HIV-infected patients face various problems, among which lipodystrophic syndrome (LS), or lipodystrophy, stands out in particular. It is this that can cause a change in a person’s appearance, in severe cases – beyond recognition. Why does this happen and are there ways to solve this problem?
What is lipodystrophy in HIV infection?
Lipodystrophic syndrome is characterized by the redistribution of fat in the human body. The term “lipodystrophy” was first used by Carr et al. in 1998. The incidence of this disorder does not have clear data and varies from 6 to 80% (https://aids.belmapo.by/downloads/method_manual&guidelines/dl/Galen_04_GALEN_08_Ru.pdf (p. 30). There are several reasons for this. Firstly, no a clear definition of lipodystrophy; secondly, there are quite a lot of little-studied factors in this area.
The occurrence of lipodystrophy is observed in both adults and children. It should be noted that this syndrome is relatively rare in young children and more often in adolescents.
The most common types of lipodystrophy are:
· reduction in fat
(lipoatrophy) on the face, legs, arms, buttocks, due to which the veins in the extremities begin to appear strongly and the cheeks look sunken;
· increase in fat
(lipohypertrophy) on the trunk. Fat can accumulate on the back and neck, forming the so-called “bull hump,” or in the abdominal area, resulting from the development of visceral obesity. Some patients note the appearance of lipomas - round, mobile formations under the skin.
Often, a loss of fat layer in some places and an increase in others occurs simultaneously. This condition is referred to as “fat redistribution syndrome.” The development of lipodystrophy can be manifested not only by visible changes. In recent years, studies have been conducted that reveal indirect evidence of the connection of this condition with such manifestations as dry skin, osteoporosis, osteopenia, ingrown nails, etc. Metabolic changes, in particular dyslipidemia, in patients with lipodystrophy are also being studied.
From 2000 to 2005 in the USA, the University of California (San Francisco) conducted the FRAM (Fat Redistribution and Metabolic Change in HIV infection) study, which consisted of two stages conducted with an interval of 5 years. At each stage, subcutaneous fat fold (SFA) thickness was measured in HIV-infected patients and MRI was performed.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a method for studying internal tissues based on the use of nuclear magnetic resonance.
At the first stage, the percentage of patients with lipoatrophy was 48%, and at the second stage it increased to 53%. Consequently, lipoatrophy does not occur immediately, but develops in some cases over a long time.
Reasons for the development of lipodystrophy
In HIV-infected patients, factors that cause lipodystrophy include long-term use of certain antiretroviral drugs. Most often, lipodystrophic syndrome occurs while taking protease inhibitors (PIs) and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). A number of drugs from the above groups supposedly damage mitochondria - the “energy factories” of cells, including fat cells, which causes atrophy of the fat layer to develop.
There is an opinion that the human immunodeficiency virus itself may be a factor damaging the mitochondria of fat cells. The presence of a genetic predisposition to the development of lipodystrophy is also being studied. However, as mentioned above, all the reasons for the development of lipodystrophy are unknown, and assumptions have not been proven and research is still ongoing. (https://aids.belmapo.by/downloads/method_manual&guidelines/dl/Galen_04_GALEN_08_Ru.pdf)
Severe lipoatrophy is most often observed in cases where ART is started when the
CD4+ lymphocyte count is 200 cells/μl or lower and is accompanied by rapid restoration of immunity.
Diagnosis of HIV-associated lipodystrophy
Because lipodystrophy develops gradually over a long period of time (about three years), a person living with HIV infection may not immediately notice the changes. To diagnose lipodystrophy, anthropometric studies and comparative data from biochemical blood tests are used. Insulin resistance is also determined if necessary.
Treatment tactics for lipodystrophy syndrome are determined after determining its type.
Treatment of lipoatrophy in HIV-infected patients
1. Changing the ART regimen if it contains drugs that promote the development of lipodystrophy.
2. Plastic surgery.
In the United States today, various methods are used to replenish the missing subcutaneous fat layer on the face and buttocks. In particular, fat substitutes are often used to restore the necessary forms.
3.
Drugs that restore the subcutaneous fat layer.
Their action is aimed at restoring the function of fat cells.
Treatment of lipohypertrophy in HIV-infected patients
1. Drugs that reduce subcutaneous fat.
In order to reduce visceral obesity, they began to use hormonal drugs approved for the treatment of patients with HIV infection.
2.
Changing the ART regimen if it contains drugs that promote the development of lipodystrophy.
3. Diet and exercise
. A balanced diet with limited animal fats combined with physical activity is necessary.
4. Plastic surgery.
Methods are being developed to help remove excess fat, in particular visceral fat. Currently, only liposuction is used, which has a number of undesirable effects, including the “return” of fat after three to six months
The positive effect of ART on the duration and quality of life of patients with HIV infection is so great that the development of lipodystrophy while taking ART cannot be a reason for its discontinuation.
Treatment of liver lipodystrophy
Diagnostic and treatment methods
This condition, as well as an unexpected rapid increase in subcutaneous fat in the abdominal area, indicates a defect in lipid metabolism. Liver cells begin to break down fats incorrectly. Scars appear in the liver tissue, which cannot cope with its usual work.
Undigested fats cause infiltration of the liver, as a result of which there is an increase in the concentration of ketone bodies, an increase in glucose levels in the blood, acetone appears in the urine, an imbalance in the acid-base balance occurs, and ultimately a life-threatening condition occurs due to the disruption of all metabolic processes in the body.
The cause of lipodystrophy is unknown. Presumably, nutritional disorders, toxic effects on the liver, diabetes mellitus, the use of certain drugs (for example, steroids), and infectious liver diseases are to blame for the occurrence of subcutaneous fat deficiency.
One of the most unpleasant consequences of lipid metabolism failure is the body’s incorrect reaction to injected insulin. The affected areas cause a lot of problems - they become ulcerated, necrotic, and even gangrene in the absence of proper therapy. Therefore, it is better to prevent such conditions and not start them.
Gynoid lipodystrophy, or cellulite, is more common in women. The fat layer must be supported by fibers that weaken with age with increasing estrogen deficiency.
Foci of lipodystrophy may appear after injections of insulin or other drugs - especially with constant use of the drugs. The disease can occur immediately after the first injections, or it can lie dormant for years and result in both generalized lipodystrophy and focal lipodystrophy, near the sites of systematic drug administration.
Developing insulin resistance is also characterized by a gain of excess fat around the waist. A large number of patients come to the Rambam clinic with such problems, and everyone receives modern treatment.
Lipodystrophy, which does not seem to directly threaten a person’s life, can be the cause of other diseases - obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular problems, diseases of the joints and spine due to weight gain, growth of fat deposits in the neck, which causes a complex of problems from poor blood supply to the blood vessels of the head to difficulty breathing and sleeping, which seriously reduces a person’s quality of life.
The Rambam clinic uses inductometry and modern ultrasound methods to correct lipodystrophy.
The situation is improved by the use of high-quality purified insulin by diabetics. In case of alcoholic liver damage, treatment of the cause of the disease is first prescribed, and only then the unpleasant consequences in the form of lipodystrophy are corrected.
The course of treatment includes drugs that improve metabolism in liver cells, metabolic drugs of the latest generation, vitamins, powerful hepatoprotectors, and, if necessary, antispasmodics and hormones. Liver restoration requires long-term treatment under the supervision of clinical specialists and requires high consciousness and willpower from the patient, and sometimes a complete revision of lifestyle.
Lipoatrophic forms can be successfully treated with electrophoresis, paraffin baths, massage in combination with inductothermy and ultrasound, which produces vibrations in the tissues at a shallow depth. This intensifies blood circulation in the subcutaneous fat layer. If necessary, the clinic’s surgeons can perform cosmetic surgeries to reduce fat deposits, improve the condition of veins and blood vessels, and increase blood microcirculation in the skin and subcutaneous fat.
If you decide to undergo treatment for liver lipodystrophy and metabolic disorders in Israel, please contact the international department of the Rambam Clinic. The department’s specialists will help you save time and effort in organizing your trip and, if necessary, provide an interpreter and an accompanying person.
Intestinal lipodystrophy
Signs
The main symptom of intestinal lipodystrophy is diarrhea, which occurs 5-15 times a day.
The stool is copious, light, and foamy. This disease is also characterized by colic in the abdomen, bloating, swelling of the legs, and pain in the joints. Lymph nodes are enlarged but painless. Possible low-grade fever. The body of a person suffering from Whipple's disease is exhausted, the patient is weakened, his skin is dry and hyperpigmented. The disease is often accompanied by headache, blurred vision and hearing, and seizures. The skin peels off and becomes covered with brown spots. Possible with intestinal lipodystrophy are heart lesions, such as myocarditis, endocarditis and pericarditis, and respiratory diseases, such as pleurisy.
Description
Intestinal lipodystrophy begins unnoticed. At first, the patient is bothered by mild joint pain or diarrhea. But then the disease begins to progress rapidly, the absorption of substances in the small intestine is impaired, and the sufferer develops malabsorption syndrome. Proteins, fats, vitamins and some carbohydrates that are not digested are excreted from the body in feces. The patient loses weight, becomes weaker, and develops hypovitaminosis, especially deficiency of B vitamins, protein deficiency and water-electrolyte imbalance.
It is believed that the gram-positive bacillus Tropheryma Whippelli is to blame. It multiplies and accumulates in macrophages. Despite the fact that macrophages normally absorb and digest bacteria and foreign particles, they cannot destroy Tropheryma Whippelli.
However, some experts believe that immune disorders play a big role in the development of this disease. There is no consensus yet on what exactly is the cause of this disease, but they are inclined to believe that the disease is of an infectious nature. However, it is known that digestive disorders occur at the level of the intestinal villi.
With this disease, the composition of the natural microflora is disrupted, so after treatment it must be restored.
Diagnostics
To diagnose intestinal lipodystrophy, an aspiration biopsy of the small intestinal mucosa is performed. Microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen reveals specific macrophages with foamy cytoplasm. Sometimes dead bacilli can be found in macrophages. They also do an X-ray of the abdominal organs, blood and stool tests.
This disease is differentiated from enterocolitis, chronic enteritis, chronic pancreatitis.
Treatment
Previously, intestinal lipodystrophy was considered a fatal disease. Patients did not survive even two years without treatment. And now she is perfectly treated with antibiotics, glucocorticosteroid hormones and pancreatic enzymes. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. True, for a complete cure you need to take antibiotics for a long time. Antidiarrheals are also prescribed.
A proper diet is very important for successful treatment. The diet should be high in proteins, vitamins and low in fat. However, you can’t do without fats completely, because some vitamins (A, K and E) are fat-soluble, and their deficiency has a bad effect on the human body. In addition, it is necessary to consume foods rich in iron, as well as electrolytes if they are not supplied enough from food. The main electrolytes of the human body are sodium chloride (table salt), potassium, magnesium.
Self-medication for Whipple's disease is not recommended.
With proper treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable, however, neurological complications are possible.
Prevention
Prevention of Whipple's disease has not been developed.
© Dr. Peter
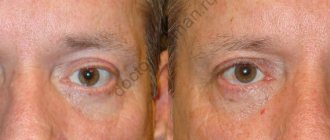
Facial lipoatrophy: 4 ways to correct the situation
Most often, we strive to get rid of excess fat, put a lot of effort into this and enjoy the results. But the opposite situation also happens, when the absence of deposits does not improve at all, but rather spoils the appearance.
Facial lipoatrophy (synonym – lipodystrophy) is a pathological disorder of metabolic processes, as a result of which volume is lost in the cheeks and/or chin area. The reasons can be both serious illnesses and a banal mistake by a cosmetologist, but the result in both cases is extremely unpleasant: the appearance suffers. Is this condition reversible? What procedures will help restore a healthy appearance? TecRussia.ru analyzes the available information and searches for the optimal solution:
↑ What lipoatrophy looks like and what are its causes
Degradation of adipose tissue can occur either rapidly or gradually over a long period of time - it depends on the factors that caused the pathology. Externally, it appears as pits on previously smooth areas of the skin. Unlike the natural consequences of aging, they appear in the most unexpected places, can be either single or multiple, of different depths, and located asymmetrically. In the most difficult cases, the fat layer “goes away” almost completely, as a result the face looks extremely emaciated, and the bones of the skull clearly appear through the skin.
Depending on the causes, there are several types of lipid tissue atrophy:
- Congenital progressive (Barraquer-Simons disease), in which fat gradually disappears from the face, neck and chest area. At the same time, the volume of the lower part, on the contrary, increases. All this is accompanied by polyuria, glycosuria, acrocyanosis and other unpleasant effects. The disease is extremely rare, in the vast majority of cases it is detected in female patients, even in childhood. A special role in its occurrence is given to pathologies of the endocrine system (failure of the pituitary gland, thyrotoxicosis), and hereditary predisposition. Among the provoking factors, doctors name severe craniocerebral injuries and generalized infections.
- Insulin - occurs as a result of the administration of a poorly purified hormonal agent or as a consequence of an atypical reaction of the immune system to it. It usually develops locally in the injection area, but sometimes the symptoms spread to a wider area, incl. on the face.
- The result of the influence of Longidase, Lidase, other drugs based on hyaluronidase, as well as glucocorticosteroids (Diprospan, etc.) - all these products are used in cosmetology for the treatment of scars. If used unjustifiably or if the dosage is exceeded, they cause atrophic changes in the injection area.
- Lipoatrophy in patients with HIV infection. It occurs due to the use of antiretroviral drugs such as Retrovir and Zerit. One of the side effects of drugs in this group is the redistribution of lipid deposits on the face and body (for example, sunken cheeks can be combined with a pronounced excess of fat in the neck).
- The result of serious diseases - cancer, autoimmune, chronic digestive disorders, etc., as well as measures to treat them, such as chemotherapy. Atrophy in these cases may be reversible, but this is not always the case: deformities often remain even after complete recovery.
↑ How to restore appearance?
The main thing that worries patients who are faced with a lack of adipose tissue on the face is how to eliminate the cosmetic defect. Of course, the first step is to understand the reasons that caused the unpleasant changes - and this can be difficult. Insulin-dependent people need to use well-purified drugs, perform injections correctly, and properly treat injection sites. For HIV-infected people, therapy consists of replacing problematic medications with analogues - but, unfortunately, this does not always give the desired effect. There is no specific treatment for Barraquer-Simons disease. It is also impossible to restore tissue destroyed as a result of injections of anti-scarring drugs.
However, to one degree or another, the situation can be corrected using methods of aesthetic cosmetology and surgery even in cases where the problematic factors have not been eliminated, but the duration and stability of the effect will be noticeably less. Next, we will analyze each of the ways to restore lost facial volume:
↑ Lipofilling
This surgical procedure involves moving the patient’s own tissues - fat is taken from certain areas of the body (most often from the inner thigh or abdomen), after which it is cleaned and pumped into problem atrophic areas. Main advantages:
- low morbidity with a short recovery period;
- the transplanted cells are related to the body, so they are not rejected;
- outwardly, the face looks as natural as possible, without swelling and without any traces of intervention;
- see also the article “Facial lipofilling”.
The disadvantages are that for a good result a series of several procedures is required, each of which is quite expensive. In addition, with severe lipoatrophy, the transplanted tissues do not take root well and the aesthetic result does not last very long. In particular, due to its low efficiency, the technique is considered completely inappropriate for use in HIV-infected patients undergoing retroviral therapy.
↑ Contour plastic
It consists of the subcutaneous injection of dense synthetic gels - fillers, with the help of which you can fill in the atrophic pits that have arisen, return the necessary volume to the face and even out its relief. Advantages of this technique:
- well-predicted result - the drug remains in the treated area and is removed only after a long time, its migration in tissues is practically excluded;
- stability - unlike fat cells, fillers are little affected by internal factors and the resulting volume will be preserved even if lipoatrophic processes in the body continue.
There are no significant disadvantages, except for the limited time of action - even the most dense and stable preparations cost no more than 1.5-2 years, after which the procedure will need to be repeated.
To eliminate the consequences of lipodystrophy, several types of gel preparations are used:
- Based on collagen - bovine, porcine or human (Evolens, Cosmoplast). Currently considered obsolete, they have a short-term effect - 3-5 months - and can provoke allergic reactions.
- Based on hyaluronic acid - specific dense fillers, such as Juvederm Voluma (analogs are available in most lines of leading manufacturers). The safest and most predictable option, rarely causing complications, optimally suited for eliminating mild to moderate facial lipoatrophy.
- Based on calcium hydroxyapatite, a component found naturally in human bones and teeth. The most famous representative is Radiesse.
- Contains poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), a polymer biocompatible with the human body. The result lasts up to 24 months. The main drug of this group, Sculptra, is actively used to correct lipoatrophy associated with HIV infection, and is considered optimal for reliable and long-term volume restoration in this category of patients.
- ArteFill is a synthetic gel based on polymethyl methacrylate microspheres (PMMA), an artificial polymer with high biocompatibility. Additionally, the composition includes bovine collagen. The main advantage is the long-lasting effect, which in some cases lasts for more than 5 years. Disadvantages - the likelihood of allergies due to the content of animal protein, as well as its low prevalence in the Russian Federation: it will be extremely difficult to find a cosmetologist who can and regularly works with this filler.
- For a long time, non-absorbable preparations based on synthetic polymers were also used for contouring in cases of atrophy of the subcutaneous fat layer. Their action is permanent and not limited in time, but is accompanied by a large number of side effects and an increased risk of complications (such as strong migration of the gel and inflammatory processes in the injection area). Even at the end of the last century, such drugs were used only for pronounced signs of lipodystrophy in patients over 55 years of age - their metabolism is slow, which reduces the likelihood of developing negative consequences. Currently, in most countries of the world the use of such fillers is expressly prohibited.
↑ Surgical transplantation
Unlike lipofilling, not individual cells are transplanted, but whole fat flaps. The risk of rejection is small, but the operation itself is more traumatic, is performed under general anesthesia, requires a hospital stay, has a recovery period and is accompanied by incisions with the subsequent formation of scars both in the donor area and in the facial area. It is carried out mainly to eliminate serious congenital or acquired deformities.
↑ Installation of implants
Special endoprostheses made of medical silicone, similar to those used to enlarge the breasts and buttocks, are used to create volume in the cheekbones and chin in the presence of particularly deep atrophic areas. The operation can be performed under local anesthesia through small incisions, and for the best effect it is advisable to supplement it with fillers or lipofilling. However, it has its drawbacks - the risks of infection and inflammation, which is especially dangerous for HIV-positive patients, as well as the formation of fibrous contracture around the implant.
↑ What conclusions can be drawn
Facial lipoatrophy is best treated when its underlying cause has been completely eliminated. The best option to correct aesthetic defects is lipofilling or the introduction of synthetic absorbable gels (depending on the degree of tissue deformation). Unfortunately, such procedures are very expensive, since a large amount of filler and/or a course of several sessions is required for a full result.
Used materials:
|