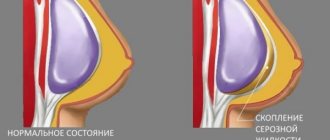
After any plastic surgery, bruises and swelling occur. This is a natural reaction of the body to damage to soft tissues and blood vessels. Due to vascular injury, fluid from the bloodstream flows into the interstitial space. Accumulating there, it compresses the lymphatic vessels and venules, thereby preventing the flow of fluid into them.
Thus, primary edema increases. It takes time to dissolve. After blepharoplasty, excess interstitial fluid from the upper and lower eyelids can move to adjacent areas of the face, for example, forming swelling in the cheekbones.
Drainage of hematoma and other methods of its treatment
The human body is riddled with blood vessels.
During domestic, industrial or sports injuries, the integrity of the wall of a particular vessel is compromised. This can lead to bleeding or hematoma formation. Hematoma is an accumulation of liquid or coagulated blood in the thickness of soft tissue. This is often a harmless phenomenon, but in some cases doctors are often faced with the need to remove a large hematoma, which can interfere with the functioning of tissues and neighboring organs. Hematomas can form:
- for all types of injuries – closed and open;
- in any part of the human body;
- for injuries of any degree - from minor (in this case, the role is played not by physical effort, but by the fragility of the vascular wall) to severe.
Hematomas can occur not only when physical force is applied to the tissues, but also several hours and days after that. An example is an internal hematoma after surgery - when sutures placed on blood vessels damaged during surgery fail. The possibility of such tissue hemorrhages must be constantly remembered. The timeliness of diagnosis, and therefore the success of hematoma treatment, depends on this.
The development of postmastectomy edema and limitation of limb mobility in the shoulder joint are greatly influenced by postoperative complications, in particular necrosis (death) of the skin, prolonged lymphorrhea (discharge of lymph), wound suppuration. Other causes of lymphedema include infections, taking tamoxifen, which can cause blood clots and deep vein thrombosis, and air travel (probably due to decreased cabin pressure).
Clinically, this condition is manifested by pain when trying to abduct and raise the arm, limited movement in the shoulder joint, increased volume of the hand, forearm, and shoulder compared to a healthy arm, a feeling of heaviness in the arm, and impaired skin sensitivity. It is possible that erysipelas may occur, requiring a complex of therapeutic measures with intensive antibacterial therapy.
Since lymphedema can appear several years after surgery, it is necessary to constantly take care of yourself, observing certain rules and restrictions:
- Try to avoid any kind of injury to the injured hand (blows, cuts, burns, sports injuries, insect bites, scratches). If germs penetrate through an abrasion or wound on the hand, inflammation can easily occur. Since the flow of lymph in the lymphatic vessels of the hand is obstructed, a sufficient number of lymphocytes capable of fighting the infection will not reach the site of microbe penetration. Keep in mind that erysipelas leads to the appearance and increase of swelling. If it happens to you once, consult your doctor about seasonal antibacterial therapy.
- When performing any work where even minimal damage is possible, use gloves. Always protect your hands from the sun and wear long sleeves in summer. Avoid repeated vigorous, counteracting movements of the “sick” hand (brushing, pushing, pulling, etc.). Do not cut cuticles when doing a manicure. In cases of damage, it is necessary to treat them with antiseptic solutions (tincture of iodine, alcohol solution of brilliant green). Watch for signs of infection. Never ignore even minor swelling of the arm, hand, fingers or chest - consult a doctor immediately.
- Maintain the necessary hygiene, use moisturizing lotions after bathing, dry your hand gently but thoroughly. Make sure all folds and skin between your toes are dry. It is not recommended to visit saunas or take hot baths. It is necessary to avoid strong temperature fluctuations when bathing and washing dishes.
- The uninjured hand should be used for injections, drawing blood, and measuring blood pressure. Do not wear jewelry or elastic bands on the hand or fingers on the side of the operation. It is better to wear rings, bracelets, watches on a healthy hand. Make sure that the armholes in your clothes are not too narrow. Bra straps should not cut into your shoulder.
- Try to accustom yourself to sleep on your back so that your weight does not compress the vessels of the arm on the side of the operation. You can adapt a pad for the “sick” hand so that it is on an elevation. This normalizes blood and lymph circulation.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects with your injured hand. As the load increases, the muscles require more oxygen, the blood flow to the arm, which is already overloaded with venous blood and lymph, increases, while the outflow from it is difficult. It is recommended to limit the load on the arm from the operation to 1 kg during the first year, to 2 kg for the next 4 years and to 3-4 kg for the rest of life. The load on the healthy arm should also be reduced. If you are carrying a bag, you should hang it on your shoulder on your healthy side. However, those women who tend to have shoulder pain should not carry a bag on their shoulder at all, as it raises the shoulder slightly, which inevitably strains both shoulders and increases the pain. Likewise, muscle tension spreads from the neck to the fingers when you keep your arm bent for a long time. If possible, put it in your shirt or pocket and relax the muscles in your arm and shoulder.
- Do not overload your injured arm: if it starts to hurt or swells more than usual, it means you have either exceeded the permissible load or created an uncomfortable position for it. You need to lie down and raise your hand up. It is recommended (Churikova L.A. et al., 2000) in these cases, 1-2 times a day to rub the following cream into the area of the sore arm and shoulder girdle on the affected side: baby cream - 1 part, olive oil - 1 part, retinol (vitamin A, oil solution) – 1 part, troxevasin ointment – 2 parts.
- Avoid any work that requires you to sit with your arm down for a long period of time. Such restrictions are needed to prevent stagnation of lymph in the lymphatic vessels of the hand. For example, you should not do laundry while bending low over the bathtub or washing the floors with your hands. If you intend to work with your hands, wear an elastic sleeve or glove. After work, be sure to do gymnastics, massage your hand, give it an elevated position for 10-15 minutes.
- Try to maintain your normal weight. Do not smoke or drink alcoholic beverages. A low-salt, high-fiber diet should be well balanced. The interstitial fluid inside the edema contains large amounts of protein, but a low-protein diet does not reduce its concentration in the lymph; rather, it can weaken the connective tissue and only worsen the situation. Easily digestible protein (fish, chicken, tafu) should be included in your diet.
General principles of medical tactics for hematomas
In the vast majority of cases, the injuries are superficial and the accumulation of blood in the tissues is insignificant. Often, medical intervention (in particular, drainage of the hematoma) is not required, since after a certain time the hematoma disappears on its own. This process occurs due to the gradual lysis (destruction) of plasma and blood cells that formed the hematoma.
The rate of resorption of a hematoma after a bruise depends on:
- the amount of blood shed;
- age (in the elderly, hematomas resolve more slowly than in children or young people);
- associated infection (in this case, the hematoma does not resolve, but suppurates);
- condition of the vessels (if they are pathologically fragile, a repeated outpouring of blood into the tissue may occur in the same location, and the hematoma simply does not have time to resolve).
Before wondering how to treat a large hematoma on the arm, you should remember that large vessels pass through this area, and the outpouring of blood that formed the hematoma may signal damage to the walls of these vessels and the threat of more pronounced bleeding.
Less commonly, hematomas occur:
- in muscles;
- in fatty tissue;
- in the thickness of the parenchymal organ;
- under the meninges;
- in brain tissue.
They are united by a common feature: blood rushes into the tissue according to the principle of least resistance. Knowing the characteristics of the tissues, it is possible to determine with great confidence where the hematoma could have formed. The success of treatment largely depends on this factor.
Medical tactics for the accumulation of blood in tissues depend on a number of nuances:
- localization of hematoma;
- patient's age;
- concomitant diseases.
Treatment of a small hematoma on a child’s head should be given no less attention than a large hematoma on the anterior abdominal wall of an athlete. And an acute infectious disease can lead to the fact that when even a small amount of blood accumulates in the tissues, suppuration can occur.
How does a breast hematoma manifest?
If the hematoma is about the size of a cherry, it is considered small. With plum - medium size. Large hematomas grow the size of a grapefruit or larger, but most often have an elongated shape and resemble a banana.
If the bleeding is under the skin, a bruise appears on the chest. With large hematomas, the mammary gland becomes enlarged, swelling occurs, and pain occurs. Sometimes there are no symptoms, but the accumulation of blood is detected during a mammogram.
Breast hematoma is often difficult to distinguish from fibrocystic mastopathy, since the symptoms are very similar, and on X-rays the accumulation of blood can easily be confused with cancer. Mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging help to establish the correct diagnosis. A breast surgeon may prescribe a biopsy.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Conservative and surgical methods of treating hematomas
Conservative treatment of a hematoma means providing first aid and eliminating the resulting accumulation of blood.
As first aid for visible hematomas, exposure to low temperatures is used. For this purpose, any container with cold contents is applied to the site of the hematoma. This could be ice from the refrigerator, a cold spoon (for a small hematoma - for example, in the eye area) or even a carton of milk from a refrigerated display case.
After a few days, in order for the hematoma to resolve faster (for example, if the patient asks how to remove a hematoma on the leg as soon as possible), physiotherapeutic methods can be used: UHF; Microwave and others.
Surgical treatment of hematomas is carried out if they are large in size, due to which there is pressure on surrounding tissues; or with symptoms of suppuration.
Opening and drainage of a subcutaneous hematoma can be carried out in a dressing room. The contents are evacuated, the resulting cavity is washed, and a sterile bandage is applied.
Hematomas that occur under the meninges and in the internal organs require emergency surgical intervention performed in hospital operating departments. During surgery, liquid or clotted blood is removed and drained. Blood is an excellent breeding ground for microorganisms. Therefore, after opening large hematomas, even if there were no signs of infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
What to do about swelling after blepharoplasty?
To ensure that excess fluid drains from the upper and lower eyelids as quickly as possible, follow these recommendations:
- sleep on your back on a high pillow - with your shoulders and head raised;
- exclude physical exercise and do not bend over for 2 weeks;
- avoid procedures accompanied by heat - baths and saunas, tanning, hot baths, heat from the stove and fireplace;
- do not swim in pools and ponds.
In addition to general ones, there are daily recommendations:
- On the 1st day after blepharoplasty there is zero physical activity. Apply dry cold to your eyelids, treat them with antiseptics, take antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
- On the 2-3rd day, you can take a shower and wash your hair, while your eyes should be protected from water. Avoid activities that dry out the cornea - don't watch TV, don't work on the computer, try to blink less often.
- On the 7-10th day, you can put on contact lenses, start reading and working with a PC without overloading your eyes.
- On days 11-14, you can start using hypoallergenic eye cosmetics.
- On the 15-60th day, you can begin to sleep in a comfortable position, resume normal physical activity and moderate thermal procedures.
In addition, follow your doctor's current instructions during your post-operative check-ups. For example, a specialist may prescribe antiseptic and antiallergic eye drops, antiseptic and absorbable ointments.
Treatment of hematoma on the head of a child
Due to excessive mobility, children often get injured. A large percentage of childhood injuries are head contusions, which are often accompanied by hematomas and the formation of “bumps.”
First aid involves applying a cold object to the site of the hematoma. This should be done in the first few hours. Important: given the imperfection of thermoregulation in children (high sensitivity to low temperatures), the use of cold in children should be dosed - about half an hour and at intervals.
We recommend visiting our clinic’s website https://www.dobrobut.com/, where you will learn in more detail about the causes and consequences of hematomas in children.
Related services: Departure of an emergency team Departure of a specialized pediatric emergency team
How is a hematoma in the chest treated?
Small accumulations of blood resolve on their own within 4–6 weeks, sometimes longer. A large hematoma needs to be drained. Most often, blood is removed using a puncture - through a needle. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It is less common to resort to surgical intervention. Usually surgery helps to finally get rid of the hematoma, but sometimes relapses occur.
Do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, do not wait for it to “go away on its own.” A visit to the doctor and examination will help to avoid complications of hematoma, exclude or timely diagnose other, more serious, breast diseases. Make an appointment with a doctor by phone: +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by the deputy chief physician for medical work of the international clinic Medica24, candidate of medical sciences Sergeev Petr Sergeevich.