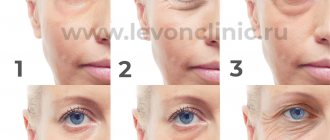
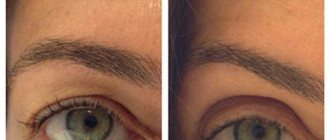
Eyelid ptosis is a drooping of more than 2 mm relative to the edge of the iris. Normally, the fold covers the iris by 1.5 mm or less; if the figure is greater or one eyelid is significantly lower than the second, we speak of pathology. The disease can occur in people of any age.
The asymmetry of the eye sizes is visually noticeable. The defect often causes vision loss. Treatment is aimed at increasing muscle tone.
Ptosis of the lower eyelid is much less common. In the early stages of development of the pathology, swelling and “bags” under the eyes are noticeable. With advanced disease, the edges of the fold are separated from the eyeball, which leads to eversion.
Causes
Correct diagnosis of the causes of ptosis of the upper eyelid allows the doctor to choose an adequate strategy to combat the pathology using therapeutic or surgical methods.
Among the reasons:
- oculomotor nerve palsy;
- weakening of muscles;
- pathology of the autonomic nervous system;
- consequences of operations;
- incorrect therapy with Botox injections;
- diabetes;
- endocrine diseases;
- ophthalmological diseases.
About the drug
Botox is a substance created on the basis of botulinum toxin. Initially, it was used differently by doctors. It was injected into the skin to eliminate ophthalmological problems and relax facial muscle tension caused by psychological disorders and nervous diseases.
Doctors noticed that the substance does not have a negative effect on the body and copes with the task perfectly. And, in addition, it significantly reduces the severity of wrinkles. This is how Botox began to be used in cosmetology. Today, injections of the drug around the eyes are the most effective way of instant rejuvenation.
.
Types of drooping eyelid
Depending on the cause of its appearance, there is the following classification of eyelid ptosis according to its form:
- Aponeurotic – stretching and weakening of muscles, loss of tone. It can occur as a complication after plastic surgery for a facelift, when botulinum toxin is administered by a non-professional specialist and with a violation of technology, or with too frequent and prolonged use of Botox.
- Mechanical – muscle damage after injury, scarring, tumor growth, which, due to its severity, does not allow the eyelid to remain in its normal position.
- Neurogenic is a pathology of the passage of the nerve impulse that controls the muscle. It is necessary to examine the brain to exclude diseases of the central nervous system (meningitis, neuritis, sclerosis).
- Age-related ptosis of the upper eyelid - aging of the body provokes stretching of muscles and ligaments, their weakening.
- False – with anatomical features (large volume of the fold), strabismus, hypotonicity of the eyeball.
There are acquired and congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid.
Methods
Soft tissue ptosis is considered an indication for surgical intervention. Indeed, the methods available to therapeutic cosmetology are very limited in this case. There are a number of good methods for relieving swelling, but it is difficult to influence muscle tone.
If the cause of ptosis is weakness of the muscle frame, then neither Botox, nor peelings, nor fillers are indicated. Iontophoresis and mesotherapy with appropriate drugs have an indirect effect. The only factor that directly affects muscle tone is electrical pulse therapy (EPT).
Current pulses, acting on excitable muscle and nerve tissue, cause contraction of muscle fibers. The main effect of EIT is muscle strengthening. Along the way, there is an increase in blood and lymph circulation, restoration of innervation, and positive changes in metabolism.
Thus, when there is a decrease in muscle tone or atrophy, electropulse therapy is the method of choice. In this case, EIT can be combined with massage, masks, mesotherapy and other methods.
Features of congenital pathology
- In the presence of Horner's syndrome, prolapse is combined with a narrowing of the pupil, decreased sweating on the face, and a deeper location of the eyeball.
- Ptosis occurs in Marcus-Gunn syndrome, when the prolapse disappears when opening the mouth, yawning, and chewing food.
- The defect occurs in Duane syndrome (a form of strabismus), in which the functioning of the nerves responsible for eye movement is impaired.
Isolated ptosis is often inherited. The disease is characterized by abnormalities in the development of the levator tendon. The cause may be congenital myasthenia gravis, cranial nerve palsy.
Tonic deformities
The first group of “loss of face” factors is a decrease in the tone of structures that should be elastic. Weakness of the skin and muscle frame.
The skin of the face is inextricably “fused” with the facial muscles. They are known to be woven into the dense layers of the dermis - this is a moving point of muscle attachment. The facial muscles do not have dense fascia, so in many ways they form a single whole with the skin of the face.
Therefore, the structures responsible for the elasticity of the cheeks are equally both skin and facial muscles.
Sometimes these are manifestations of painful conditions - paralysis of the facial muscles. In this case, the deformations are usually asymmetrical.
Characteristics of acquired ptosis
The problem occurs as a result of trauma, tumors, age-related changes, and stroke, which causes levator (facial nerve) palsy.
A possible complication due to excessive use of botulinum toxin preparations or violation of technology. The muscles paralyzed by Botox do not provide lymph outflow, fluid accumulates, pulls the tissue down - the eyelid droops. This problem can arise due to individual intolerance to the drug and the unprofessionalism of the cosmetologist.
There are several stages of pathology:
- partial ptosis of the upper eyelid (1st degree) – 1/3 of the pupil is closed;
- incomplete ptosis of the upper eyelid (2nd degree) – half to 2/3 of the pupil is closed;
- full (3rd degree) – the pupil is completely closed.
One eyelid or both may be drooping. With the first degree of eyelid ptosis, a person does not feel discomfort. With incomplete and complete prolapse, the following symptoms may be observed:
- difficulty blinking;
- the eye does not close completely - the mucous membrane dries out, irritation appears;
- a burning sensation, as if sand had been poured into the eyes;
- appearance of everted mucosa;
- frequent conjunctivitis;
- headache, eyes.
With advanced pathology, vision is impaired, double vision occurs, and strabismus occurs. With neurological ptosis of the upper eyelid, the eyeball sometimes sinks, and the size of the pupil may change.
Description of the procedure
After a preliminary examination, the patient lies down on a chair. The doctor determines the injection sites; for this it is necessary to study the patient’s facial expressions. Afterwards, he draws the drug into a sterile syringe and injects it shallowly under the skin. Doctors at the Aesthetic Club work only with certified drugs and use disposable sterile syringes. This makes the procedure completely safe.
To correct wrinkles around the eyes in women, on average, 12 to 30 units of Botox are required
.
The injections themselves do not cause pain. The injection needles are so thin that the punctures are almost not felt. There are no traces left after them either. When leaving the salon, the patient does not have to worry about his appearance.
The skin around the eyes begins to slowly smooth out. The final result will be visible in 10-14 days. The muscles around the eyes will lose their previous activity and will contract less when expressing emotions. But there will be no doll-face effect. People around you will start asking how you managed to become so prettier. After all, the skin around the eyes early becomes covered with a fine network of wrinkles. And by smoothing them out, you can visually return 5, 10, or even 15 years.
Diagnostics
To prescribe treatment, it is necessary to determine the root cause of the disease. In the early stages, the prolapse is almost invisible. The doctor determines whether ptosis is congenital or acquired in order to rule out brain diseases. If the patient cannot remember when the problem began, the specialist will prescribe additional tests.
Diagnostic stages:
- inspection, determination of the degree of prolapse;
- checking visual acuity and fields, pressure inside the eye, examining the fundus;
- conducting eye biomicroscopy;
- checking muscle tone and blinking function;
- ultrasound examination, electromyography;
- radiography;
- MRI of the brain;
- testing for binocular vision;
- consultation with a neurosurgeon, endocrinologist, neurologist.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Botox is prescribed to eliminate the harmful effects of facial expressions on the skin. The face is the first to age: this is how muscle contractions affect it. When a person often frowns or smiles, this affects the condition of the skin. Every now and then she is forced to stretch and move. As a result, creases form on it. The skin around the eyes is especially affected. Indications for the use of Botox for the skin around the eyes are:
:
- increased tone of the facial muscles in this area;
- presence of facial wrinkles;
- age-related skin changes.
Contraindications
The procedure is carried out as prescribed by the doctor. It is allowed to take place no earlier than 18 years of age.
Direct contraindications include infections and inflammatory diseases at the time of the procedure. Whether it is chronic illnesses in the acute stage, or a banal acute respiratory infection, the doctor will suggest waiting until complete recovery. Doctors at our clinic will definitely conduct a survey before prescribing the procedure.
The procedure is prohibited during pregnancy and lactation.
Also, if there is inflammation, rash, or other diseases on the skin, you will have to postpone the session.
Features of treatment
After finding out the reasons, the doctor selects adequate treatment. When congenital pathology is detected in the early stages, if vision is not impaired, comprehensive prevention is sufficient. To treat ptosis of the upper eyelid, they resort to conservative methods - without surgery - or perform surgical interventions. If the problem occurs after injury or nerve damage, it is recommended to wait 1 year. During this time, proper treatment can restore nerve function without surgery.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to remove ptosis of the upper eyelid with threads. Non-surgical methods of blepharoplasty with threads give good results for drooping eyelids. Rehabilitation lasts 2 weeks, the results last a long time. The thinnest biocompatible threads create a strong frame and provide support to weakened tissues.
Lifting with moving electrodes and myostimulation
Stimulation can be carried out with stationary (myostimulation) or movable (lifting) electrodes. How to choose the right way to work?
Firstly , we do stimulation where there is relaxation and muscle ptosis. As a rule, these are the cheeks, chin, neck and upper eyelid.
Secondly , it is more convenient to work with movable electrodes on the delicate area of the upper eyelid, and stationary electrodes in the lower third of the face and neck.
And thirdly , areas with muscle tension cannot be stimulated. Even without this, the muscles are too spasmodic. Most often it is the forehead, the orbicularis oculi muscle, and the area around the mouth. In these areas, against the background of muscle spasm, there is dryness and atrophy of the skin, wrinkles. Here the skin needs to be nourished (iontophoresis, microcurrent therapy) with moisturizing substances, antioxidants and vitamins.
Detailed video (webinar recording) about upper eyelid lifting from N. Bakhovets, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Treatment of prolapse after Botox
The drug, which is obtained from botulinum bacteria, is used to disrupt the passage of nerve impulses to the muscles and completely relax them. Inaccurate or incorrect insertion can lead to problems.
Experts recommend waiting until the effect of botulinum toxin wears off. This can take from 2 weeks to six months. To improve the situation and not wait long, therapy is carried out. Elimination of blepharoptosis is performed using physiotherapy: massage, electrophoresis, UHF, microcurrents. The administration of Proserin, vitamin B, and neuroprotectors are also prescribed. This treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox promotes rapid resorption of the drug.
How long does the aesthetic result of the procedure last?
This procedure is characterized by the accumulation of a rejuvenating effect. After the first injection of Botox between the eyebrows, the “anger” wrinkle will smooth out for a period of 4 to 6 months. The effect of any initial procedure using botulinum toxin will last the same amount of time, but after repeated administration of the drug, a more lasting effect develops. In the future, the procedure is carried out no more than 1-2 times a year.
The durability of the aesthetic result depends on the duration of presence of botulinum toxin in the tissues. According to the chemical structure, this toxin is a protein and is gradually destroyed by enzyme systems. It takes 4 to 6 months to completely eliminate botulinum toxin, after which the need for repeated correction arises.
Surgical intervention
Surgery to eliminate prolapse is prescribed at an advanced stage, when the quality of vision is impaired. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting. The procedure involves shortening the relaxed muscle by cutting or removing part of it. The muscle is also folded and stitched. The suture is hidden in a natural fold of the skin; after a while it dissolves, or the suture is removed after 3-5 days. Rehabilitation lasts 1 month, the patient is observed by a surgeon. Surgical treatment has a favorable prognosis - the patient gets rid of the defect for life, the risk of complications is minimal.
Neuro-like impulses
Stimulating a weakened muscle is a simple and straightforward idea. Why has the technique not yet become widespread? The fact is that the eyelid area is very sensitive to electrical stimulation. Due to the proximity of the periosteum, the use of rectangular, sinusoidal and many other shapes of impulses causes severe pain. Therefore, for procedures in the periorbital region, only devices with neural-like impulses close to physiological ones can be used. The special shape of the pulse allows the procedure to be carried out comfortably and effectively, using a sufficiently large current.
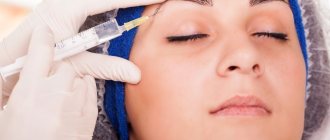
How are Botox injections done?
Botox around the eyes is used only after preliminary preparation, medical examination and exclusion of contraindications. At a preliminary consultation, the cosmetologist examines the skin, identifies defects and determines the required dosage of the drug.
A week before the procedure, you should stop taking antibiotics and drugs that worsen blood clotting. It is also necessary to avoid visiting the sauna and bathhouse, as well as playing sports and any physical activity, which will allow the drug to be evenly distributed under the skin.
It should be noted that the procedure should be carried out only by a qualified specialist, since it requires a certain technique and experience of the doctor.
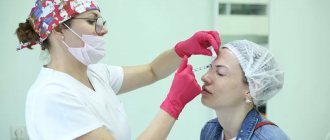
Botox under the eyes is administered in the following steps:
- The skin is cleansed of cosmetics and impurities using a special product.
- Injection points are marked.
- An anesthetic gel is applied.
- Using a syringe with a thin needle, the drug is injected into the area around the eyes.
- The skin is treated with an antiseptic, which reduces the risk of infection in microtraumas.
Why does this happen and what to do if your eyelids droop
The cause of the phenomenon is age-related changes. Over time, the skin loses its elasticity and tone, and folds begin to form on it. This is caused by an age-related decrease in the synthesis of elastin and collagen - the two main structural proteins that form the skin framework. For the skin of the eyelids, which are particularly thin, even the slightest loss of these connections immediately manifests itself as ptosis (drooping and/or sagging).
Of course, such a violation requires correction. Indications for it are:
- too massive eyelids, forming a “tired” face;
- enlarged folds of skin formed by the upper eyelids;
- drooping of the lower eyelids with the formation of “bags”;
- accumulation of fatty deposits in the periocular area;
- moving the corners of the eyes downwards.
These are cosmetic reasons that do not objectively harm human health. Nevertheless, it is sometimes necessary to correct sagging eyelids for medical reasons, since this disorder can lead to:
- entropion (turning of the eyelids);
- exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeball).
Contraindications
General contraindications to botulinum therapy:
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- infectious skin lesions (fungus, herpes);
- oncology;
- diabetes;
- acute respiratory infections;
- myasthenia gravis;
- taking medications (antibiotics, antidepressants, muscle relaxants).
Injecting Botox specifically into the eye area is prohibited if you are diagnosed with:
- hernias of the upper and lower eyelids;
- facial paralysis;
- round eye syndrome;
- wounds, ulcers, fresh scars on the face;
- dysfunction of the circular muscle (paresis, dystrophy);
- weakness of the lower eyelids;
- chronic dry eyes;
- severe myopia, strabismus (in some cases).