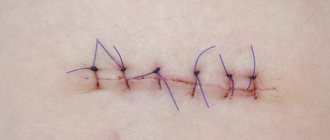
Any surgical intervention is a certain stress for the body. The task of the doctor who performs the operation is not only to do everything carefully and correctly, but also to prepare the patient for further recovery. A common method of joining biological tissues is suturing.
The materials used are different in type and structure; this feature is due to the specifics of the external or abdominal operation. These can be absorbable threads, which after some time disappear without a trace, metal staples or synthetic threads, which are impossible to get rid of without a doctor. Removal of suture staples is a popular service, which is performed in our clinic by an experienced surgeon.
Scar treatment and rehabilitation rules
How to treat seams after blepharoplasty is also an important question. The surgeon will give you an exact list of medications. First of all, these are ointments that promote tissue regeneration, helping to heal faster. Drugs that stimulate the resorption of bruises are also used. Eye drops must be prescribed - antibiotic or moisturizing, in some cases both types may be prescribed at the same time.
How to heal stitches after blepharoplasty, what else needs to be done?
In addition to proper care of the operated area, it is also important to follow a number of rules. In the first week, you should not rub, scratch, or touch the injured area (except for the treatment period). For the first three days, it is not advisable to allow water to get into your eyes. During the recovery period, you cannot visit the bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool, lift weights, bend over, or play sports. It is also necessary to protect your eyes from ultraviolet radiation.
Retinal ballooning
Ballooning is a surgical procedure used to repair uncomplicated retinal detachment. The indication for it is a localized defect without signs of layer rupture and bleeding into the vitreous body. The process uses a miniature device consisting of a balloon filled with liquid.
How the operation works:
- The patient is placed on the surgical table, anesthesia is administered, and after it has taken effect, a small incision is made on the membrane of the eye at the point where it contacts the conjunctiva.
- A miniature flexible catheter with a balloon is inserted into the incision. When its end reaches the detachment site, the doctor will release the balloon and place it over the defect.
- Once the balloon has stabilized, it is filled with liquid. Having increased in volume, it presses the retina to the underlying vascular layer.
- After fixation of the retina, the balloon is emptied and removed using a catheter. For additional strengthening, the doctor can use laser coagulation.
- A suture is placed on the incision.
The effectiveness of this operation is very high, but it is used less and less. The reason is a prolonged postoperative period and a high probability of hematoma formation inside the eye. Also, such an operation is characterized by a long-term complication - cataracts.
On what day are stitches removed after blepharoplasty?
If the surgeon used absorbable sutures, the healing process will be faster and you will not need to visit a doctor for removal. But this method is mainly used for internal incisions. The classical technique involves the use of traditional suture materials to reduce the risk of divergence of the incision edges.
In this case, the period after which the sutures are removed after blepharoplasty takes an average of 4-6 days. On the date appointed by the surgeon, you must come to the clinic and go through a very quick procedure for removing the suture material. Patients are also very interested in feedback on whether it hurts to remove stitches after blepharoplasty, which is understandable - surgical manipulation in such a sensitive place as the skin of the eyelids causes fear in some. But despite unjustified fears, removal is absolutely painless. The material is removed easily, without pain or discomfort for the patient, in just a few seconds. So there is no need to be afraid of the procedure.
Retinal filling
Retinal filling is a classic surgical procedure, the purpose of which is to reduce the space between the membranes of the eye.
It is used for retinal detachment, accompanied by the accumulation of exudate (fluid) underneath it. The filling is carried out using a silicone sponge, which is inserted into the eye cavity and placed above the detachment site. Depending on the location of the pathological focus, filling can be:
- radial
- with the sponge placed along a line running from the center of the retina to its edge. Used for detachment of a small fragment of the retina; - sectoral
- with the placement of the sponge on a wedge-shaped area, the narrow part of which is located in the center of the retina, and the wide part - along its edge. Used when detaching a sufficiently large fragment of tissue; - circular
- with a sponge placed over a large area of the retina, used for extensive detachment.
The filling helps prevent the inner membranes of the eye from tearing and creates the pressure needed to remove fluid from underneath the retina. Over time, this layer fuses with the underlying vascular fundus.
Operation stages:
- Preparation. The retina is examined to determine the exact size, shape and location of the detached fragment. A week before surgery, blood tests are done to identify possible contraindications. Based on the measurements taken, a silicone filling is made.
- Before the operation, the patient is placed on the surgical table and anesthesia is administered.
- The ophthalmologist makes an incision in the conjunctival membrane, installs a drainage system to maintain stable pressure in the eye and prevent air from entering its cavity.
- A sponge is implanted through the incision, placed in place of the detachment and fixed with sutures.
- Excess fluid is removed from the eye cavity, and if necessary, a small volume of a special gas mixture is injected so that the filling fits tightly to the retina.
- Sutures are placed on the membrane of the eye.
This operation prevents further development of pathology and completely preserves the vitreous body in complicated diseases of the organs of vision. Its disadvantage is the inability to 100% restore lost vision and the presence of unpleasant consequences: weakening of the muscles responsible for eye movements, increased intraocular pressure and cataracts.
Duration of rehabilitation
As mentioned earlier, recovery takes place in several stages. The first is characterized by a change in tissue color, swelling, and possible pain and itching. This period takes about a week. At this time, proper scar care is important, the rules of which we outlined above. By the end of the period, swelling and redness disappear, in rare cases they can linger for several weeks - this depends on individual factors and is extremely rare. During this same period, the suture material will need to be removed. When the sutures are removed after blepharoplasty, the doctor will tell you, this usually happens 3-6 days after the operation.
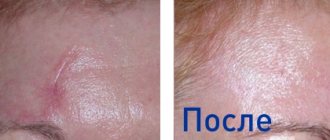
New tissues are formed over the course of a month. At this time, the scars appear reddish and noticeable, but gradually lighten and become less noticeable. Two months later, the final results are summed up. In rare cases, recovery takes longer, but this does not happen often.
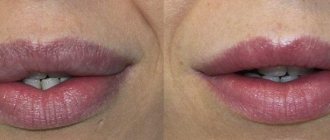
Blepharoplasty can be recommended for both women and men. In the photo: blepharoplasty of the upper and lower eyelids.
Types of retinal surgeries
In surgical ophthalmology, it is common to divide retinal operations into two types:
- Planned interventions
are procedures that are performed at a time convenient for the patient. They are used in situations where the pathological process is relatively stable, there is no risk of rapid progress and a sharp deterioration of the condition. Elective eye surgeries are performed for uncomplicated retinal detachment without signs of retinal rupture or degeneration. - Urgent interventions
are procedures that are carried out as quickly as possible after diagnosis. Such operations are indicated for complicated retinal diseases with a high risk of hemorrhage, rupture, infection, etc. They are scheduled for the next day or 2-3 days.
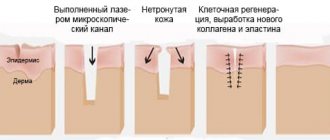
The official classification of procedures divides them into classical surgical or microsurgical interventions and minimally invasive procedures. Classic retinal surgery is performed through small incisions in the lining of the eye. They are used to strengthen and restore damaged areas of the retina. Minimally invasive surgeries are performed without compromising the integrity of the cornea and other eye structures. They are carried out using laser, wave and beam technologies.
Important! Many people mistakenly believe that safe vision restoration is only possible using modern technologies, including lasers. However, it is worth considering that some vision pathologies can be corrected exclusively with the help of classical surgery.
Both groups of interventions, carried out using modern equipment, show an effectiveness of over 95%. The only difference between them is the duration of the postoperative period. After a minimally invasive procedure, it lasts no longer than a month and requires almost no rehabilitation, and after a conventional operation it lasts up to six months with multiple restrictions.
When should you see a doctor?
Complications after such an operation are rare. But you should still pay attention to symptoms such as:
- long lasting pain in the incision area,
- the appearance of compactions,
- increase in scar area,
- suppuration,
- fluid leaking from the seam,
- prolonged increase in body temperature,
- nausea.
If the stitches itch or pull after blepharoplasty, what should you do?
This question is asked by patients who have undergone surgery. In the eye area there may indeed be a feeling of itching and a sensation of “stretching” tissue. This is completely normal and there is no need to panic. But scratching the surgical area is not allowed, even in case of very severe itching, so as not to damage the injured areas even more. Medications prescribed by your doctor can help reduce itching and discomfort. If the sensations are too intense and do not decrease after removal of the sutures, you should consult a surgeon.
Seam divergence
Quite rarely, but there are situations when the stitches come apart. This does not pose any threat to the implant itself, but it can lead to infection in the wound. This is why it is so important to make an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible, who will re-stitch the stitches and be sure to treat the tissue with an anti-germ solution.
In case of infection, the course of recovery is selected individually; it may include taking antibiotics and other medications. To avoid repeated violation of tissue integrity, you need to brush your teeth very carefully while the edges of the gums are healing and only with a soft brush. Your doctor will help you choose the optimal device.
The mucous surface is greatly irritated by smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. It is also recommended to temporarily avoid coffee and tea, as they increase blood flow to the surgical site. Chewing is allowed only on the opposite side and as slowly and carefully as possible.
previous post
Up to what age can dental implants be done?
next entry
How to speed up healing?
First of all, strictly follow all the instructions and recommendations of your surgeon. Following medical instructions is the main task of the patient, who strives to recover as quickly as possible. It is necessary to follow the prescribed dosages of medications and ointments and the regimen for caring for the injured area. Some drugs or their components can cause an allergic reaction, so you should not prescribe medications yourself. Only a surgeon can tell you what to coat the sutures after blepharoplasty.
It is also necessary to follow the prohibitions established by the surgeon. This is, first of all, protection from bending over and any actions that cause a rush of blood to the head, protection from ultraviolet rays, exclusion of sports and physical activity, visits to the bathhouse, sauna and swimming pool. Following the rules and prohibitions will help the tissues heal faster and make rehabilitation easier.
Retinal replacement surgery
Retinal implantation is a relatively new type of surgical intervention in ophthalmology. With its help, restoration of vision is possible even in cases of irreversible blindness caused by rupture, extensive degeneration and detachment of the retina, as well as loss of vision due to diseases of the optic nerve.
Thanks to the installation of an implant, it is possible to restore a person’s ability to see the contours of objects and distinguish between light sources and colors. Artificial materials are not capable of restoring 100% vision.
Currently, retinal implantation is in clinical trials and is therefore not available.
Surgeries to strengthen the retina
Prophylactic strengthening is a standard minimally invasive retinal surgery performed on patients who are predisposed to retinal detachment and at high risk of retinal rupture. It aims to reduce the likelihood of vision problems in the future. For uncomplicated pathologies, they are used as therapeutic procedures - for pinpoint “soldering” of tissue to the vascular layer.
Strengthening is performed in three ways:
- Cryopexy
- exposure to ultra-low temperatures on the retina.
- Laser coagulation
— point impact on the retina with a laser beam.
- Pneumoretinopexy
- procedure using gas.
The cryopexy method is used when there is a risk of retinal detachment or degeneration due to severe myopia. The procedure is performed with local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The disadvantage of this technique is that it is effective only for small and fresh defects.
Laser coagulation is a more universal method that is used for all types and forms of retinal detachment and rupture. Depending on the type of pathology, there are several types of procedures:
- barrier retinal restoration is used for central detachment;
- panterinal - a technique suitable for eliminating extensive detachment;
- peripheral - a preventive procedure, during which coagulation is carried out precisely in the “weakest” areas of the retina;
- focal restoration - used for small detachments and tears.
This is the most affordable, fastest and least traumatic way to restore the retina without incisions and penetration into the eyeball. The procedure is carried out contactlessly using a special laser unit.
Pneumoretinopexy is considered the most traumatic method of strengthening the retina. The operation is performed under general anesthesia using a syringe filled with gas. It is injected over the detachment site to put the retina back in place. After a few hours, laser coagulation is performed to consolidate the effect. A serious drawback of the method is the excessively long postoperative period after retinal surgery, which reaches six months.