Root causes of facial asymmetry
Facial asymmetry can have a pathological and physiological origin, and in prof.
In relation, it is of interest to neurologists, plastic surgery, maxillofacial surgery, anthropology, psychology, dentistry, forensic medicine, and cosmetology. What are the causes of facial asymmetry? What to do if there is strong asymmetry?
A certain number of people turn to plastic surgeons and cosmetologists about an asymmetrical face, or rather elements. But much more often, the disproportion is determined by a specialist when examining other defects or by a plastic surgeon who must perform a volumetric plastic surgery.
The symmetry and shape of all points mainly depends on the structure of the cartilage and bones of the skull (facial), as well as on the tone and volume of the masticatory and facial muscles that pass to the vessels and nerves, the degree of development, the thickness and volume of subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Of the large number of manifestations of the facial skull, which also includes osteochondral structures, the nose is considered the most important aesthetic and cosmetic formation. Its sizes and shapes not only determine this aesthetics, but are also considered to be the main ones in the formation of asymmetry. Of course, if you look very carefully, differences and unevenness in the contours of the eyebrows, the depth of the nasolabial folds, as well as in the different shapes of the corners of the mouth, the position of the wings of the nose, in different shapes and sizes of the ears, and so on can be expressed.
Correction of facial asymmetry is not considered necessary.
The absence of ideal asymmetry not only in the face, but also in other parts of the body and skeleton is mainly determined by personal morphological and anatomical features of development, both for various reasons that manifest themselves throughout the entire life course, and of a congenital nature.
Externally, a violation of facial asymmetry is almost invisible, and occurs in absolutely all people. Deviations in proportions that range from three to five degrees or from two to three millimeters are the physiological norm.
The approach to deciding whether facial asymmetry needs to be eliminated is greatly influenced by the diagnosis of the causes.
"Heavy chin"
The next type of bite – mesial – is one of the most recognizable; people sometimes call it a “heavy chin”. With this type of bite, the lower jaw protrudes forward relative to the upper jaw, which causes the chin as a whole to protrude just as strongly. Once in the foreground, the chin begins to visually appear much larger. In this position, the lower temporomandibular joint experiences increased tension, which also causes the neck muscles to tense. The facial expression often seems either offended or tense.
Neuroscience's relationship to asymmetry
If we talk about the disease from the neurological point of view, facial asymmetry is primarily revealed by a lack of symmetry in the cerebral hemispheres. Each of the large hemispheres carries out microregulation of sensations (that is, sensory), as well as motor skills of the corresponding halves of the body, in different ways. At the same moment, the acceptance by one person of the facial expressions of another also depends on the degree of reaction between the hemispheres of a particular person.
Neuroscience as a science considers the problem of facial asymmetry as a personal perception by the observer.
In other words, one person’s conclusion about asymmetry can be erroneous, while another person, due to the peculiarities of the interaction of the hemispheres, can come to the opposite conclusion.
That is why in neurology the following types of facial asymmetry are distinguished, which should also be accepted in plastic surgery and cosmetology when finalizing the issue of correcting facial asymmetry.
Morphological or static type
This type of asymmetry disorder is characterized by the presence of differences in the resting state by other elements in structure, proportions, shapes and sizes. The reasons for all these differences mainly lie in personal developmental properties, diseases of the facial and masticatory muscles, the consequences of the disease and traumatic injuries, and pathology of the bones of the facial skull.
Functional (dynamic) type
It mainly consists of asynchronous contractions of the facial muscles and those formed during facial expressions. For example, an asymmetry that was absent at rest or simply a slight disproportion at rest is formed or seriously intensified when the lips are stretched out with a tube or a smile. The dynamic form of facial asymmetry is associated with acquired or congenital pathology of the muscles of facial expression, residual effects of damage to the facial central nerve, or a peripheral one in the form of Bell's palsy. With all this, the severity of asymmetry depends on the degree of damage to the facial nerve.
Advice from the orthodontist at the clinic named after. Leonida Gorbunova
Our orthodontist's main advice is that you should not be afraid of changes in your facial features both while wearing braces and after they are removed. If there are any changes, they will be quite minor. Except in cases where the malocclusion was too pronounced, but in this case you will be pleasantly surprised by your new appearance (read the article Distal bite). Of course, we recommend sticking to your treatment plan and visiting your doctor as many times as he prescribed and exactly on the specified dates.
Posted by:
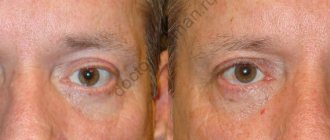
Correcting asymmetry
Therapy for this pathology is based on the causes, as well as establishing the degree and type of pathological condition and prescribing treatment for the corresponding pathology in combination with the use of neurotrophic methods.
Since the most common cause is neuropathy of the facial nerve, the main principles of treatment are:
In the use of appropriate neurological traditional drug therapy;- Use of stabilized hyaluronic acid fillers;
- Carrying out thread lifting, or surgical correction;
- Injections of botulinum toxin preparations on the affected or healthy side.
In addition, in almost all cases, special gymnastics exercises against facial asymmetry can be used, as well as electrical stimulation sessions, unless of course you have contraindications to its implementation.
Bolulotoxin injections
Various types of botulinum toxin preparations can be used for botulinum therapy:
- Dysport.
- Botox
- Lantox.
In case of paresis and paralysis, correction with these means is done on the healthy half of the face, because it is there that increased muscle tone is formed.
In the case of the presence of muscle contractures, synkinesis and hyperkinesis, injections are given to the dependent muscles. Often, such therapy can rehabilitate facial asymmetry without surgery within four to six months.
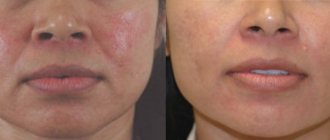
Dermal gels
At the next stage, soft tissue volumes are adjusted and contouring is performed using hyaluronic acid fillers.
All medications included in the comprehensive therapy can make it possible to achieve high aesthetic and functional results in patients with long-term and severe forms of paralysis of the facial muscles.
Preparations of stabilized hyaluronic acid can not only remove the disproportion of areas and rehabilitate the aesthetic condition, but also have an excellent effect by improving microcirculation and trophic processes in tissues.
Thread lifting and surgical treatment
In such cases, when facial asymmetry is characterized by serious severity in the amount of more than five centimeters, surgical correction is necessary, because conservative treatment methods will not help.
At the same time, in case of paresis, in the presence of certain concomitant diseases, local defects of the terminal sections or the 1st branch of the facial nerve, or the patient’s refusal of surgical intervention, correction is possible using minimally invasive thread lifting, that is, a tightening.
Basically, thread lifting is done in combination with botulinum therapy, and correction after surgery with stabilized hyaluronic acid fillers or during lipofilling surgery, that is, autologous fat.
The combination of all these methods can significantly improve the patient’s condition, significantly increase his quality of life and facilitate the so-called social adaptation.
Gymnastics for facial asymmetry
There are different exercises, here are the main ones:
Close your eyes very tightly, then quickly relax your eyelids;- Strongly stretch your lips folded forward and pronounce the letter I;
- Imitate the greatest inhalation, while pressing the wings of the nose with your fingers;
- Move your tongue in a circle in your mouth in front of your teeth;
- Slowly move the lower jaw to the left and right sides, while holding the position for two seconds;
- Smile alternately with the corners of your lips;
- Raise your eyebrows and at the same time your eyelids as high as possible;
- Frown your eyebrows very slowly and forcefully.
When performing gymnastics, we advise you to apply special loads to the problem part. The number of repetitions of each of the above exercises on the problematic side must be at least 20 times, and on the healthy side at least 10.
Small chin and downturned lips
Let's start with the types of abnormal bite caused by insufficient development of the lower jaw or excessive development of the upper jaw: distal and deep bites. Distal occlusion, also known as prognathic, is a type of abnormal occlusion characterized by the protrusion of the upper front teeth forward relative to the lower ones. With this type of bite, the chin is visually smaller, and the upper lip may protrude or protrude too far forward. In this case, the face often acquires a surprised or hesitant expression, even if its owner is angry at that moment or, on the contrary, happy. Such a bite also causes improper distribution of the load when chewing, which is why the back teeth wear down faster than the front teeth. This can lead to the fact that the bite also begins to “deepen”, which, in turn, can lead to drooping of the corners of the lips.