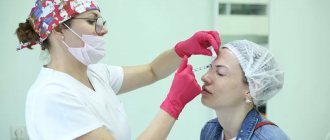
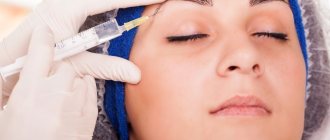
When can you massage after Botox?
After the procedure, skin care should be careful. After injections, it is forbidden to be in a horizontal position for the first 3-4 hours, as there is a risk of uneven distribution of the drug. In order for the effect of Botox to last as long as possible, it is forbidden to grimace, perform any active actions with facial muscles, as well as press and massage the face.
Why are mechanical effects so undesirable after Botox injections? If you massage immediately after the procedure, the risk of developing unwanted side effects increases, including the spread of botulinum toxin to adjacent tissues.
A few hours after the injection, the injected drug is absorbed by the nerve endings of the treated area. Botox can spread from the injection point to adjacent tissues up to 2 cm in the first few hours. Therefore, it is in the first days that it is so important to exclude any touching of the face, pressure, scratching and massage; only not too active mobility of the facial muscles is allowed. In addition, any massage is performed in a face-down position, which is also strictly prohibited.
Any impact on areas treated with Botox is allowed only after the rehabilitation period has expired, not earlier than 2-3 weeks. After this period, massage is not only useful, but also mandatory, since such manipulations improve appearance. But it is worth considering that before booking a massage, you should consult a doctor.
Complications are not the most pleasant part of our profession. However, every doctor experienced adverse events at least once during his professional career. We must know how to help patients get out of difficult situations. In this article I will examine in detail the most common types of complications after the introduction of toxins.
Introduction
The appearance of botulinum neuroproteins on the market has created a real revolution in the world of aesthetic medicine. Botulinum toxin injections are one of the most popular and sought after procedures. Their number is constantly growing, the accessibility of the procedure is increasing, and, consequently, the number of consumers is increasing. But at the same time, the percentage of complications after botulinum toxin injections also increases.
Typology of complications
My vision of the problem of complications after botulinum therapy is based on a continuous 10-year experience of working with drugs of this group, as well as on the practical aspects of their treatment. I divide complications after botulinum therapy into true and false.
Below we will analyze in detail which complications are true and false, and how to correct them.
True Complications
These are complications associated directly with the action of botulinum neuroprotein:
- ptosis and paresis - complications resulting from strong muscle relaxation as a result of the direct action of a large dose of botulinum toxin on the muscle (ptosis of the eyelid, drooping eyebrows, impaired articulation, fluid pouring out of the corner of the mouth),
- asymmetries - complications associated with violation of injection technique in the form of incorrect location and level of botulinum toxin injection, inadequately selected doses or diffusion of botulinum toxin into neighboring muscles (asymmetry of the eyebrows, corners of the mouth, asymmetry when opening the mouth, pursing of the lip, change in the shape of the chin).
No ptosis or paresis is corrected by additional administration of botulinum toxin. Therapeutic measures are aimed at the speedy restoration of muscle activity and muscle reinnervation. Unfortunately, in most cases, therapy has more of a psychological effect than a clinical one.
Treatment of excessive muscle relaxation after injections of botulinum neuroprotein can be carried out according to the following scheme:
- PRP therapy - three times a week,
- B vitamins orally (milgamma compositum, neuromultivitis) and mesotherapeutic injection of the affected area (vitamin B12, milgamma) - once every two days,
- mesotherapy with DMAE solution - twice a week,
- microcurrent therapy (3–5 times a week), myostimulation (1–2 times a week),
- RF therapy - once a week. These procedures can be used independently or combined with each other. The total number of physical procedures should not exceed five per week. For example: RF therapy procedure, myostimulation procedure, three microcurrent therapy procedures, • pinch massage of the complication area - daily,
- facial gymnastics - three times a day for 15 minutes daily,
- placenta preparations in an ampoule twice a week to bioactive points or intramuscularly in the complication area.
For ptosis of the upper eyelid, eye drops 0.5% “Iopidine” (“Apraclonidine”) have a temporary effect.
The drug is an agonist of alpha-2-adrenergic receptors of smooth muscles and, when it enters the eyeball, causes contraction of the Müllerian muscle, which helps to raise the upper eyelid by 2-3 mm within several hours.
Instill 1-2 drops 3 times a day. If the patient has pathology on the part of the visual organs, consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary before use.
Patient 1 [Photo 1.1] complained of drooping upper eyelid two weeks after botulinum toxin injections in the area between the eyebrows in a total dose of 10 U (100 U toxin). The drooping eyelid began to bother me on the sixth day after the injection [Photo 1.2]. Over the next week, the ptosis progressed [Photo 1.3].
From day 14, for two weeks, the patient received therapy according to regimen 1; two weeks after the start of therapy, we can observe an average positive trend in the resolution of ptosis of the upper eyelid [Photo 1.4].
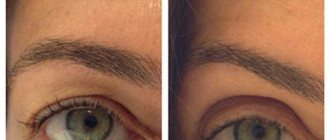
Unlike ptosis of the upper eyelid, ptosis of the eyebrows is manifested by an overhang of the skin fold of the fixed part of the upper eyelid; drooping of the movable eyelid is not observed. This complication is caused by excessive relaxation of the m. frontalis, especially its lower parts. Restorative therapy should be carried out on the half of the forehead where the complication occurred. Patient 2 notes a sagging skin fold in the area of the right eyelid three weeks after injections of botulinum toxin into the forehead and eyebrow area [Photo 2.1].
When trying to raise the eyebrows, one can observe severe blocking of the frontalis muscle [Photo 2.2]. The patient was prescribed therapy according to regimen 1. Ten days after the start of therapy, we can observe positive dynamics in the resolution of the complication [Photo 2.3].
Asymmetries in most cases are corrected by additional administration of botulinum toxin. I use intradermal injections of small doses of botulinum toxin to avoid reversal of asymmetry.
To enhance the restoration of neuromuscular transmission, patients are prescribed Neuromidin 10 mg tablets orally, 1 tablet 1-2 times a day for 14 days.
Thus, in patient 3, both ptosis of the right eyebrow and asymmetry of the left are simultaneously present. The reason is excessive relaxation of the fibers of the frontal muscle on the right and insufficient blocking of the tail m. corrugator on the left, the mobility of the frontal muscle in the lower parts on the left is preserved. In this case, the injection technique could have been violated in the form of an incorrectly selected dose of botulinum toxin and its injection points. All this led to the overhang of the skin fold of the upper eyelid on the right and to the raising of the head and body of the eyebrow on the left. This complication can be partially corrected in the following way: inject a highly concentrated solution of botulinum toxin in a dose of 2–2.5 U (500 U toxin) intradermally at the indicated points on the left, with the needle directed upward, and also use local restorative therapy in the area of the frontal muscle on the right.
Patient 4. Photo 4.1 shows the patient before the injection of botulinum toxin into the m. mentalis. To correct chin wrinkles, botulinum toxin was injected in a total dose of 8 U (500 U toxin) bonewise into the chin area. However, two weeks after correction we can observe a change in the shape of the chin [Photo 4.2]. This complication is associated with a violation of the injection depth and uneven blocking of m. mentalis. In the lower sections, this muscle is corrected deep into the bone, while in the upper sections, injections should be carried out superficially. In patient 4, this rule was violated, resulting in a complication in the form of a “shovel-shaped” chin.
It can be corrected by superficially introducing small doses (0.5–1 U per injection) of botulinum toxin in the upper parts of the chin from 3–4 points.
Patient 5. Nine days after botulinum toxin injections into the m. depressor anguli oris in order to raise the corners of the lips, the patient began to notice asymmetry when opening her mouth. In this situation, botulinum toxin was injected to a greater depth than necessary, as a result of which the fibers of the deeper m. depressor labii inferioris, which led to its relaxation and uneven lifting of the lip on the right.
Patient 6 received injections in the m. depressor anguli oris on both sides in a dose of 3 units on each side. Another 3 units were introduced into m. mentalis (100 units - botulinum toxin). Injections into m. platysma were not carried out.
A few days later we observe asymmetry in a wide smile. On the left, botulinum toxin affected m. depressor anguli oris, and the corner of the mouth rose. About blocking m. depressor anguli oris indirectly indicates the compensatory cord m. platysma on the left side.
- M. depressor anguli oris and m. platysma work in synergy, and their isolated shutdown can lead to activation of the concomitant muscle.
On the right side of the face, a dose of botulinum toxin, probably instead of m. depressor anguli oris was introduced into m. platysma, and m. depressor anguli oris was not blocked. For m. platysma, a dose of 3 U of botulinum toxin is insignificant, so we do not observe any effect, but we can see an active left m. Depressor anguli oris, which continues to pull the corner of the mouth down.
The doctor’s tactics in this case are to wait 2-3 weeks. It is possible that the muscle fibers are unevenly blocked and the result of botulinum toxin injection will change. If the picture remains the same, it is necessary to inject botulinum toxin in a similar dose in m. depressor anguli oris on the left, as well as injections into the cords of m. platysma - to prevent strengthening of cords.
False complications
Complications that are not a direct consequence of the effect of botulinum toxin on a specific muscle. I consider the so-called “compensatory manifestations” and swelling to be false complications:
- compensatory wrinkles are associated with redistribution of tone in a specific muscle,
- compensatory facial expressions are associated with blocking of individual muscle groups and the appearance of facial activity in other areas where it was not characteristic before; compensatory hypertrophies are associated with muscle blocking, in which friendly muscles begin to hypertrophy, taking over the function of the blocked ones,
- swelling - when facial muscles contract, they help to “push” fluid from the tissues into the lymphatic capillaries, thereby improving lymphatic drainage. Excessive muscle blocking leads to deterioration of lymphatic drainage and the formation of pastosity.
All “compensatory manifestations” can be successfully corrected by additional administration of botulinum toxin, but it is more justified to anticipate their occurrence during the main procedure by performing preventive injections.
Compensatory wrinkles: patient 7 [Photo 7.1] six days after botulinum toxin injections in the forehead and between the eyebrows developed small wrinkles above the eyebrows [Photo 7.2]. Correction involves intradermal administration of botulinum toxin in a dose of 1–1.5 U (500 U per injection). It is necessary to wait 2-3 weeks after the main procedure before correction.
Compensatory facial expressions: in patient 8 [Photo 8.1] after injections into the m. orbicularis oculis, when smiling, wrinkles began to appear in the area of the bridge of the nose [Photo 8.2], although previously this facial movement was not characteristic. Correction involves injections of botulinum toxin into the m. nasalis.
Compensatory hypertrophy: in patient 9 , 12 days after injections into the masticatory muscles (no prophylactic injections were performed into the m. temporalis), the temporal muscles became sharply outlined and enlarged. The patient requires additional injection of botulinum toxin into the temporal muscles.
Swelling: Patient 10, eight days after botulinum toxin injections into the orbicularis oculi muscle to correct crow's feet, developed severe swelling in the area of the paint bags [Photo 10.1]. Anti-edematous therapy was prescribed according to scheme 2; in photo 10.2 we can see the patient a week after the start of therapy.
Decongestant therapy for facial pastiness after injections of botulinum neuroprotein can be carried out as follows:
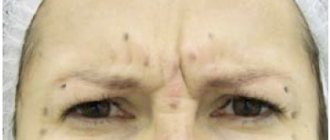
- injections of drugs that stimulate lymphatic drainage according to the markings [Fig. 1 and 2], taking into account the paths of lymphatic drainage to the locations of regional lymph nodes. Lymphatic drainage cocktails, combination preparations with sodium succinate, peptide preparations, rutin-melito,
- limiting salt intake in food and drinking regime,
- microcurrent therapy daily,
- lymphatic drainage massage.
False complications are easier to correct than true ones and often go away on their own.
Conclusion
We see that there can be many complications after botulinum toxin injections for the purpose of correcting age-related changes, and they are all different and often insidious. However, continuous improvement of knowledge in the field of anatomy, physiology and pharmacokinetics of the action of botulinum toxin gives us the strength and ability to wield this unique instrument, which in the hands of a true professional can work wonders!
Author: Anastasia Mashkina, cosmetologist, dermatovenerologist, certified trainer, Moscow.
Magazine: Appearance. Esthetic guide №2(30)
What are the benefits of massage after Botox?
Massage is a beneficial procedure due to:
- improving skin elasticity and firmness;
- reducing pain and discomfort;
- reducing muscle tension;
- normalization of blood circulation.
In addition, massage helps the products used to penetrate deeper into the skin, increasing their effectiveness, which affects the appearance of the skin.
Facial massage is performed in the following ways:
- easy kneading;
- vibration;
- trituration;
- stroking.
Facial massage helps:
- delay the appearance of new wrinkles;
- get rid of a double chin;
- start the processes of collagen and elastin production;
- make the skin smooth and elastic;
- get rid of swelling.
It is worth remembering that massage on the area treated with Botox in the first 3-4 weeks is unacceptable. After this period, the specialist, at the patient’s request, prescribes a massage course, which consists of massaging the skin along certain lines.
Basic tips after completing the procedure
Although a botulinum toxin injection is much more harmless than a surgical operation, there are a number of restrictions associated with them, neglect of which can lead to undesirable and difficult to predict results that are rather unpleasant.
First of all, the procedure should not be done at all in such cases as:
- use of antibiotics;
- lactation or pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- various infectious diseases;
- oncology;
- blood diseases;
- alcoholism and mental disorders.
Due to the fact that Botox produces a time-limited effect, this procedure should be repeated after some time. Immediately after the procedure, you should stay in the clinic under the supervision of a medical professional so that at the first sign of possible complications you can quickly eliminate them. During the first hour, the doctor may suggest making a face - squinting, frowning, etc. Such actions help the drug to be distributed more uniformly among the muscles responsible for facial expressions.
The recommendations at the end of the Botox injection procedure are simple, but failure to follow them can lead to unfortunate results.
Recommendations for the first seven days
During the first two days after Botox, bruises and swelling may appear under the eyes. In cases where recommendations are not followed, they will definitely appear.
In order to remove them, it is usually enough to apply a compress every three hours. You need to hold it for fifteen to twenty minutes. You can hide them with concealer, but not on the first day.
To maintain the effect after the injection, you should not take blood thinners and tetracycline antibiotics. Relaxers, alcohol and psychotropic substances are strictly prohibited.
To eliminate the possibility of hematomas during the first week, you should avoid eating hot peppers, onions, garlic and ginger.
Tips for the first two weeks
The results of the procedure will appear within two weeks. There are no special recommendations for this period of time.
This period after the administration of botulinum toxin does not require special recommendations. As a rule, the specialist sets the time for a planned consultation in order to understand the effect of the drug and, if necessary, make adjustments.
You should not consume medications and alcohol, and also stay in the sun for a long time. When it is impossible to avoid interaction with ultraviolet radiation, you need to use sun protection creams.
Intense exercise is also harmful. You should return to sports gradually and no earlier than after a month.
Any patient who receives Botox injections should not forget the advice of specialists. Following them already ensures half the success of the procedure.