Types of hyperpigmentation
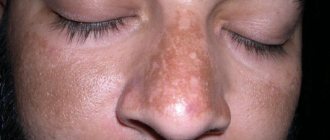
In everyday understanding, hyperpigmentation is a cluster of freckles. However, this is just one type of this skin defect. Depending on the causes, severity and nature of pigmentation, several more varieties can be distinguished.
- Melasma - brown symmetrical spots localized on the neck, shoulders, and sometimes the face
- Chloasma – dark brown spots of irregular shape, most often appearing on the face
- Secondary hyperpigmentation - dark or light brown spots that arise as a result of previous skin diseases: neurodermatitis, eczema, etc.
What is melanin
This is the main pigment that colors numerous tissues of the human body. Its production occurs in special cells - melanocytes. And if the pigment accumulates excessively or, conversely, there is not enough of it, then noticeable spots appear. In addition to melanin, there are also pigments: bilirubin, lipochromes, and other products of cell metabolism. The skin color of each person depends on the synthesis of melanin, and this process is controlled by tyrosine. From it, under the action of an enzyme associated with copper, a pigment is formed. Its synthesis begins with the formation of promelanin; during biochemical reactions and under the action of enzymes it is converted into its final form. The cells that produce pigment are mainly found in the epidermis, with the exception of the skin of the feet and palms. Moreover, the number of pigment cells in dark-skinned and light-skinned people is the same. Possible disorders can manifest themselves in the form of hypopigmentation (light areas appear on areas of the skin) and hyperpigmentation (dark spots appear on areas of the skin).
Causes of hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by the deposition of melanin pigment under the skin. Depending on its amount, the skin can take on different shades - from flesh to dark brown. This process plays a protective role for the body: melanin is able to absorb ultraviolet rays, protecting the skin from excessive solar activity. This is why pigmentation increases in the warm season. If the process of melanin synthesis is normal, then, as a rule, there are no special problems with the appearance of the skin. When certain functions of the body are disrupted, hyperpigmentation appears. It can intensify during periods of hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause), with metabolic disorders in the body, hormonal imbalance, as well as with some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Some medications, such as antibiotics, can also provoke hyperpigmentation. Heredity and skin type play a big role in this process: the lighter it is, the more susceptible it is to hyperpigmentation. Prolonged exposure to the sun without using protective creams can also cause excessive freckles.
Principles of treatment of hyperpigmentation
Basic principles of hyperpigmentation treatment:
- Normalize hormonal levels, cure systemic disease (if any).
- Reduce skin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, restore microflora and skin barrier function, enhance antioxidant protection.
- Reduce melanin synthesis in pigment cells.
- Block the transition of melanin from pigment cells to epidermal keratinocytes as much as possible.
- Stimulate and control constant skin renewal.
- Protect skin from ultraviolet radiation, pollution and other external influences.
A fairly well-known skin whitening ingredient is hydroquinone . Its mechanism of action is based on blocking the conversion of tyrosine into the melanin precursor - dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA). As a result, pigment synthesis is inhibited, and the skin gradually becomes lighter. To increase effectiveness, hydroquinone is combined with tretinoin, glycolic acid and corticosteroids. It should be remembered that hydroquinone has a number of side effects: destruction of melanocytes, ochronosis (skin coloring in a yellowish or bluish tint), carcinogenic effects, etc. For example, in the United States, the period of use of hydroquinone is legally limited, and only products containing no more than 2 % hydroquinone (products with a concentration of 2–4% are prescribed by a doctor).
Tranexamic acid acts in several directions at once - it directly blocks the formation of melanin in cells and eliminates pigment that is already present in the skin. When using it, melanocytes stop synthesizing melanin, and the skin gradually brightens until the color is completely evened out. Among the advantages of tranexamic acid, it is worth noting its non-toxicity and the fact that it does not irritate even very sensitive skin. In addition, it reduces the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, and, consequently, the risk of re-development of hyperpigmentation after treatment.
Papaya extract (Carica Papaya Extract) contains a large amount of vitamin C. It brightens the effect on the skin, accelerates its recovery after sunburn and tanning, helps narrow pores and increase tone.
Extract reduces the synthesis of melanin in pigment cells, reduces skin sensitivity to the sun and reduces the transfer of pigment from melanocytes to the upper layers of the skin.
Bearberry extract (Arctostaphylos Uva Ursi Extract) contains arbutin, which inhibits tyrosinase synthesis. Studies have shown that 0.01% bearberry extract in a cosmetic product inhibits enzyme activity by 34%, 0.1% extract - by 77%, and more than 0.3% bearberry extract completely blocks tyrosinase.
For some types of hyperpigmentation, azelaic acid can be used in treatment. It does not affect freckles, simple and senile lentigo, seborrheic warts and hyperpigmented nevi. However, it can be prescribed for melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, burns, mechanical and chemical damage to the skin.
You can fight hyperpigmentation with retinoids . It is believed that they suppress the activity of tyrosinase and are able to directly influence melanocytes through the receptor apparatus. Additionally, the power of salicylic peels and alpha hydroxy acids .
In table 1 shows the main points of action on hyperpigmentation and the ingredients used for this.
Table 1. Points of action for hyperpigmentation and ingredients used
| Impact points | Ingredients |
| Inhibition of tyrosinase activity | Hydroquinone, resorcinol, kojic acid, arbutin, deoxyarbutin, ascorbic acid |
| Chelation of tyrosinase with copper | Ellagic acid, kojic acid |
| Suppression of glycolysis of tyrosinase | Glucosamine, N-acetin-glucosamine, tunicamycin |
| Melanosome transfer | Niacinamide, protease inhibitors |
| Inhibition of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone binding to melanocytes | N-undecylenoyl-phenylalanine |
| Decreased tyrosinase activity | Retinoids |
| Antioxidant action | Vitamin C, vitamin E |
| Anti-inflammatory activity | Hydrocortisone, phytosterol, glycyrrhetinic acid, tranexamic acid, chamomile extract |
| Activation of cellular renewal | Retinoids, salicylic acid, alpha hydroxy acids, adenosine monophosphate |
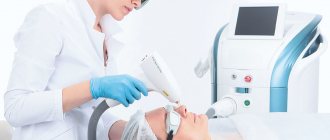
Most forms of hyperpigmentation can be successfully treated using hardware cosmetology . Two approaches are mainly used: fractional photothermolysis and selective photothermolysis using IPL and lasers.
Fractional photothermolysis allows you to destroy micro areas of pigmented skin, which leads to its lightening. At the same time, it is important not to use aggressive parameters of the procedure, so as not to provoke post-inflammatory pigmentation. The use of non-ablative fractional lasers is successfully combined with the application of active ingredients to the skin, some of which are listed in this article. In this case, the fractional laser acts as a transport system that increases the permeability of biologically active substances into the skin.
IPL therapy and lasers operating in the visible part of the spectrum are also successfully used to treat hyperpigmentation and are especially effective in cases where the pigment is superficial and located on light skin. The principle of operation of such devices is selective heating of melanin and destruction of the structures that contain it.
Questions from our users:
- hyperpigmentation after depilation
- hyperpigmentation around the eyes
- hyperpigmentation post-acne treatment
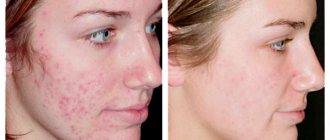
- hyperpigmentation photos before and after treatment
Methods to combat hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation does not pose a danger to human health, but it is a cosmetic defect that spoils the lives of many representatives of the fair sex and causes serious psychological discomfort. Home remedies (peelings, scrubs and other cosmetics) may not only not bring the desired result, but also aggravate the defect. There is no point in experimenting on your own - after all, today there are many effective professional means of combating skin hyperpigmentation. The following treatment methods are used at the Ego Estetic clinic.
- Phototherapy is one of the safest and most effective methods in the fight against hyperpigmentation. The skin is treated with special light waves with the exception of ultraviolet rays. Depending on the nature of pigmentation, the cosmetologist selects the optimal length and power of the light wave, which contributes to the destruction of melanin. As a result, the skin color is evened out. Skin whitening is possible immediately after the first procedure. With severe hyperpigmentation, several sessions may be required: on average from 4 to 6. After a year, the course of procedures can be repeated to consolidate the result. It is not recommended to carry out procedures in the summer.
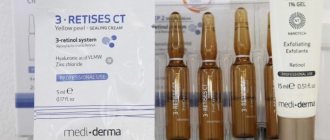
- Chemical peels. The effectiveness of chemical peels in the fight against hyperpigmentation is due to the body’s response to microdamage to the skin. Peeling activates regenerative processes in skin cells, as a result of which metabolic processes accelerate. This allows you to eliminate shallow skin pigmentation, and at the same time renew the upper layer of the epidermis, restore a healthy complexion, and enhance the effect of nourishing and moisturizing cosmetics. The Ego Aesthetic clinic uses glycolic and yellow peeling, as well as Kojicol Gel, to combat hyperpigmentation. This effective remedy for restoring the appearance of the skin has a beneficial effect not only on its color, but also on its overall tone.
- Mesotherapy with whitening cocktails. The method allows you to deliver active substances directly to the cells of the epidermis, affecting pigment spots from the inside. Performed by experienced cosmetologists using the finest needles, the injection procedure is effective, safe and painless.
In the fight against hyperpigmentation, a lasting effect can only be achieved with a comprehensive and professional approach to treatment. That’s why you shouldn’t try to cope with this problem on your own; contact our specialists.
Why do age spots form on the skin?
Pigment spots form when melanocyte cells in certain areas of the skin begin to produce too much of the natural pigment, melanin. It is responsible for coloring human skin, hair, and irises. The higher the concentration of melanin, the darker the color becomes. At a young age, the pigment is formed under the influence of bright sunlight. Thus, our body is protected from ultraviolet radiation.
But at a more mature age, hyperpigmentation may already appear, which is a consequence of the thinning of the basement membrane, which separates the epidermis (upper layer of skin) from the dermis (underlying layer of skin). As a result, the pigment embedded in the deep layers of the skin begins to appear on the surface, unevenly forming age spots.
Pigment spots also form under the influence of various hormonal changes. The skin is hormone-dependent, so sex hormones have a significant effect on the processes of epidermal cell division, the secretion of sebaceous glands, the function of hair follicles, and the synthesis of melanin. Fluctuations in their levels in women’s bodies (during the ovulatory cycle, pregnancy, menopause, taking oral contraceptives) affect all these processes. For example, 1/3 of women using oral contraceptives have melanosis, that is, the accumulation of melanin in the tissues of internal organs and skin. In addition, the mechanisms of melanin synthesis are also influenced by other hormones, for example, adrenocorticotropic, thyroid-stimulating, somatotropic hormones of the pituitary gland.
Thus, skin pigmentation occurs as a result of a cascade process triggered by ultraviolet radiation, in the development of which the nervous and hormonal systems take part.
There is another theory according to which the excess synthesis of melanin is affected by free radicals (oxidants), the excess and accumulation of which occur in conditions of a lack of antioxidants - chemical compounds that suppress oxidative processes. As a result, skin cells with damaged DNA structure appear and areas with increased pigmentation are formed.
The likelihood of age spots occurring is higher in people with fair skin and directly depends on the number of hours spent in bright sunlight: often age spots appear even in young people after a vacation in the south.
Read also
All articles Quality and skin problems
Forehead
- Forehead wrinkles
- Eyebrow wrinkles and folds
- Replenishment of the volume of the temporal region
Face
- Wrinkles around the eyes
- Hernias of the eyelids
- Drooping eyelid skin
- Dry eyelid skin
- Correction of the nasolacrimal trough
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Correction of the nasal bridge
- Enlargement and reshaping of cheekbones
- Age-related volume deficit on the face
- Nasolabial folds
- Rabbit wrinkles
Lips
- Lip augmentation and reshaping
- Correction of drooping corners of the lips
- Elimination of dry lips
- Purse-string wrinkles around the lips
- Marionette wrinkles
Manifestations and recognition of the causes/forms of melasma
The reasons for the appearance of pigmented formations may vary. Common provocateurs include medications, age, specific conditions (expectation of motherhood, menopause), new generation contraceptives, hormonal imbalance. The forms of hyperpigmentation themselves also differ. Private problems:
- melasma (symmetrical spots of different diameters);
- chloasma – large and small formations located on the face/arms/neck in a chaotic order;
- Freckles are the most well-known form of hyperpigmentation (ephelides);
- lentigo;
- secondary defects (darkening of the skin after skin diseases);
- photodermatosis and other types of hyperpigmentation.
As for symptoms, in 92% of cases they are limited to visual manifestations. This simplifies the recognition of the form of hyperpigmentation (melanosis, melasma), but often leads to delayed treatment. The latter is bad for 2 reasons.
- Some forms of age spots are able to accumulate UV radiation and increase in volume or move from the outer layer into the deep dermis.
- Being a signal of the need to treat hormonal/endocrine imbalance, hyperpigmentation indicates the need for prompt examination.
As a rule, the essence of diagnosing a skin defect comes down to the use of a Wood's lamp (allows you to determine the localization of spots in the epidermis/dermis) and a dermatoscope. The main job of a diagnostician is to find the cause of hyperpigmentation.
Therefore, as part of recognizing the type of hyperpigmentation, the dermatocosmetologist recommends visiting a gastroenterologist, urologist, gynecologist, immunologist, and endocrinologist. The provocateur of hyperpigmentation may lie in the gastrointestinal tract, hormonal program, or urogenital organs.
Brown spots on legs: treatment features
Initially, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination to the patient, one of the key points of which is ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels.
During the procedure, existing changes in the veins are detected, on the basis of which the doctor will be able to offer the patient a suitable treatment method or a combination of both. Brown spots on the ankle can be eliminated:
- endovasal laser coagulation of vessels is a modern effective method of treating varicose veins, which involves “welding” the vessels with the thermal effect of a laser beam;
- miniphlebectomy is an operation during which damaged vessels are removed through small soft tissue incisions.
If the patient additionally has spider veins, the phlebologist may recommend removing them using sclerotherapy. It involves injections of a special sclerosant drug, which helps glue the walls of the damaged vessel and stop their blood flow.
Subsequently, if brown spots on the legs persist, patients may be offered additional laser treatment of the problem area to eliminate pigmentation.
All procedures are performed under local anesthesia and take no more than an hour. The patient can leave the clinic the same day and return to work and other daily responsibilities the next day.