For an effective treatment result, it is extremely important to perform the injection correctly. Do not use for intra-articular injection! The administration of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) can only be performed by specialists authorized to do so in accordance with local legislation. Laboratory TOSCANI LLC is not responsible for the consequences of improper use of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant).
Side effects
Periarticular, intramuscular and perineural administration of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) is well tolerated. In rare cases, local secondary effects are possible: pain, a feeling of warmth, and extremely rarely allergic reactions. Adverse events should be reported to local TOSCANI Laboratories LLC representatives. Interaction with other medical devices To date, there is no information regarding the incompatibility of HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) with other solutions for intra-articular use.
Delivery form
HYALRIPAYER®-10 (chondroreparant) is supplied in a glass bottle of 5.0 ml (1 needle included in the kit). Contents are sterilized.