Vaginoplasty using penile inversion method
Gender-affirming genital surgery for transgender women includes orchiectomy, penectomy, vaginoplasty, and labiaplasty. Vaginoplasty is the main surgical stage, which determines the technical features of the intervention. But vaginoplasty, like any other gender-affirming surgery, is not mandatory, so not all transgender women resort to it, being happy with their bodies without it.
Typically, in transgender women, the entire scope of genital gender-affirming interventions (penectomy, orchiectomy, vaginoplasty, labiaplasty) can be performed in one stage.
Benefits of gender-affirming genital surgery for transgender women:
- Reducing gender dysphoria. For many transgender women, awareness of the presence of female genitalia is an integral part of their gender identity, and their absence, accordingly, is the cause of persistent gender dysphoria. Surgical intervention in such a situation may be the only way to achieve psychological comfort.
- Reducing the problems associated with staying in public gender-segregated places (hospitals, public toilets and locker rooms). The absence of external genitalia defined as “female” and the presence of organs defined as “male” in a transgender woman can cause transphobia and aggression in other people.
- There is no need for bandaging and tightening the perineum and other practices (moving the testicles into the inguinal canals) to hide the genitals.
- Eliminating the source of male sex hormones in the body. In transgender people who have not had their testicles removed, the goals of hormone therapy include creating the desired hormonal profile (female for transfeminine individuals) and suppressing the baseline hormonal levels with antiandrogen medications. In transfeminine women undergoing bilateral orchiectomy, the dose of hormonal medications may be reduced and antiandrogen medications may be discontinued.
- The presence of organs defined as “male” in a transgender woman can be an obstacle to building personal and sexual relationships.
Criteria for genital surgery (penectomy, orchiectomy, vaginoplasty, labiaplasty) in transgender women (WPATH, version 7):
- Documented persistent gender dysphoria
- Patient's ability to make an informed decision and consent to surgery
- Legal age
- Monitoring by physicians of the patient’s serious concomitant medical and mental health problems
- 12 months of continuous hormonal therapy
Why is a 12-month period of continuous hormonal therapy necessary before metoidioplasty?:
- The experience of living for a 12-month period of time in the chosen gender (full-time) allows a person to adapt to a new role and evaluate the correctness of his decision before performing gender-affirming surgical interventions. This strategy allows you to minimize the likelihood of detransition.
- A 12-month period of hormone therapy allows you to assess individual risks and contraindications for hormone therapy, as well as its effects.
- Previous hormonal therapy may reduce symptoms of post-castration syndrome after testicular removal
What types of vaginoplasty are there?
Several vaginoplasty techniques have been described for transgender women: penile inversion vaginoplasty (penile skin flap inversion), penoscrotal flap vaginoplasty, Perovic technique (using a urethral flap), and intestinal segment vaginoplasty. In the 1930s, vaginoplasty using skin grafts was popular. One of the pioneers of this technique was Abraham. The advantages of this technique are: one-stage, low incidence of complications, the ability to create a vagina of sufficient depth and capacity. But this technique also has a number of significant disadvantages (vaginal prolapse, the presence of a scar in the donor area, circular narrowing and wrinkling of the vagina, lack of erogenous sensitivity and natural hydration of the vagina), which limited its spread and prompted specialists to search for more effective techniques.
What determines the choice of vaginoplasty technique?
- Patient's wish
- Individual anatomical features and clinical situation of the patient
- Surgeon Preferences and Experience
- The presence or absence of contraindications to a certain type of vaginoplasty
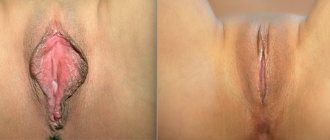
What is penile inversion vaginoplasty?
This is a surgical operation that involves removing the penis, testicles, creating a vagina from the skin of the penis (inversion) and the labia from the skin of the scrotum. This surgical technique is the gold standard and first line of genital surgery for transgender women.
What is the technique of penile inversion vaginoplasty?
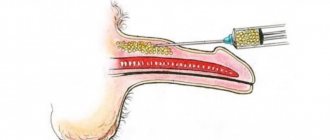
The operation begins with a circular incision in the skin of the inner layer of the foreskin of the penis, 1 cm from the glans (the so-called subcoronary access). The skin of the penis is separated from the spongy and cavernous bodies along its entire length and brought down to the root (base) of the penis. Next, a longitudinal incision will be made in the skin of the scrotum along the midline from the root of the penis to the perineum. Using this midline incision, both testicles are isolated and removed in turn. The vessels of the testicles and vas deferens are ligated. Next, the skin of the penis is turned inside out, brought out into a midline incision in the area of the scrotum and perineum and prepared for vaginoplasty - the end of the skin tube is sutured (this part will become the dome of the neovagina). Next, two longitudinal incisions are made in the deep fascia of the penis (Buck's fascia) on the sides of the dorsal neurovascular bundle from the glans penis to its root. This makes it possible to separate the dorsal neurovascular bundle from the cavernous bodies along its entire length to preserve the innervation and blood supply to the glans penis. Next, the head of the penis is separated from the cavernous bodies and a small part of the head (about ¼ part) of the penis adjacent to the neurovascular bundle is resected along with the remaining skin of the inner layer of the foreskin and used to create the clitoris and its mantle. Then the formed clitoris on the neurovascular bundle is also transferred to a midline incision in the scrotum and perineum. The operation is then continued using the perineal approach. The midline skin incision of the scrotum is continued into a T-shaped incision (Mercedes type) in the perineal area. Next, the corpus spongiosum is separated along its entire length from the corpora cavernosa; the corpora cavernosa are isolated to the lower branches of the pubic bones. At that level, the cavernous bodies are crossed and removed. Leaving a large volume of cavernous bodies can make sexual intercourse difficult and cause pain during sexual arousal. The corpus spongiosum is crossed at the border of the bulbous and penile sections and removed. Then the tendon center of the perineum is crossed, the anterior wall of the rectum is separated from the prostate, creating space for the neovagina. The inverted skin of the penis is placed in the formed cavity and fixed with separate sutures to the prostate capsule to prevent neovagina prolapse. In the area of the anterior wall of the neovagina under the pubic symphysis, a longitudinal incision of up to several centimeters is made, through which the clitoris and urethra are removed. Clitoroplasty is performed to form the clitoral mantle. This is an important stage of the operation, since the exposed clitoris can reduce the aesthetic result of the operation and cause discomfort for the patient. The remaining bulbous urethra is incised longitudinally and the external urethral opening is formed. Finally, excess scrotal skin is removed and the labia majora are formed from it.
What conditions are necessary to perform penile inversion vaginoplasty?
Since with the penile inversion technique the vagina is formed from the skin of the penis, the anatomical and functional results depend on the size of the penis. A history of circumcision of the foreskin also reduces the amount of plastic material for vaginoplasty. In conditions of deficiency of penile skin, the penile inversion technique is supplemented with the use of a scrotal skin flap.
Advantages of the penile inversion technique:
- One-stage operation
- Natural appearance of the external genitalia
- Good aesthetic result
- Use of local tissues without additional flaps
- Preservation of erogenous and tactile sensitivity of the external genitalia and vagina
Disadvantages of penile inversion:
- The result of the operation depends on the initial size of the penis
- Lack of natural hydration of the formed vagina, the need to use lubricants during sexual intercourse
- The need for periodic bougienage to maintain adequate vaginal depth and capacity
What are the features of the postoperative period after penile inversion vaginoplasty?
Bougienage of the formed vagina is necessary in the postoperative period to maintain its depth and capacity and prevent narrowing. Typically, bougienage begins 10 days after surgery, using a set of smooth dilators (smooth dildos) of different sizes. The approximate bougienage scheme is as follows: bougienage 3 times a day for 15-20 minutes for 3 months, then 2 times a day for 6 months, then several times a week. But the bougienage scheme can be individual for each patient. Regular sexual intercourse is beneficial for preventing vaginal narrowing, but cannot be a complete alternative to bougienage.
What are the possible complications of penile inversion vaginoplasty?
Intraoperative complications:
- Bleeding
- Rectal injury
- Damage to neurovascular bundles
Early postoperative complications:
- Bleeding from urethral tissue
- Partial necrosis of skin flaps
- Necrosis of the neoclitoris
- Hematoma in the surgical area
Late postoperative complications:
- Rectovaginal fistula
- Vaginal stenosis (narrowing)
- Prolapse (loss) of the vagina
- Stenosis of the external urethral meatus
What is the essence of the Perovic modification of vaginoplasty with penile inversion?
With this modification of the operation, the skin of the penis is incised longitudinally and a urethral flap is sewn in along the entire neovagina. The inclusion of a urethral flap in the vagina increases the erogenous sensitivity of the vagina and creates natural hydration.
What documents are required to perform vaginoplasty within the standards of care for transgender people?
A psychiatrist's report is required with a diagnosis and recommendations for hormonal therapy and gender-affirming surgical interventions.
What examination is necessary before performing penile inversion vaginoplasty?
List of tests and examination for hospitalization:
- General blood analysis
- General urine analysis
- Blood chemistry
- Coagulogram (PI, INR, APTT, fibrinogen)
- Blood tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C
- Blood type, Rh factor
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder with determination of residual urine, prostate, scrotal organs
- Uroflowmetry
- Ultrasound duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities
- ECG
- Fluorography
- Therapist's conclusion
- Endocrinologist's conclusion
Vagina from the colon2
There is another method of creating a vulva - using the large intestine. However, research on the outcomes of this procedure is limited. The advantage of the operation is that the intestinal tissue is capable of producing mucus (lubrication of the future vulva).
While the vaginal hydration from the penis tissue will be artificial. This is the only advantage of colon vulvaplasty so far. The operation is used when the first method fails or when penile plastic surgery is impossible.
Many patients need repeated cosmetic surgery after gender reassignment. This is labiaplasty. Repeated surgery gives doctors the opportunity to work with already healed tissue, giving the lips an aesthetic appearance and positioning the urethra in the right place. This surgery is less invasive and is intended to cosmetically correct the appearance of the vulva.
How to prepare for surgery 5
Hair usually grows on the skin of the scrotum and other parts of the body where skin grafts are taken during surgery. It is worth asking your doctor where exactly he intends to extract additional skin material. And several weeks and even months before the appointed time, undergo a full course of laser or electrolysis in order to permanently get rid of hair in the areas of the future vulva.
It is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions the day before and the morning before the operation. Usually you cannot eat anything in the evening, since the patient will have to be put into general medicated sleep.
And a few more tips:
- It’s worth talking to people who have already walked this path, asking about their experiences, feelings and impressions.
- Do not be afraid to consult with a doctor as much as necessary, ask all the questions you are interested in, no matter how stupid and inappropriate they may seem.
- Write down a plan for your new future, in particular, reproductive. It may be worth talking to your doctors about freezing your sperm sample.
- Enlist the support of family and friends. It will be very useful after surgery.
The operation costs, on average, about $20,000. This is only the first procedure. A second labiaplasty operation requires additional costs. In addition, some patients also undergo mammoplasty and other procedures for complete transformation. The total cost of a new life in a new body depends on the patient's financial well-being, insurance and region.