Menu
- About the MoESBT Charter
- Organizing Committee
- Membership Regulations
- How to join
- News
- Events
- Partners
- Vacancies
- Mechanisms of action of Botulinum toxin
- Training Training centers
- Thematic seminars on botulinum therapy
- News portal botulin.ru
Home / Minisites / Merz
Manufacturer
Instructions
A drug
| Registration certificate Merz |
I APPROVED
Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation G. G. Onishchenko 02/08/2010 No. 01–11/25–10
Registration certificate No. LSR-004746/08
Dosage form: lyophilisate for the preparation of a solution for intramuscular administration
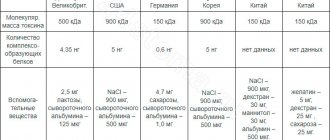
Xeomin is a botulinum toxin produced by a strain of the bacterium Clostridium botulinum type A, freed from complexing proteins.
Composition (1 bottle)
: botulinum toxin type A 100 units, sucrose 4.7 mg, human serum albumin 1.0 mg.
Description:
White lyophilisate.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
peripheral muscle relaxant.
Biological properties and pharmacodynamics:
Xeomin acts selectively on peripheral cholinergic nerve endings, inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.
Entry into cholinergic nerve endings occurs in three stages: binding of the molecule to external membrane components, internalization of the toxin by endocytosis, and translocation of the endopeptidase domain of the toxin from the endosome to the cytosol. In the cytosol, the endopeptidase domain of the toxin molecule selectively cleaves SNAP-25, an important protein component of the mechanism that controls the membrane movement of exo-vesicles, thus stopping the release of acetylcholine. The end effect is relaxation of the injected muscle. The effect of the drug begins, on average, within four to seven days after the injection. The effect of each procedure usually lasts three to four months, although it can last significantly longer or shorter. Indications for use
: blepharospasm, idiopathic cervical dystonia, (spasmodic torticollis) of a predominantly rotational form, hand spasticity after a stroke, hyperkinetic folds (expression wrinkles) of the face.
Contraindications:
The drug is contraindicated in people with allergies to the components of the drug, with disorders of neuromuscular transmission (masthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, prescribed with caution for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, for neurological diseases resulting from degeneration of motor neurons and other diseases with disorders of neuromuscular transmission) .
The drug is not administered at elevated temperatures and acute infectious and non-infectious diseases. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. The drug is not administered to children and adolescents under 18 years of age. Directions for use and dosage:
The drug should only be administered by physicians with special training and experience in handling botulinum toxin and electromyography equipment.
The doctor sets the dosage and number of injection sites into the muscle individually for each patient. Dissolution of the drug:
When diluting the drug, do not open the bottle by removing the stopper. Remove the protective plastic cap from the bottle. Immediately before diluting the contents of the bottle, the central part of the stopper should be treated with alcohol. The injection solution is prepared by piercing the stopper with a sterile needle and introducing a sterile sodium chloride solution for injection, 0.9%, into the bottle. Carefully turn the bottle, mixing the lyophilisate with the solvent until completely dissolved. After dissolution - a clear, colorless solution. The drug should not be used if, after dissolution, the resulting solution is opaque or contains visible flakes and particles. The drug is dissolved in the required volume, according to the table. Solvent volume (ml) U/0.1 ml 0.5 20 1.0 10 2.0 5 4.0 2.5 8.0 1.25
The dosages recommended for Xeomin cannot be used for conversion when using other drugs containing botulinum toxin. Since the drug does not contain antimicrobial agents, it is recommended to use it immediately after dissolution. If necessary, the dissolved drug can be stored in the original bottle for up to 24 hours in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2 to 8 ° C, provided that the dissolution was carried out under aseptic conditions.
Blepharospasm:
After dissolution, Xeomin is administered with a sterile 27–30 G needle. The recommended initial dose is 1.25–2.5 units (0.05–0.1 ml) at each injection site; the drug is injected into the medial and lateral parts of the circular muscle of the eye (m. orbicularis oculi) of the upper eyelid, and into the lateral part of the circular muscle of the eye of the lower eyelid. If vision is impaired due to spasms in the forehead, lateral orbicularis oculi muscle, and upper face, additional injections may be given to these areas. The effect of the drug begins, on average, within four days after the injection. The effect of each procedure usually lasts three to four months, although it can last significantly longer or less. If the effect of the initial dose was insufficient (lasting less than two months), with repeated procedures the dose of the drug can be doubled. The initial dose should not exceed 25 units per eye. No dose greater than 5.0 units should be injected into each site. When treating blepharospasm, the total dosage over twelve weeks of treatment should not exceed 100 units.
Indications for use
Xeomin effectively eliminates the entire complex of facial wrinkles, including:
- vertical and horizontal wrinkles on the forehead,
- crow's feet and other fine wrinkles around the eyes,
- superficial wrinkles in the eyebrow area and between the eyebrows (on the bridge of the nose),
- small wrinkles around the lips, in the corners of the mouth and along the edges of the nose,
- superficial neck wrinkles,
- fine wrinkles in the décolleté area, including vertical bunches of wrinkles.
An additional indication is increased sweating (sweating).
Spasmodic torticollis:
When treating spastic torticollis, the dosage should be selected individually for each patient, depending on the position of the neck and head, the location of pain, muscle volume (hypertrophy, atrophy), the patient’s body weight and his response to therapeutic procedures. In treatment practice, the maximum dose of the drug during one procedure should usually not exceed 200 units, but dosages up to 300 units are possible. A dose of the drug exceeding 50 units should not be administered to the same place. Treatment for spasmodic torticollis includes injections into the sternocleidomastoid muscle, levator scapulae muscle, scalene muscle, splenius muscle, and/or trapezius muscle(s). Injections into both sternocleidomastoid muscles should not be given as this increases the risk of adverse drug effects (particularly dysphagia) that occur with bilateral drug injections into this muscle or at doses greater than 100 units. For injections into superficial muscles, 25, 27, and 30 G needles are used, and for deep muscles, a 22 G needle is used. In spasmodic torticollis, electromyography may be necessary to determine the muscles involved. Injecting into several places allows the drug to evenly cover muscle areas affected by dystonia (especially when injecting into large muscles). The optimal number of injection sites depends on the size of the muscle. The effect of the drug begins, on average, within seven days after the injection. The effects of each treatment last approximately three to four months, but may last significantly longer or shorter. The interval between procedures should be at least ten weeks.
Cost of the procedure
Elimination of expression wrinkles with the drug Xeomin: 1 unit – 300 rubles 50 units – 13,000 rubles
Before carrying out the procedure, a consultation with a cosmetologist is necessary. More detailed information about visiting a cosmetologist and the cost of services can be obtained by calling: +7 (3452) 65-94-32. Or leave a request for a call back, we will call you back within a day.
The professionalism and experience of the doctor, correctly selected doses, the correct method of administering injections, strict adherence to sterility and many other important factors are the key to an excellent result.
Carry out injection cosmetic procedures only in specialized clinics with experienced cosmetologists, take care of yourself, love yourself and be irresistible!
The article was checked by: Deputy General Director of the Nanoesthetic Clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences, cosmetologist, trichologist, Elena Andreevna Makhneva.
Hand spasm after stroke:
The drug is administered using suitable sterile needles (for example, for superficial muscles use 26 G needles with a diameter of 0.45 mm and a length of 37 mm, for deep muscles use 22 G needles with a diameter of 0.7 mm and a length of 75 mm). Electromyography may be necessary to determine the muscles involved. Injecting into several places allows the drug to evenly cover the muscles affected by dystonia (especially when injecting into large muscles). When treating spasticity, the dosage should be selected individually, depending on the size, number and location of the muscles involved, the degree of severity, and the presence of local muscle weakness. Suggested dosages are presented in the table:
| Clinical symptom Muscle | Units |
| Hand bent at the wrist: | |
| Flexor carpi radialis | 50 |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | 40 |
| Clenched fist: | |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | 40 |
| Flexor digitorum profundus | 40 |
| Arm bent at the elbow: | |
| Brachioradial | 60 |
| Biceps | 80 |
| Shoulder | 50 |
| Pronated forearm: | |
| Pronator quadratus | 25 |
| Pronator teres | 40 |
| Thumb adducted to palm: | |
| Flexor pollicis longus | 20 |
| Adductor pollicis muscle | 10 |
| Flexor pollicis brevis/oppons pollicis muscle | 10 |
When treating spasticity, the recommended dosage per course of treatment is 170–400 IU, depending on the location of the spasmodic muscles. Improvement occurs within the first 2 weeks, reaching its maximum by the 4th week. The effect usually lasts 12 weeks.
Hyperkinetic folds (expression wrinkles) of the face:
The use of the drug for the treatment of facial wrinkles in persons under 18 years of age and over 65 years of age is not recommended due to the lack of clinical experience. Vertical wrinkles between the eyebrows (glabellar wrinkles): recommended injection volume -0.1 ml (4 units) - injected into each of 5 areas: 2 injections into the m.corrugator on both sides and 1 injection into the m.procerus, which corresponds to the total dose 20 units. In some cases, it is possible to increase the total dose to 30 units. Before and during injection, apply pressure with the thumb and index finger below the upper edge of the orbit to prevent diffusion of the solution into this area. During injection, the needle should be directed upward and medially. To reduce the risk of eyelid ptosis, injections should be avoided near the levator palpebral muscle. and at the insertion of the orbicularis oculi muscle. Injections into the m.corrugator should be carried out in the medial part of the muscle and in the central part of the muscle belly, at least 1 cm above the upper edge of the orbit. Reduction in the severity of vertical wrinkles between the eyebrows (glabellar wrinkles) usually develops within 2-3 days, the maximum effect is observed by the 30th day, and lasts up to 4 months after the injection. The intervals between injections should not be less than 3 months. If the treatment result is unsatisfactory, alternative treatment methods are used.
Price comparison between Botox, Dysport and Xeomin
The cost of injections of all three drugs differs from each other.
For example, an injection with Botox will be more expensive than with Dysport, but we must not forget that one hundred units of Botox are equivalent to five hundred units of Dysport.
Thus, to achieve the same effect, you need to purchase five times more Dysport than Botox . On average, the cost of a unit of Botox is 350 rubles, and a unit of Dysport varies between 150-200 rubles.
The price for Xeomin is about 300 rubles and more.
Blepharospasm:
Common: ptosis (6.1%), dry eyes (2.0%). Uncommon: paresthesia, conjunctivitis, dry mouth, skin rash, headache, muscle weakness. In addition, when using a similar drug containing botulinum toxin type A and used in clinical trials along with Xeomin, the following side effects were observed. They are also possible when using the drug Xeomin. Common: superficial keratitis, lagophthalmos, irritation, photophobia, lacrimation. Uncommon: keratitis, ectropia, diplopia, dizziness, diffuse skin rash/dermatitis, entropion, focal facial paralysis, facial weakness, fatigue, visual disturbances, blurred vision. Rarely: local swelling of the skin of the eyelid. Very rare: acute angle-closure glaucoma, corneal ulceration.
Contraindications
Contraindications for administration:
- poor blood clotting;
- muscle weakness;
- neurological diseases;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- allergy to the drug;
- elevated temperature, febrile state;
- infectious diseases;
- acute form of chronic diseases;
- HIV, syphilis;
- autoimmune disorders;
- mental illness;
- recovery period after surgery;
- skin diseases in the area requiring correction;
- diabetes;
- treatment with antibiotics, anticoagulants;
- high degree of myopia;
- hernia on the eyelid;
- drug addiction, alcoholism;
- epilepsy;
- malignant formations;
- menstruation.
Spasmodic torticollis:
Common: dysphagia (10%), muscle weakness (1.7%), back pain (1.3%). Uncommon: inflammation or pressure at the injection site, headache, asthenia, increased sweating, tremor, hoarseness, colitis, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth, bone pain, myalgia, skin rashes, itching, peeling skin, eye pain . In addition, when using a similar drug containing botulinum toxin type A and used in clinical trials along with Xeomin, the following side effects were observed. They are also possible when using the drug Xeomin. Very common: pain at the injection site Common: dizziness, high blood pressure, numbness, general weakness, cold symptoms, general malaise, dry mouth, nausea, headache, muscle stiffness, irritation at the injection site, rhinitis, upper respiratory tract infections . Uncommon: shortness of breath, diplopia, fever, ptosis, speech disorders. The severity of dysphagia varies from mild to severe with the possibility of aspiration; In rare cases, this requires medical attention. Dysphagia may persist for two to three weeks after injection, but a case of three-month dysphagia has been reported. Dysphagia develops in a dose-dependent manner; According to clinical studies, dysphagia is rare if the total dose of the drug does not exceed 200 units per procedure
Advantages and disadvantages
Xeomin contains no proteins, which means there will be no addiction to the drug. When administering Xeomin, a small but effective dose , compared to the same Botox. Xeomin can be used at any age. The disadvantage of this tool is that it has not been fully studied .
Advantages of Xeomin over Botox
- Favorable storage conditions. Xeomin, unlike Botox or Dysport, does not need to be kept in the cold. Undiluted product can be stored at +25 degrees Celsius. The advantage is that any other drug cannot be transported in violation of the conditions - this will affect its effectiveness, which does not apply to Xeomin at all.
- Minimum negative consequences. There are no proteins in Xeomin that would cause an immune reaction in the body, but Botox does have such proteins. Thus, the risk of rashes or swelling in the injection area is practically reduced to zero.
- There is no risk of drug ineffectiveness. Since there are no proteins in Xeomin, this means that antibodies to it will not be produced. This eliminates addiction or insensitivity to the product.
- The product does not “spread” into tissues . The Xeomin molecule is smaller than the Botox molecule, but the former, due to its increased ability to attract, migrates less frequently. This is the advantage of the drug in preserving facial expressions and preventing the possibility of tissue sagging.
- A smaller dose is required for the desired effect . The reason is the weak ability to spread under fabrics.
Disadvantages of Xeomin compared to Botox:
- Unsuitable for the treatment of hyperhidrosis. The reason again lies in the weak spreading of Xeomin.
- Less lasting effect . The results from injections do not last as long as from other botulinum toxins.
- Insufficient knowledge . Botox has been used all over the world for many decades, but Xeomin has only recently begun to gain popularity.
Arm spasticity after stroke:
Common: headache, sensory disturbances, feeling of heat. In addition, when using a similar drug containing botulinum toxin type A, and used in clinical trials along with Xeomin, the following side effects were observed. They are also possible with the use of Xeomin. Common: hypertonicity, ecchymosis, local pain, muscle weakness, irritation or hemorrhage at the injection site. Uncommon: depression, sleep disturbance, paresthesia, incoordination, amnesia, vertigo, orthostatic hypotension, nausea, dermatitis, itching, rash, arthralgia, bursitis, asthenia, pain, hypersensitivity at the injection site, anxiety, peripheral edema. Some side effects may be related to the underlying disease.
Hyperkinetic folds (expression wrinkles) of the face:
Usually, undesirable effects are observed in the first week after using the drug and are temporary. Undesirable effects may be related to the active substance and/or the administration procedure. The expected pharmacological effect of botulinum toxin is localized muscle weakness. Ptosis of the eyelids can be caused by the injection technique and is associated with the pharmacological action of the drug. As with any injection, local pain, tenderness, itching, swelling and/or hematoma may occur; it is also possible to develop superior vasovagal reactions. such as fainting, circulatory problems, nausea or tinnitus associated with anxiety before the injection. The following adverse reactions have been reported with the use of the drug: Often: skin itching, headache, impaired muscle function at the injection site, feeling of heaviness. Uncommon: flu-like symptoms, feeling of tension at the injection site, bronchitis, nasopharyngitis, feeling of "nodules in the skin", swelling of the eyelids, ptosis, blurred vision, raised eyebrows, nausea, muscle twitching and spasms, local weakness of the facial muscles. In addition, the comparator drug, which contains a conventional botulinum toxin complex type A and has been used in several clinical studies (the data collected to date suggests that both drugs are equally active), is known to develop the following undesirable effects, which are likely to occur. may also be observed when using Xeomin. Uncommon: injection, paresthesia, dizziness, blepharitis, eye pain, dry mouth, photosensitivity, dry skin.
Common side effects:
The information presented below is based on data on the effects of other complex preparations containing botulinum toxin type A. Information about severe negative effects that may be associated with damage to the cardiovascular system, such as arrhythmia and myocardial infarction, including death, is extremely insignificant. Whether these deaths were caused by injections of botulinum toxin type A or concomitant cardiovascular diseases is not certain. One case of anaphylactic shock has been reported after administration of a complex drug containing botulinum toxin type A. Side effects such as exudative erythema multiforme, urticaria, psoriasis-like rashes, itching and allergic reactions have been noted, but they are due to the action of a complex drug containing botulinum toxin type A not confirmed. Sometimes after injection of botulinum toxin type A, fluctuations in the electrophysiological background were noted in some distant muscles; this side effect is not associated with muscle weakness or other electrophysiological abnormalities.
pharmachologic effect
Xeomin acts selectively on peripheral cholinergic nerve endings, inhibiting the release of acetylcholine. Entry into cholinergic nerve endings occurs in three stages: binding of the molecule to external membrane components, internalization of the toxin by endocytosis, and translocation of the endopeptidase domain of the toxin from the endosome to the cytosol. In the cytosol, the endopeptidase domain of the toxin molecule selectively cleaves SNAP-25, an important protein component of the mechanism that controls the membrane movement of exo-vesicles, thus stopping the release of acetylcholine. The end effect is relaxation of the injected muscle.
The effect of the drug begins within four to seven days after the injection. The effect of each procedure usually lasts three to four months, although it can last significantly longer or shorter.
Overdose:
High doses of Xeomin can lead to the development of severe muscle paralysis in areas remote from the injection sites (in particular: general weakness, ptosis, diplopia, difficulty speaking and swallowing, as well as paralysis of the respiratory muscles, leading to the development of aspiration pneumonia). In case of overdose, hospitalization with general supportive measures is necessary. In case of paralysis of the respiratory muscles, intubation and artificial ventilation of the lungs are necessary until the condition normalizes
Precautionary measures:
Immediately after the injection, the remaining solution in the vial or syringe should be inactivated with sodium hydroxide solution (0.1 N NaOH). All auxiliary materials that have been in contact with the drug must be autoclaved or inactivated with a solution of 0.1 N NaOH (for at least 18 hours). Spilled medication should be wiped up with an absorbent cloth soaked in sodium hydroxide solution. Release form:
100 units per bottle.
1 bottle in a plastic tray in a cardboard box along with instructions for use in Russian. Storage and transportation conditions:
at room temperature (not higher than 25 C).
Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life
: 3 years.
A drug that has expired cannot be used. Conditions of release:
the drug is released only to specialized medical institutions.
D-60318, Germany, Frankfurt am Main Complaints about the quality of the drug with the obligatory indication of the batch number and date of manufacture should be sent to the Federal State Budgetary Institution GISC named after. L. A. Tarasevich Rospotrebnadzor at the address: 119 002, Moscow, per. Sivtsev Vrazhek, 41, telephone, fax (495) 241-92-38 and to the Representative Office in Russia at the address: 125 040, Moscow, 1st st. Yamsky field 9/13, phone, fax: (499) 257-02-З4.