Any surgical intervention ends with suturing. And plastic surgery is no exception. After breast lift surgery, the surgeon must put sutures at the incision sites, and the appearance of postoperative scars largely depends on how professionally this is done.
But the surgeon’s professionalism alone is not enough. Aesthetics are also greatly influenced by how responsibly the patient approached caring for the operated area during the rehabilitation period. If all the surgeon’s recommendations were carefully followed and implemented, and established prohibitions were not violated, then the scars will be completely invisible. If the rules of care were actively violated, then achieving impressive aesthetics will be very difficult, and breast lift stitches, or rather, the marks from them will leave quite noticeable.
What types of seams are there?
Currently, the following types are used in plastic surgery:
- surgical,
- cosmetic,
- adhesive,
- staples.
Surgical - classic tightening sutures. They are not used too often, mainly when it is necessary to tighten a large incision if other types of sutures cannot cope with such a volume. As opposed to surgical, cosmetic are the most common subtype. Can be used as both intermediate and final fixation. To apply cosmetic sutures, threads are taken from lavsan, catgut or vicryl; monocryl and pds materials are also used. A special feature of such threads is their ability to self-absorb after a certain period. Thus, cosmetic sutures are sutures that do not require removal (with the exception of intradermal cosmetic sutures made with prolene, which require removal).
Due to a number of specific nuances, invisible (made with the help of special bio-glue) and staples are not so common and are used in plastic quite rarely.
How to enlarge breasts without scars?
Is it possible to enlarge the breasts without “consequences” in the form of scars? Yes, at the present stage of development, aesthetic medicine offers women an effective and safe method of breast enlargement without consequences in the form of postoperative scars. We are talking about lipofilling, or bust enlargement through transplantation of the patient's own fat cells.
Briefly about the autolipotransplantation method. Adipose tissue cells are used as transplant material, the source of which is areas of the patient’s body with good development of subcutaneous tissue. Most often, the graft is obtained from the subcutaneous tissue of the buttocks, thighs or abdomen.
Fat cells are removed very carefully using water-jet liposuction. The peculiarity of the technique is that the tissues of the donor area are minimally injured, and the plastic surgeon receives intact and viable adipocytes. In the laboratory they are cleaned of impurities and dead cells; The transplant material is enriched with growth factors to improve survival rate, after which it is injected into the parenchyma of the mammary glands using atraumatic needles.
The beauty of the technique is that the operation is performed without incisions on the skin. The integrity of the skin is not compromised, stitches are not needed, which means that there can be no scars after mammoplasty using lipofilling. Other advantages include the absence of a difficult rehabilitation period, rapid healing, the possibility of repeated correction, and the absence of the risk of aesthetic and medical complications after surgery. After lipofilling, there cannot be capsular contracture, which is one of the possible complications of plastic surgery with implants.
Where are they located?
- Mastopexy, or lift, is performed using one of the following techniques:
- periareolar,
- vertical,
- B-shaped (Spare technique),
- T-shaped.
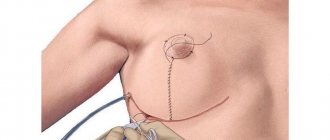
With the periareolar technique, a circular incision is made around the nipple areola, after which excess skin tissue is removed and the gland is attached to the muscle. The most common method that works well in working with first degree ptosis, pseudoptosis or small bust size.
To eliminate second-degree ptosis, a vertical mastopexy is performed with a circular incision along the edge of the areola and a vertical incision to the fold under the breast. Finally, with significant ptosis, a T-shaped (anchor) mastopexy is indicated with a circular incision along the edge of the areola, a vertical incision to the fold, and also a horizontal incision directly in the breast fold itself.
Periareolar, vertical and anchor technique: incisions.
There is also a mammoplasty technique, when breast lift is combined with breast augmentation with implants.
How is recovery after mammoplasty going by day?
First day: in the hospital .
The woman remains in the hospital on the first day after the operation, so that if complications develop after anesthesia, doctors can promptly provide her with the necessary assistance. If there are no complications, the patient is discharged home on the second day. Before discharge, the woman receives detailed individual recommendations from the surgeon regarding recovery after mammoplasty and prescriptions for medications that will relieve pain, help reduce discomfort and swelling, protect against infection and speed up recovery.
The first days and weeks after surgery. From the first day after breast augmentation, pain occurs. The degree of their severity depends on the specifics of the surgical intervention (depth of implant installation, its volume, surgical access) and the individual characteristics of the body, in particular, the pain threshold. As a rule, a woman assesses the intensity of pain as moderate or severe. To reduce pain, the plastic surgeon prescribes analgesics.
Swelling develops from the first day and intensifies during the first week. Along with swelling, bruises and hematomas appear. The increase in edema is explained by the development of the body's response to damage. The purpose of protective reactions is to isolate the damaged area, erect a powerful barrier to pathogenic microorganisms and create optimal conditions for regenerative processes.
Hematomas, swelling and bruises are the body’s natural reaction to damage. Breast enlargement is accompanied by a significant violation of tissue integrity, and therefore even severe swelling should not frighten or alarm. Breast aesthetics in the first days after mammoplasty are far from ideal, and this should be taken calmly.
The first weeks after surgery . From the second week the severity of swelling decreases. The pain gradually disappears. At first they become tolerable without analgesics, and completely disappear by the end of the second week. At the same time, hematomas and bruises disappear, so that by the end of the second or third week, normal breast contours are already formed, although scars at the site of surgical access are still noticeable.
The first months. The rehabilitation period after mammoplasty lasts several months. By the end of the first month, discomfort, pain, swelling and discomfort practically do not bother you. Only minor residual effects are possible, the severity of which depends on the degree of breast enlargement. When increasing by 1-1.5 sizes, positive dynamics increase faster, and when increasing by 2-3 sizes, recovery takes longer.
From the second month, the only consequence of surgical intervention is a postoperative scar. With the submammary approach, it passes under a fold of skin and is visible in the supine position. With the periareolar approach, the scar runs along the edge of the pigmented area of the areola, making it practically invisible. The axillary approach is considered optimal in terms of scar severity: the scar is hidden in the armpit and is almost impossible to notice.
How long do stitches take to heal?
The time it takes for sutures to heal after a breast lift will vary for each patient due to a number of factors that affect the speed of recovery. First of all, this is the general condition of the body - health, the presence of any diseases, the individual ability of tissues to regenerate, and the like.
If you are predisposed to allergies, sometimes swelling and redness of the tissue may occur in the area where the stitches are placed. This is not a complication, but a normal reaction of the body, which does not occur in all patients. In this case, healing will take a little longer, but such a reaction does not entail any serious consequences.
Finally, the speed of healing is also influenced by how the recovery period went and how responsible the patient was in caring for her bust after surgery. Taking medications prescribed by a doctor according to the schedule, giving up a number of things and habits, and following the recommendations given by the operating surgeon contributes to a faster recovery.
Symptoms of inflammation
The signs of inflammation are well known and when this complication occurs, very often even a non-specialist will be able to make a diagnosis. Symptoms of suppuration are usually divided into local signs and general ones.
Local symptoms include:
- redness of the skin at the site of inflammation
- increased temperature at the site of inflammation
- the appearance of pain, which intensifies as suppuration develops
- the presence of swelling or edema at the site of inflammation
- dysfunction in the place where suppuration develops
Such signs of inflammation are characteristic of any suppuration.
If the suppuration is small, then only local signs are noted, and general ones may not be observed. Common features include:
- increase in general body temperature
- weakness, fatigue
These are symptoms of general intoxication, which indicate that the process of inflammation is not limited to any particular area, but affects the entire body. This is always an alarming sign, as there is a possibility of inflammation spreading to neighboring areas with a health risk.
How to diagnose suppuration?
The diagnosis is based on symptoms and data from laboratory and instrumental studies. We have already talked about the symptoms. In 90% of cases, the diagnosis is made easily even with a superficial examination. In cases where diagnosing suppuration causes difficulties, they resort to ultrasound diagnostics and blood tests.
During ultrasound, when there is suppuration, an accumulation of fluid around the implant is usually visible. Most often, the volume of liquid ranges from 10 to 30 ml. You can also evaluate how thick the liquid is, whether there are any denser inclusions, etc. These signs may indirectly indicate suppuration.
In a general blood test, the number of leukocytes and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increase. These are also laboratory signs of inflammation.
Prevention of suppuration
The main preventive measure is strict adherence to aseptic standards. Simply put, all the instruments, dressings, surgeon’s hands, etc. must be sterile during surgery. This is the primary norm in all clinics. It is strictly observed. Several control measures are used to control sterility, so the use of non-sterile instruments and materials is practically impossible.
Very often we hear about the prescription of antibiotics after surgery to prevent suppuration. During operations such as breast reduction or breast lift, this is partly justified, since during these operations, conditionally pathogenic flora can enter the wound from the milk ducts. For clean operations, this measure is redundant, since the likelihood of infection is negligible.
Rehabilitation period
After the breast lift, compression garments are applied to the breasts and must be worn for three months. Underwear needs to be worn around the clock, so make sure you have a removable pair. Also, at first you will need to sleep only on your back, in a slightly elevated position. Sleeping in the stomach position is prohibited.
In the first 10 days you should not shower. Do not rub your breasts. For two to three months you will have to forget about going to the bathhouse, sauna, solarium, pool or beach, and also give up sports and physical activity. Loads on the shoulder girdle should especially be avoided, so lifting heavy objects is strictly prohibited.
Finally, it is not recommended to make drastic changes in body weight after surgery, as this will affect the appearance of the breasts and negatively affect the outcome of the surgery. Following all the rules and observing the prohibitions will help shorten the rehabilitation period and achieve the best possible aesthetics of both the breast itself and postoperative scars.
Does a lift affect breastfeeding?
One of the common questions that patients ask is: “Will the surgery interfere with breastfeeding the baby?”
Modern techniques used during periareolar mastopexy do not violate the integrity and functionality of the milk ducts, therefore, the ability to breastfeed is not lost. An experienced surgeon will move the nipple-areolar complex without damaging the milk ducts. Sutures after a breast lift, or more precisely, scars left after the operation, also do not affect the feeding of the child. But after vertical and especially after T-shaped mastopexy, breastfeeding is completely excluded, since the risk of mastitis increases significantly. It should also be taken into account that pregnancy and breastfeeding in the near future will affect the condition of the breasts - shape, size, position, etc. This may affect the aesthetics obtained from the surgery. It is highly undesirable to become pregnant within a year after correction. If you plan to have a child in the near future, then it is better to give birth first and only then make a correction. You can seek the help of a surgeon 5-6 months after the end of the lactation period.
Causes of suppuration
The main reason for suppuration is infection from the environment entering the surgical wound through damaged skin, since any operation is accompanied by a skin incision. However, not only the environment, but also foci of chronic infection in the body can become a source of infection.
Currently, there is a conditional division of sources of infections:
1. Exogenous infections. These are infections that come from the environment. The main source in this case is dressing material, the hands of medical staff, and instruments. All materials and instruments that touch the wound must be thoroughly sterilized.
Air is one of the main sources of wound infection. In modern operating rooms, air is supplied sterile under positive pressure. However, air is never completely sterile; a small amount of bacteria is always present in it.
Also, one of the sources of infection can be the milk ducts. This is especially important if lactation has recently ended. Very often there is discharge in the milk ducts. It always contains bacteria. During surgery, especially when accessed through the areola, the risk of infection from the milk ducts is very high.
2. Endogenous infections. These are infections that are present in the body as chronic sources of inflammation. These include chronic tonsillitis, chronic sinusitis, adnexitis and others.
Infection from chronic foci of infection occurs through the bloodstream (hematogenous route) or through the lymph flow (lymphogenous route of spread). At the same time, for the development of inflammation, in addition to the infection itself, a decrease in general immunity is also necessary.