1.General information
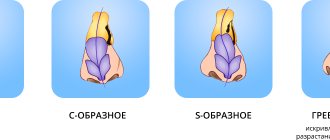
Despite all the randomness of mutations and natural selection, the results of evolution are always natural and appropriate in terms of adaptation. The nose of higher mammals, including humans, is divided into two parts by an osteocartilaginous septum. Due to this, the total area of the mucous membrane, which performs a number of important (primarily cleansing) functions in the act of breathing, increases, and also a kind of reserve of the nasal respiratory passages is formed: if the canal is obstructed or the outer wall of the nose is destroyed on one side, the second nostril will take over the entire load and to some extent compensates for the loss.
Therefore, the nasal septum should normally remain intact (“intact”, i.e. intact, undamaged), and ideally also straight. In fact, in most people, especially men and especially in old age, it is curved to one degree or another.
A lot of publications are devoted to curvatures of the nasal septum, respiratory disorders in this regard, the need or undesirability of correcting its shape for aesthetic reasons alone; this is the most popular topic regarding this anatomical formation.
However, specialists in the field of otorhinolaryngology and plastic surgery sometimes encounter a rarer and more specific problem: perforation, perforation of the nasal septum with the formation of a permanent connection between the right and left halves of the nose.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment of sinus perforation during tooth extraction
The tactics for managing a patient with perforation depends primarily on the condition of the sinus itself and the time of detection of this defect. This defect should only be treated by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of perforation of the main sinus of the upper jaw has the following objectives:
- Closing the defect.
- Prevent the process of inflammation in the sinus.
- Prescribe treatment if there is inflammation.
- If there are foreign particles, they must be removed.
If the perforation was immediately noticed and there are no signs of infection, then the treatment measures are as follows:
- Preservation of a blood clot in a tooth socket.
- Take measures to prevent its infection (application of a tampon with iodine solution).
- Apply stitches to the gums, if necessary.
- Treatment is carried out until the granulations grow and the defect is closed.
- The tampon is not removed from the hole.
- If the defect does not close on its own, it is covered with a plastic plate. It is fixed to the teeth.
- Prescribing a course of drug therapy aimed at counteracting inflammation.
If the perforation is complicated by gum rupture and penetration of foreign particles into the soft tissues surrounding the tooth socket, plastic closure of the defect is performed on the same day. Or after some time, when you are confident that the fabric will hold the seams. Before this, all foreign bodies are removed and areas that have undergone necrosis are excised. The manipulation is performed under x-ray control to make sure that there is no foreign body. If penetration of a foreign body into the cavity occurs, then it is necessary to perform surgery in a hospital setting.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removal of a tooth from the maxillary sinus (its fragments) and other foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas.
- Closing the defect.
2. Reasons
The causes of “depressurization” of the nasal septum are divided into several large groups. The most common and obvious is mechanical injury, but the peculiarity here is a fairly large percentage of iatrogenic injuries (literally “caused by a doctor”).
Perforation can become a side or forced consequence of medical manipulations and surgical interventions. The leaders among them, unfortunately, are the aforementioned septoplasty (surgical straightening of the septum to relieve difficulty breathing) and rhinoplasty (aesthetic and medical correction of the shape of the nose).
There is also a group of purely pathological factors, under the influence of which a perforated septal defect is formed:
- specific infections that corrode cartilage tissue (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.);
- atrophic process as a complication of inflammatory;
- purulent tissue melting in acute abscessing focal infections;
- systemic autoimmune and endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, connective tissue pathology, sarcoidosis);
- oncological process with germination into the septum and violation of its integrity;
- excessive, prolonged and uncontrolled use of nasal sprays and drops, especially hormone-containing ones;
- addiction to drugs inhaled through the nose;
- self-harm when trying to place an object in the nose or, conversely, remove a foreign body from the nose, real or imaginary (in children, as well as in persons in an inadequate mental state or in a state of intoxication).
Visit our Microsurgery page
Methods for determining perforation
This pathology can be identified only on the basis of a characteristic clinic. If there is any doubt, a full range of diagnostic procedures is performed, including instrumental methods.
To diagnose a bone plate defect and subsequently eliminate it, it is necessary to perform the following manipulations when examining the patient:
- Carefully examine the tooth socket after the tooth root has been removed.
- Perform sounding of its bottom.
- Ask the patient to pinch their nose and exhale through the nose. The air will escape into the mouth through the tooth socket.
- If the patient puffs out his cheeks, air passes into the nasal cavity. But this technique can provoke sinus inflammation and should not be used frequently.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- probing the dental and perforation canal using a thin probe;
- CT scan;
- radiography, in the pictures you can see the defect and foreign bodies;
- general blood analysis.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical picture of a perforated nasal septum depends on a number of factors (primarily size and location), and therefore varies widely in different cases. Thus, with a small communication in the posterior (deeper) part of the septum, subjective discomfort may be completely absent; in this case, the defect is discovered by chance, during an ENT examination for another reason or during a medical examination.
In more pronounced, clinically significant cases, the following manifestations are typical:
- nasal breathing with whistling, especially during inhalation (due to the fact that the inhaled air flow ceases to be laminar and becomes turbulent, vortex);
- feeling of a “stuffed” nose and difficulty breathing;
- certain painful sensations (not always);
- bleeding and purulent discharge from the nose (with infectious and inflammatory etiology);
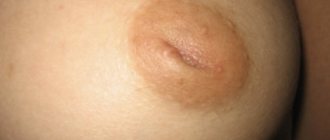
- deformation of the nose if the perforated defect reaches a significant size and grossly disrupts the normal distribution of mechanical stress in the anatomy of the nose.
Diagnosis of perforation itself is carried out directly during examination, while diagnosis of its causes in some etiologically subtle cases can take a lot of time and require a multidisciplinary thorough examination.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
How to treat a cracked nasal septum
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. When treating the disease, regular rinsing of the nasal cavity with special honey solutions is prescribed, which help eliminate dryness and crusts. This treatment is recommended only for small holes and cracks. For large perforations, operations are performed according to the following method:
- tardi, when a 5-centimeter hole in the nasal septum is closed with a piece of mucous membrane transplanted from the inside of the upper lip;
- Fairbanks and Friedman, used for holes with a diameter of 2 cm. In this case, both the patient’s own tissue and artificial graft material can be used;
- surgical suturing, which is used for microscopic holes in the septum.
Any method leads to the elimination of the hole and improvement of nasal breathing functions.
4.Treatment
In many cases, perforation of the nasal septum does not require any active treatment: it is enough for the patient to receive recommendations on maintaining a normal or gentle (regularly moistened from the outside) “microclimate” in the nasal cavity. In case of secondary perforation caused by another pathological process, it is virtually pointless to take any measures if the root cause is not eliminated (for example, the patient continues to take drugs, does not treat the underlying disease, continues to abuse “breathing” drops, violates the antibiotic regimen prescribed by the doctor , and so on.).
Finally, with a large defect and severe breathing difficulties, the question of reconstructive surgery is raised.
Despite the relatively simple access, the intervention itself is very problematic from both a technical and biological point of view, and until recently such operations have not always resulted in long-term success. The fact is, firstly, that the partition has a complex multilayer structure, which must be restored layer by layer. Secondly, the nasal mucosa is inelastic and has a number of specific properties due to its functions; transplantation or autotransplantation of a mucous flap from other areas usually does not solve the problem of dryness, crust formation, etc. Today, the method of choice is a flap of homogeneous nasal mucosal tissue or temporal fascia (connective tissue membrane).
What is perforation of the maxillary sinus?
The formation of a defect in the maxillary sinus is a complication during manipulations on the upper jaw. A hole is formed between the oral cavity and the main sinus. This can happen when removing the molars of the upper jaw (molars and premolars) or during prosthetics. And also for complex endodontic treatment of tooth roots and removal of cystic formations. The defect is formed at the site of the tooth socket.
How to recognize damage?
In cases of damage to the nasal septum, an accurate diagnosis can only be made by a qualified otolaryngologist after an individual examination.
However, there are a number of signs that signal the possible appearance of this defect:
- The formation of dry crusts that cause severe discomfort.
- Frequent nasal bleeding.
- Characteristic wheezing and whistling when inhaling and exhaling.
- Painful sensations in the nasal cavity, disruption of its patency.
- Frequent liquid discharge from the nose, sometimes with traces of pus and an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms of the disease are more pronounced if the perforation is located closer to the tip of the nose. If it is located further, then signs of the disease may be completely absent, and only a doctor can identify them.
Perforation of the nasal septum can cause chondritis, an inflammation of the cartilage. To restore the natural outflow of air, a special plug can be inserted into the patient or damaged tissue can be regenerated.
The main symptom of perforation is a characteristic whistling sound when breathing. Since the uncontrolled entry of air onto the nasal epithelium dries it out, crusts may form in the nasal cavity at the site of damage.
In some situations, a person may suffer from frequent and heavy nosebleeds. If the damage to the septum is too extensive, the patient may experience deformation of the shape of the nose (for example, it “sinks inward”).
Inconveniences caused by perforation of the nasal septum, consequences:
- Frequent occurrence of inflammation of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. They form because a hole in the septum prevents air from flowing normally through the upper respiratory tract.
- Loud snoring, which prevents others from sleeping peacefully.
- The appearance of apnea syndrome - stopping breathing due to too much ventilation of the upper respiratory tract.
- Oxygen starvation of brain tissue.
- Noticeable deformation of the nose, its curvature to the side, or “sagging” inward.
- Constant shortness of breath with any physical activity. The appearance of this symptom in such a situation is usually not associated with pathologies of the heart or lungs.
- A person often experiences pain and dizziness, and there is memory loss, which is caused by oxygen deprivation.
Interestingly, perforation can be asymptomatic.
Plastic surgeon Anil Shah
Advantages of treatment in our clinic
Summing up, we can understand that it is very easy to get a septal defect in the cavity of the upper jaw. This depends both on the actions of the dentist and on the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient.
When seeking treatment at our clinic in Moscow, you can be sure that you are guaranteed not to have such complications. We prevent complications.
To do this, we prescribe a mandatory set of preventive measures to prevent them:
- We conduct a complete examination of patients before performing any dental procedures.
- We perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s anatomical and topographical features.
- We follow all stages of dental procedures.
You will be satisfied with the quality of dental services if you contact us at the clinic. Our clinic has the most modern equipment at the level of the standards of the best European and American dental clinics. We can offer you a full range of all diagnostic procedures in one place. Our doctors have been trained in the world's leading dental centers and are proficient in the latest treatment and prosthetic techniques. We will help even in the most difficult cases. We develop an individual course of treatment taking into account all the characteristics of the patient. We use only proven treatment methods and materials of the highest quality. Our clinic has made the highest quality dental services available. You can view the full range of our treatment and diagnostic capabilities on our website.
Why does perforation of the nasal septum occur?
The defect may occur due to:
- mechanical damage to the nose;
- complications of rhinoplasty and septoplasty;
- diseases that destroy connective tissue - sarcoidosis, lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- infections affecting cartilage - syphilis, tuberculosis, staphylococcal infection;
- malignant tumors in the nose;
- constant use of vasoconstrictor sprays;
- chronic diseases of the nasal mucosa;
- exposure to narcotic or harmful working substances entering through the nose.
Consequences of perforation of the maxillary sinuses
If the presence of a defect is not noticed and the patient, despite the symptoms, does not consult a doctor, this threatens the onset of serious and dangerous consequences for health.
Possible consequences:
- Severe inflammatory reaction.
- Formation of osteomyelitis.
- Generalization of infection.
- Development of abscess and phlegmon.
- Loss of healthy teeth in the fistula area.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
To avoid the formation of complications, the patient should visit the dentist in case of any problems after tooth extraction.
Rehabilitation period
Elimination of perforation in the nasal septum is considered a rather complex operation, so the patient should spend a certain period of time in the hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Usually this period does not exceed 1 week. It is not recommended to engage in work activities for the next 2 weeks.
Restrictions that should be followed during the rehabilitation period:
- limitation in physical activity, sharp gradation of temperature;
- avoiding any injury, damage to the face and nose for at least 1 month after the intervention;
- do not use vasoconstrictor nasal drops and sprays;
- Impeccable adherence to a balanced diet;
- carefully monitor the level of humidity in the home and avoid drafts;
- try to avoid dusty rooms;
- give up nicotine and alcoholic beverages for at least 2 weeks after surgery;
- strict adherence to the doctor’s advice regarding the care and hygiene of the nasal cavity.
During the rehabilitation period, you should refrain from eating too hot or cold food or drinks. The best option is to consume food and liquid at room temperature.
In some cases, after surgery, the patient may experience bloody discharge from the nose. For the next few days, he will have to use isotonic nasal drops 3-4 times a day.
In addition, in order to avoid inflammatory processes, it is necessary to lubricate the nasal cavity with a cotton swab soaked in antibacterial ointment.
Sometimes an external nasal splint may be placed on the patient's nose, followed by an adhesive bandage.
On the 5th day after surgery, the sutures are usually removed (if non-absorbable suture material was used). If the site of injury is restored slowly, this period can be increased on the recommendation of a doctor.
Perforation of the nasal septum is a disease that necessarily requires intervention from qualified medical professionals.
Cartilage tissue is unable to tighten on its own, so there is a high risk of expanding its diameter and deforming the shape of the nose.
Treatment at home can only relieve painful symptoms for a while, but it is unable to bring complete healing and restoration of damaged tissue.
It is recommended to undergo a preventive examination of the nasal cavity at least once a year by an otolaryngologist in order to identify symptoms of the disease in the early stages.