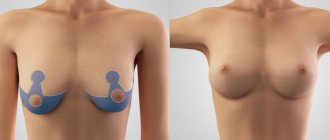
Breast ptosis (or mastoptosis) is a term used to describe the loss of firmness and drooping of a woman's breasts. It is a common belief that mastoptosis occurs after breastfeeding - however, this statement is not true.
Breast ptosis is a genetically determined feature or a natural effect of aging. Factors that determine its speed and severity include breast size, age, heredity, body mass index, and number of pregnancies.
Degrees of ptosis
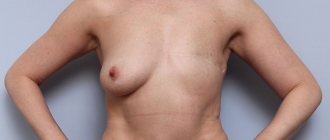
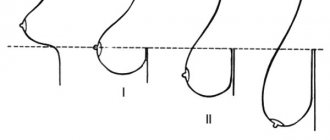
It is customary to distinguish three degrees of mastoptosis. They differ depending on the location of the nipple relative to the inframammary fold (the so-called line of attachment of the mammary glands to the skin that covers the chest).
1st degree
The nipple is located approximately at the level of the inframammary fold. This indicates the presence of slight sagging.
2nd degree
We are talking about 2nd degree if the nipple falls below the inframammary fold, but is still located above the rest of the breast tissue. This is a sign of moderate mastoptosis.
If the 3rd degree of ptosis is detected, this is a severe prolapse, when the nipple is located significantly below the inframammary fold, and the breast itself, if you put your palm under it, covers all your fingers.
How is a breast lift performed?
Immediately before the operation, the plastic surgeon applies special markings and carries out antiseptic treatment of the intervention area. The patient is then put under anesthesia. Incisions are made along the marking lines in accordance with the selected mastopexy method:
- with a linear lift - the first incision is made along the edge of the areola, then 2 vertical parallel incisions are made towards the inframammary fold; if the nipple-areola complex is displaced, the incision is made above the areola;
- with an areolar lift - if it is necessary to move the nipple-areolar complex, an incision can be made in the upper lobe of the areola in the shape of a crescent to eliminate the part of the dermis that creates asymmetry; with the circular technique, the surgeon performs 2 excisions: in the immediate vicinity of the nipple and at a distance of several centimeters;
- with an anchor lift , 3 incisions are made: around the areola of the nipple, a vertical incision from the lower part of the nipple to the inframammary fold and a horizontal incision going around the breast from below;
- with a reduction lift , the same incisions are made as with the anchor technique, but in addition it is necessary to move the nipple-areolar complex to a higher position and reduce the circumference of the areola.
During the operation, the surgeon (if necessary) removes excess glandular tissue, moves breast tissue, drains excess skin, forms a nourishing vascular pedicle of the nipple-areolar complex (if it is moved) and gives the nipple a new shape. At the final stage, the edges of the wound are connected, sutured and, if necessary, drains are installed.
Anchor breast lift
Breast lift with reduction
Correction of breast ptosis
Treatment without surgery
Many women are interested in conservative treatment of ptosis. Unfortunately, it can be called effective in very rare cases.
Threadlifting with mesothreads, recommended by some cosmetologists, can eliminate only the initial degree of sagging. At the same time, just carrying out procedures will not be enough: they must be combined with special physical exercises, massage, proper nutrition, etc.
That is why in most cases of using this technique, patients are disappointed.
Breast enlargement with ptosis
For those wishing to gain not only firm, but also large mammary glands, plastic surgeons recommend breast augmentation with simultaneous lifting (mastopexy). At the same time, other shortcomings can be eliminated: for example, breast asymmetry, unaesthetic shape, large nipple size.
Mastopexy
Mastopexy, or surgical breast lift, is a radical, but at the same time truly effective method of correcting ptosis. During the operation, the stretched skin is excised, which returns the breast to its previous shape and lifts it.
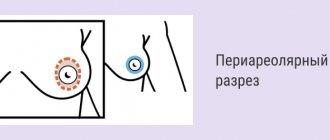
A surgical lift can be periareolar or vertical. The first type of operation is most often performed with simultaneous breast augmentation or for stage 1 mastoptosis, while the scar remains around the areola. A vertical lift is effective even with severe sagging, but it leaves two scars.
This operation is carried out only in Tsvetnoy Boulevard. It is performed under general anesthesia and requires long-term rehabilitation.
Cosmetic procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
Mastopexy: what is it?
For ptosis (or drooping) of the mammary gland, surgical lifting is used - mastopexy.
The cause of ptosis of the mammary glands can be various factors: pregnancy and breastfeeding are the most common of them. Too rapid weight gain, filling of the mammary glands with milk during lactation, with their subsequent “emptying” at the end of feeding, hormonal changes and other factors lead to the fact that the breasts quickly change their volume. Also, ptosis of the mammary glands occurs due to age-related changes in tissue: loss of elasticity and firmness occurs, which is replaced by loss of tone and sagging of the skin with ptosis of the mammary gland as a result of these processes:
- breast changes due to age-related factors;
- sharp fluctuations in weight, leading to rapid changes in the volume of the female glands, decreased tissue tone and the inability to recover independently;
- hereditarily determined structure and shape of the breast;
- changes in the structure of the glands as a result of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- pronounced asymmetry of the glands.
Classification of breast ptosis
There are several types of ptosis:
- true - the position of the nipple with the areola below the inframammary fold;
- glandular - sagging of the mammary gland, in which the nipple is higher than the inframammary fold;
- false - also called pseudoptosis, the mammary gland decreases in volume, and the lower sections are drooping, while the nipple has a normal position.
Based on the degree of prolapse, the following types of ptosis are distinguished:
I degree - location of the nipple at or below the level of no more than 1 cm of the inframammary fold.
ІІ degree – the nipple is approximately 2-3 cm below the fold, but above the areola.
III – location of the nipple below the fold by more than 3 centimeters, along the edge of the contour of the gland.
Indications for mastopexy
The operation is performed for aesthetic reasons, at the request of the woman herself, to give an aesthetically attractive breast shape.
Mastopexy options
To improve the shape of the breast, specialists use various surgical options. The main task is to rid a woman of an aesthetic defect that significantly impairs the quality of life. Doctors restore natural beauty by normalizing the location of contours, nipples, and tightening the mammary glands.
The mastopexy process consists of the following steps:
- upward movement of the areola and nipple;
- removal of overstretched skin in the lower pole of the breast;
- upward displacement and fixation of breast tissue to the fascia of the pectoral muscles;
- increasing breast volume, if necessary;
- uniform positioning, matching the edges of the treated tissues and applying fixing sutures.
Types of mastopexy:
- Periareolar;
- Vertical, with anchor type of cut;
- With one-stage endoprosthetics;
- Endoscopic.
Periareolar mastopexy
Carried out when:
- first degree prolapse of the gland;
- small size;
- elongated shape.
The operation involves a small incision around the areola of the nipple, excess glandular tissue is removed and sutures are applied to fix the tightened breast. The manipulation allows you to maintain sensitivity; the scars with this option are very thin, and over time they smooth out even more and become completely unnoticeable. The duration of the operation is up to 1 hour. The recovery period is up to one week; you can return to your professional duties on the 3rd day. An excellent effect is also achieved if this method of mastopexy is combined with endoprosthetics - the installation of artificial breast implants.
Vertical mastopexy
Indicated for second degree ptosis, the maximum diameter of the removed flap is up to 17 centimeters. An incision is made around and above the nipple, then cut vertically down to 5 centimeters, to the fold of skin under the gland. If necessary, it is possible to remove part of the glands; at the end of the operation, the breast tissue is fixed to the fascia of the pectoral muscle. Sutures are placed on the skin.
The duration of the operation is 2-3 hours. Painful sensations may last 3-4 days, you can start working in about a week. But for complete and effective healing, you need to wear compression garments for a month. After vertical mastopexy, scars remain quite noticeable in the first 6-12 months, which gradually thin out and smooth out.
Anchor incision surgery
Indicated for grade III ptosis and pseudoptosis. The same incision is made as for a vertical mastopexy, plus a horizontal incision is made in the fold under the breast. But most often, with these indications, an anchor incision is used - it is made around the areola, on the inframammary fold and vertical, connecting these two incisions. When the operation ends with sutures, they resemble the shape of an anchor. This operation is considered the most effective for improving the shape of the breast with severe ptosis. The disadvantages of the method include:
- duration - from 3 hours or more.
- noticeable scars remain.
- long recovery period - you can return to work only after 2 weeks.
Important: after anchor mastopexy, physical activity is not contraindicated for 3 months.
Endoscopic breast lift
A modern method that makes scars almost invisible. During the operation, small punctures are made into which an endoscope and manipulation instruments are inserted. The surgical area is displayed on the screen, and the specialist removes excess tissue by separating it from the skin and excision, then fixing the gland in the desired position.
The endoscopic method allows for minimally noticeable scars, the recovery period is significantly reduced, and the operation is easier to tolerate. This option of mastopexy is possible with moderate ptosis and a small organ size.
Mastopexy with simultaneous endoprosthetics
- The most effective technique in all respects, which has a number of advantages: Restores the shape of the mammary gland
- Increases its volume
- The chest is fixed in the desired position
In the practice of specialists, we regularly encounter patients who have undergone endoprosthetics for unresolved ptosis. As a result, the degree of ptosis increases and instead of graceful forms, pronounced prolapse of the mammary glands occurs. For this reason, plastic surgeons recommend it to women after breastfeeding, pregnancy, age-related changes and other factors that contribute to ptosis. combine endoprosthetics with mastopexy.
Proper preparation for surgery
For maximum effectiveness and good results after mastopexy, you must listen to your doctor's recommendations when preparing.
- Undergo a complete breast examination:
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- Mammography;
- ECG;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- RW analysis;
- Analysis for HIV, hepatitis, AIDS;
- Analysis for the presence of acute and chronic inflammatory processes.
Also, if necessary, an examination of the woman’s internal organs is carried out.
A detailed inspection is provided:
- By a general practitioner: to exclude diseases of internal organs for which surgery is contraindicated.
- An anesthesiologist: to determine the dosage and method of administering painkillers, the type of anesthesia.
- Mammologist: to examine the breast for contraindications to plastic surgery.
Before the operation begins, the surgeon makes marks along which incisions and tightening of the glands will be made.
Rehabilitation period after breast lift
The duration of the rehabilitation period directly depends on the complexity of the operation performed and its type. In the first days after surgery, only hygienic rubbing is allowed; almost any manual manipulation is excluded. Regardless of the mastopexy technique, wearing special compression garments is recommended for (at least) 4 weeks. In addition, for a month (the exact timing is determined by the doctor individually), you must follow the following recommendations:
- exclude physical activity and sports;
- minimize habitual rates of smoking and consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- refuse to visit the solarium and bathhouse, open reservoirs and swimming pool;
- Avoid exposing your chest to direct sunlight.
As a rule, primary rehabilitation takes 10 - 20 days. The final result can be assessed 4 to 9 months after surgery.
Causes and symptoms of ptosis
Let's consider the probable causes of eyelid ptosis:
- Underdevelopment of the muscle that is responsible for raising the upper eyelid is usually a congenital pathology.
- Previous neurological diseases.
- Paralysis of the muscles in the eye area. This often happens after a stroke.
- Damage to the oculomotor nerve.
- Age-related changes.
- Unsuccessful plastic surgery.
- Various types of injuries.
- Botulinum toxin injections in the eye area.
The exact cause of ptosis can only be determined after diagnosis.
It is worth noting that eyelid ptosis is not only an aesthetic defect. Very often, with this diagnosis, vision deterioration and a number of other unpleasant symptoms occur.
Let's look at the symptoms that accompany eyelid ptosis:
- Discomfort in the eye area.
- Rapid eye fatigue, which is associated with constant muscle tension.
- Often patients are unable to close the eye completely due to ptosis, which can cause dry eyes. In some cases, the opposite situation is observed, and the patient is bothered by tearing.
- Visually noticeable drooping upper eyelid.
- Pain when trying to close the eyelids.
- Frequent exacerbation of conjunctivitis and other inflammatory and infectious eye diseases.
- Severe ptosis leads to the development of strabismus, double vision and decreased visual acuity.
When is surgery scheduled?
The indication for surgery is the patient’s desire to get rid of a cosmetic defect and discomfort. The decision on the advisability of surgical intervention is made by the attending physician; in some cases, the disease can be treated conservatively.
The operation also has contraindications. The intervention is not carried out if at least one factor from the list is present:
- Inflammatory or infectious diseases in the acute stage.
- Serious neurological abnormalities.
- Menstruation period in women (ideal time for surgery is 5-7 days of the cycle).
- Old age of the patient.