Lentigo melanoma is a relatively rare disease. According to statistics, it is diagnosed in 5-10% of all melanoma cases. The foundation for the formation of this pathology is Dubreuil’s precancerous melanosis, named after the scientist who first described it. This researcher studied in detail the facial skin defects of women who spent a long time outdoors and were exposed to intense sun exposure.
Most often, lentigo melanoma is found in people who do not perceive tanning well, as well as in anyone who has certain dermatological abnormalities caused by sun exposure. Such defects include solar keratosis.
Common affected areas are the ears, upper cervical region, facial part of the skull, and distal arms and legs. In addition, people with a large number of freckles are at risk. In most cases, the disease affects older women.
Stages of disease development
The development of this disease is divided into several stages. In certain situations, the stages are blurred, but most often they are well defined. It all starts with Hutchinson's lentiginous freckle. This skin defect is not malignant. The polymorphism of its cellular components is at a low level, and there is no invasion of the skin layers.
After this comes the so-called lentigo stage. With its onset, the pathology takes the form of a pigment spot. Melanocyte atypia gradually increases and their invasive growth begins. The intensity of the growth depends on whether there is damage to the basement membrane in the deeper layers of the skin. Malignant lentigo, which is a pathomorphological precursor of melanoma, gradually progresses.
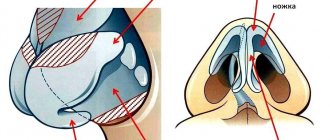
In fact, lentigo maligna is the 1st stage, which has a clear clinical picture. This formation looks like an irregularly shaped spot, similar to an ordinary geographical map. The boundaries of the spot are clearly visible; its surface is rather dull. Lentigo maligna has an uneven color: the general background is brownish, diluted with dark spots. The dimensions of the spot are quite large: up to 20 cm.
The stage of radial growth of the cancer focus is associated with the described form of the tumor. It lasts a long time (up to several years). The spot grows, taking on the appearance of a skin plaque with an irregular shape. The peculiarity of malignant lentigo is that it does not always progress to the stage of full-blown melanoma (such a transition is absent in half of the cases). But despite this, all people with this deviation are recommended to undergo surgical excision of the affected area.
Kinds
- Sunny . This type of lentigo is characterized by the appearance of multiple small spots on the body. They are most often found in fair-skinned people or those who sunbathe for long periods of time.
- Youthful . It is expressed in the appearance of freckles in young children. It usually goes away on its own, with the transition from adolescence to adulthood. There have been no cases of degeneration of this type of lentigo into malignant ones.
- Senile. Appears in old age and is most often localized on the hands, feet and face.
The spots are of various sizes and blurry outlines. - Hepatic or senile. Diagnosed in people 40-45 years of age and older against the background of diseases of the digestive system.
- Chloasma . The appearance of hyperpigmentation in one area of the skin, which has clear boundaries. Often develops during pregnancy or menopause in women.
- Malignant. It is a single spot with uneven edges, the color of the spot is very dark or brown with black spots, the formation is constantly increasing in size and can reach 20 cm or more.
- Ink . It manifests itself in the formation of many black spots on the body, similar to drops.
Also, lentigo always accompanies such systemic diseases as:
- Genodermatoses.
- Hereditary central lentigiosis of Touraine. With it, without connection with external influences, fine hyperpigmentation on the body occurs throughout a person’s life. This disease appears before the first attack of epilepsy and can be combined with nocturnal enuresis in a child and his retardation in mental and physical development.
- Touraine's periorificial lentigiosis, which is combined with polyps in the stomach and small intestine.
- LEOPARD syndrome, a genetic pathology expressed in cardiac dysfunction, slow growth and weight gain in the baby, as well as the formation of large lentigo spots throughout the baby’s body.
- McCune-Albright disease, with a clear triad of symptoms: the formation of hyperpigmentation, disruption of the endocrine system, pathologies of the development of the musculoskeletal system.
Description of the expanded stage
Evidence that lentigo maligna has developed into a full-fledged cancer focus is a change in pigmentation on the surface of the spot. It takes on a variegated color, its boundaries become more complex. Over time, areas of scar tissue atrophy form on the formation; the terrain changes. A node forms on the spot, having a lighter shade than the adjacent areas. There is often bleeding or serous discharge from nodular tissues. The manifestation of itching indicates that vertical germination of the cancer focus into the dermal layer has begun. Lentigo completely transforms into melanoma. The process of metastasis gradually begins.
Treatment
To eliminate a cosmetic defect in a benign course of the disease, the following procedures are used:
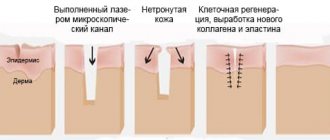
- photorejuvenation, a technique of exposure to light fluxes that trigger regeneration and restoration processes in the epidermis;
- laser peeling, “removes” cells with excess pigmentation from the surface of the skin;
- mesotherapy, a technique using synthetic and natural preparations that whiten the skin;
- dermabrasion, mechanical hardware scraping of pigment cells from the skin;
- chemical peeling, a method of removing pathological cells by applying special preparations to problem areas;
- cryodestruction, freezing of pigment spots at ultra-low temperatures.
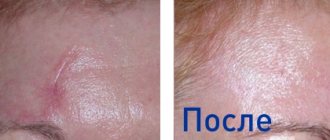
Before and after cosmetic stain removal
Video:
malignancy is suspected , touching tumors and applying cosmetology methods to them is strictly prohibited! To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a full examination: examination of the pigment spot under a microscope, blood tests for tumor markers, biochemical tests, biopsy and histology.
Surgical methods are used to treat melanomas; the faster they are removed, the higher the chance of recovery for patients.
Differences between benign and malignant lentigines:
- do not grow, do not itch, do not change color;
- do not bleed, do not crack;
- do not cause any discomfort other than external ugliness.
Different types of melanomas
Histomorphological description of the disease
The highest concentration of atypical melanocytes in the pathology under consideration is present in the basal region of the epidermis. As for the epidermis itself, it looks atrophied, its papillary processes become very thin or disappear altogether. Modified cancer cells are characterized by an elongated and, quite often, spindle-shaped shape. The nuclei of such cellular components are highly polymorphic, their coloring is rather weak; the cell cytoplasm has an increased concentration of vacuoles. The concentration of melanin varies; This explains the different colors of melanoma areas. Atypically changed cellular components grow deep into the skin along the hair follicles, as well as through other adnexal components. This type of development leads to the fact that superficial elimination of the cancer focus is often useless. Under the layer of progressive melanocytes, mononuclear cells infiltrate.
Lentigo melanoma has a significant difference from the superficial variety. The fact is that it develops quite slowly, so the likelihood of extensive metastasis is low. The simplest visual method for determining the stage of disease progression is the color of the tumor. The stage should be designated according to the following principle:
• brownish color – indicates an early stage; • tissue darkening is present – an intermediate stage of progression; • there are impurities of purple or bluish tints – the disease has become an advanced form, invasive germination is taking place; the risk of metastasis is high.
In certain situations, the cancer focus becomes grayish, pink or whitish. According to some dermato-oncologists, this is due to partial resorption of the pathological formation, which, in rare cases, is provoked by the influence of the human immune system.
HOW TO PROTECT FROM LENTIGO?
As for treatment, the following are considered effective for lentigo:
- Laser treatment. Eliminates visible defects, promotes skin renewal, and provokes natural regenerative programs.
- Chemical peeling. Here - treatment by lightening the skin with retinoids or ascorbic/kojic acids.
- In some cases, before starting treatment, photoprotection is recommended - treatment of the affected area with light at high temperatures. Helps strengthen the skin's protective mechanisms.
- With frequent relapses of lentigo, diathermocoagulation treatment can be used. In this case, by attracting high temperatures, protein coagulation and complete exfoliation of the neoplasm are achieved.
Independent practice of treatment comes down to the effective selection of UV protection products and a competent diet. In some cases, vitamin treatment is recommended.
Causes
Lentigo is nothing more than an accumulation of excess melanin - a coloring pigment. These spots can either be inherited or appear unexpectedly in adulthood. Unfortunately, doctors have not yet fully studied this disease.
The following reasons for its appearance have been precisely defined: 1. Old age. Lentigo on the face is very common in people over 70 years of age, sometimes these spots begin to appear after 40. 2. Young age. The so-called juvenile lentigo in children and adolescents is known. Its causes are unclear; with the onset of adulthood, the spots disappear on their own. 3. Skin injuries. Occurs at the site of superficial wounds. 4. Excessive insolation. Excess ultraviolet radiation always has a negative effect on the skin, solar lentigo is proof of this. 5. Lentiginosis, or congenital lentigo, is inherited and manifests itself not only on the face, but also on the body together with other unpleasant pathologies: heart disease, congenital deafness, etc. 6. Malfunctions of the liver and intestines. There are cases where lentigo spots disappeared after surgical operations on the gastrointestinal tract.
How to remove age spots?
The first place you can start removing age spots is the services of cosmetologists. For example, many beauty salons use specialized lightening creams, peelings for these purposes, and also resort to removing stains with a laser.
1). Peelings
Peels are made using chemicals (fruit acids) that have different compositions. Using peeling, the cosmetologist acts on a specific area of the skin where there is increased pigmentation. The main task of peeling is to obtain smooth, even skin.
2). Photo pigment removal
When carrying out the phototherapy procedure, a special IPL Quantum device is used, which operates with a light wave that destroys only melanocytes and does not damage the skin. Thanks to this, healthy tissue remains intact.
3). Laser removal of age spots
The principle of the laser removal procedure is to heat the melanin, which leads to its destruction. The laser beam damages the pigment and it is removed when the skin is renewed. According to cosmetologists, the result obtained after the procedure lasts throughout life.
SkinLazerMed Medical Center offers you every type of cosmetic procedure that quickly, easily and effectively removes age spots on the skin. Consultation with the center’s specialists is free, and prices are the most reasonable in St. Petersburg.
Dark spots
Dark spots
A pigment spot is an area of excessive accumulation of melanin: a special pigment found in various layers of the epidermis.
Freckles (ephelids): small areas of oval or round shape, from light red to dark brown. Occurs predominantly in people with fair skin (phototypes 1 and 2)
Chloasma are dark brown-brown spots, generally uneven and varying in size, with sharp boundaries and a smooth surface. Most often, such age spots occur in women during pregnancy, and usually disappear after pregnancy. In most cases, chloasma forms on the skin of the face, but can also affect areas of skin on the inner thighs and abdomen. But there are often cases when this type of age spots appears in non-pregnant women, and even in men. In addition to pregnancy, the causes of chloasma include some gynecological diseases, liver diseases, the use of oral contraceptives, as well as prolonged exposure to the sun. As a rule, when the cause is eliminated, chloasma disappears.
Photodermatosis : a manifestation of increased sensitivity of the skin to UV radiation. Expressed in the form of itchy redness on the skin and rash.
Post-acne : if acne was severe and was accompanied by open, difficult-to-heal inflammation, then a permanent pigmented spot remains in place of the resolved acne.
Lentigines are compacted pigment spots of brown or black-brown color, which generally rise slightly above the skin level. Their shape has sharp outlines (most often it is round or elongated), and their sizes can vary. Lentigo can occur either in single or multiple quantities, forming a profuse rash on any area of the skin. Pigment spots such as lentigo come in two types:
Juvenile lentigo , which is usually genetic, and appears in children under the age of 10 years. In this case, small pigment spots resembling moles most often form on the body (less often on the face).
Senile lentigo is spots that occur in older people, especially on exposed areas of the skin most exposed to sunlight (face, shoulders, hands). Senile lentigo is usually distinguished by its larger size, which can reach up to 2 centimeters in diameter.
Main reasons:
- Endocrine disorders
- Post-inflammatory processes of the skin - acne, post-acne (scars)
- Any skin trauma
- Age-related changes
- Pregnancy (a special case in which treatment of pigmentation is undesirable)
- Excessive tanning
- Taking certain medications (hormonal contraceptives, antibiotics)
- Chemical exposure
- Side effects of some cosmetic procedures.