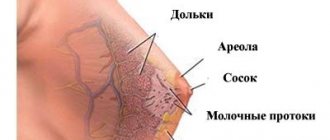
Most representatives of the fair sex are sure that breast implants are a spherical material filled with silicone. However, this opinion is erroneous. Manufacturers all over the world produce various variations of breast products, differing in: type of filler, diameter, volume, shape, surface texture. Therefore, every girl should definitely consult a specialist before choosing a future implant.
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS: PREOPERATIVE MEASUREMENTS
FULL NAME._____________
Age___Weight___Height___Bodice size before surgery___
Expected Result:
Four types of future breast profiles are shown schematically. The features of these 4 types should be explained to the patient in detail; the choice of one or another type of implant will depend on this and it will be clear how to choose the right implants.
Filler
The main types of filler are saline (physiological) solution with a salt content of 0.9% and gel (silicone). Our clinic uses only high-quality silicone implants.
Silicone gel is quite thick, provides good elasticity, and can maintain its shape even if the implant ruptures. It comes in different densities, which expands your choice. The densest is the most stable and retains its shape better than others. They are filled with anatomical endoprostheses, providing a natural appearance to the breast. The disadvantage is the relatively large weight. After about 15 years, the breasts sag under their weight and correction is necessary.
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS BASED ON THE PATIENT’S WISHES
- TYPE 1. The patient expresses a desire for a slight breast enlargement, which has a natural (teardrop-shaped) shape with a slight fullness of the upper slope. The patient understands that with her initial parameters it is possible to install a larger implant, but nevertheless insists on a conservative increase. The surgeon should think about low-profile implants.
- TYPE 2. The patient wants to install implants with the largest possible volume, but at the same time does not want to end up with breasts that have an unnatural appearance, that is, excessive fullness of the upper slope. The patient does not want it to be noticeable that breast augmentation surgery has been performed. The surgeon can choose round implants with a medium profile or anatomical implants with a medium (high profile).
- TYPE 3. The patient wants a large breast enlargement and does not mind if the breasts have a slightly unnatural (unnatural) appearance, that is, a well-filled, rounded upper pole of the mammary glands will be noticeable to others. The surgeon chooses round implants above the average profile (medium “plus”) or anatomical implants with an ultra-high profile.
- TYPE 4. The patient wants breast augmentation with implants of the largest possible volume and understands that this will create a completely unnatural appearance and it will be obvious to others that an operation has been performed. In this situation, the surgeon uses round implants with a high or ultra-high profile.
Indications for use
Short implants are used in a limited number of clinical situations and are intended for installation in the lateral parts of the jaw. In other areas, it is not recommended to implant ultra-short implants; the reasons will be discussed in more detail below. Simply put, short implants are only suitable for restoring posterior teeth in situations where installing longer titanium roots is not possible.
Short implants for the upper jaw
Short implants are placed on the chewing teeth of the upper jaw when there is a lack of bone tissue, but it is not possible to perform a sinus lift. This may be due to individual anatomical features, the presence of contraindications to bone grafting, or financial factors (sinus lifting is a fairly expensive procedure).
Short implants for the lower jaw
In most cases, short implants in the lower jaw are also placed when there is a deficiency of bone tissue and there is no possibility of its growth. In addition, many nerves and vessels are concentrated in the lateral part of the lower jaw: if there is a risk of damage to them, the doctor may recommend installing a short implant.
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS ACCORDING TO THE PATIENT’S INITIAL DATA
To understand how to choose implants correctly, the surgeon must evaluate tissue turgor, the so-called “skin pocket”. This is important in terms of assessing the real possibility of filling this “pocket” with an implant. So:
- ELASTIC - indicates that the breast may have a small space for the introduction of implants, which will strongly compress and put pressure on the chest, reducing the projection of the prosthesis. In this case, it is best to install low or medium profile implants.
- MODERATE (MEDIUM) - evidence that the skin pocket is slightly relaxed, but at the same time not excessive. Here it is possible to install implants with an average or above average profile.
- FLABLE (LOOSEN) - indicates a noticeable loss of elasticity and the presence of excess skin. In this situation, surgery with the installation of high-profile implants is indicated.
Important nuances
Breast surgery requires a responsible attitude. Therefore, it is important to contact a clinic that specializes in such operations. This means that surgeons have the appropriate qualifications and extensive professional experience, which minimizes the likelihood of any health risks and obtaining a result that is not what was expected. Otherwise, when using unsuitable tools and equipment, using uncertified endoprostheses and materials, and with low qualifications of the doctor, problems may arise, namely:
- implants that do not correspond to the individual characteristics of the patient will end up looking inharmonious and unnatural;
- improper installation of breast prostheses can lead to their contours appearing above the skin, which reduces the aesthetic value of the operation to zero;
- discomfort even after the completion of the recovery period, when the implants feel like a foreign body.
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS: WE MAKE MEASUREMENTS
- The distance from the jugular notch to the nipple (Sternal Notch to Nipple - SN-N) is carried out with a measuring tape. It can vary from 16-18cm in short patients, to 19-21cm in tall patients with small breasts. This parameter is important for assessing the symmetry of the location of the nipples.
- The distance from the middle of the collarbone to the nipple (Clavicle to Nipple - CN) is also determined with a measuring tape. This line is called the median meridian.
- The width of the base of the breast - (Breast Base Width - BBW) is determined using calipers with a slide rule. It is one of the main parameters in the question “How to choose implants?”. In some cases (wide interbreast distance - more than 3-3.5 cm), for example, in patients with tubular breasts or a narrow base of the mammary glands, the width of the base of the breast can be increased due to implants. Accordingly, the interthoracic distance decreases to the average size.
- Breast Height - BH - distance from the inframammary fold to the upper border of the mammary glands. This parameter is important in choosing the height of anatomical implants.
- Medial Pinch - is determined by gripping (pinching) the skin with subcutaneous fat between the index and thumb along a conventional axis between 11 and 5 o'clock on an imaginary dial. Determined by special calipers.
- Lateral Pinch - the measurement technique is the same as for the medial pinch, along a conventional axis between 1 and 7 o'clock. The dimensions of the medial and lateral tucks are important for choosing the width of the implant base.
- Upper Pole Pinch - measured by capturing the skin with subcutaneous fat in the upper pole of the mammary gland in the projection of the conventional axis between 3 and 9 o'clock. The thickness of the upper tuck is important for choosing the method of installing implants - under the gland (subglandular) or partially under the muscle (submuscular). Considering that there is a double layer of tissue between the two fingers gripping the skin with subcutaneous fat, the true value of tissue thickness will be equal to ½ pinch test. For example, if the pinch test is 2 cm, then the true tissue coverage over the implant will be half, that is, 1 cm. It is believed that if the pinch test in the upper pole is less than or equal to 2 cm, then the round implant can be contoured and, therefore, its upper pole should be placed under the muscle. According to D. Hammond, for subglandular placement of anatomical implants, a coating thickness of ½ cm is sufficient (pinch test is 1 cm).
- The distance from the nipple to the inframammary (submammary) fold - (Nipple to IFM - N-IFM) - is measured with a centimeter tape from the nipple to the IMS (SMS). For small breasts with good skin turgor, this distance is 5-6 cm on average.
- The distance from the nipple to the inframammary fold when the skin is stretched - (Nipple to IFM (stretched)) - is determined at the maximum stretch of the breast skin in the lower pole. This test can be used to judge the firmness and elasticity of the skin. If this distance is more than 7-8 cm, then along with endoprosthetics, the possibility of performing a periareolar or vertical breast lift cannot be ruled out.
- Areola diameter - measured along the vertical and horizontal axis. Allows you to determine the size of the areolas, their asymmetry, the need to reduce the diameter, and the possibility of performing periareolar access. For example, with small areolas (about 3 cm), installing implants, especially anatomically shaped ones with a more cohesive gel, using periareolar access will present certain difficulties for the surgeon and lead to unnecessary trauma to the patient’s tissues surrounding the incision.
- Interthoracic distance (true cleavage) is the distance between the medial (internal) borders of the mammary glands. Measured with a measuring tape.
In patients with small breasts, the average is 3-3.5 cm. This parameter can exceed 3 or more centimeters in patients with tubular breasts or a narrow base of the mammary gland. In such cases, the width of the base of the future implant should, accordingly, increase by ½ the difference between the true and desired cleavage (but not less than 3 cm). For example, a patient’s true cleavage is 5 cm. In this case, to the selected width (see below) of the future implant, you need to add ½ the difference between the true (5cm) and the desired cleavage (3cm), that is, half of 2 (1cm).
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS: WHAT TO PAY ATTENTION TO
When filling out this “Observations” section of the worksheet, the surgeon notes all the structural features of the mammary glands, chest, existing asymmetry, etc.
Breast shape: - tubular, round, conical, wide, narrow, etc.
Breast examinations - the presence of any formations, lumps, scars, etc. is determined.
Chest volume (presumably) Right_____________ Left_____________
Difference_____________
Asymmetry: Chest_____________Chest_____________
Nipple level_____________
Submammary fold_____________
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS: PLANNING THE OPERATION
Type of operation: - what is planned by the surgeon - augmentation (increase), revision or reconstruction.
Planned date of surgery: ____________
Planned change in the level of the inframammary fold: raising, lowering, or remaining unchanged.
Preferred size: Volume ____________
Profile:_____________Base Width (measured with slide rule calipers) - BBW_____________
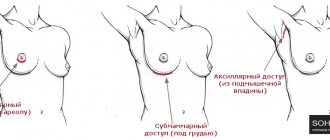
Access: Submammary, periareolar, axillary, other (check as appropriate).
Implant location: subpectoral, subglandular (under the gland), subfascial (mark as necessary).
Implant base: (basic width)___________ (determined by the formula: width of the base of the breast - (minus) ½ thickness of the fold of the medial pole - (minus) ½ thickness of the fold of the lateral pole.
TYPES OF IMPLANTS
Implant type:
- round;
- teardrop-shaped (anatomical).
HOW TO CHOOSE ROUND IMPLANTS
- The gel chosen is Mentor’s Cohesive I (the softest gel) or Cohesive II (a denser gel). Similar to Cogesive II - Mak Gan has round implants with Soft Touch gel). Round implants with a denser gel are preferable to install in patients with poorly developed subcutaneous fat and breast tissue, that is, when there is a risk of “waves” (ripples) appearing due to the softness of the gel.
- Select a profile: Mentor has medium, medium plus, high, super high.
HOW TO CHOOSE ANATOMICAL IMPLANTS
Selected according to 3 main parameters:
- width;
- height;
- profile (projections).
Mentor has 5 types of teardrop implants. Mak Gan (formerly Inamed corporation, then Allergan) has similar implants of the Matrix system. See the comparative table of teardrop-shaped implants from these 2 companies.
When choosing round implants, the main parameter can be taken as the basic width of the implants, as well as the volume and projection. To understand how to choose implants, D. Hammond offers the following algorithm.
So, for example, having chosen the basic width of the implant after appropriate measurements, the next step is to select the volume and projection (or vice versa).
It is clear that an interval in choosing the width of the implant within 5-6 mm is quite acceptable, since each surgeon can measure the base of the mammary gland or the thickness of the covering tissue (pinch test) differently.
Many surgeons, when choosing implants, focus on volume as the main parameter, then the next steps will be to select the appropriate base width and projection (or vice versa).
When choosing drop-shaped implants, in addition to width, volume and projection, the height of the future prosthesis is also taken into account, which is selected according to the height of the patient’s chest. For this purpose, there are anatomical implants of full, medium and low height (see the comparative table of implants using the example of Mentor and Mac Gun).
Manufacturers
Implants from different manufacturers have their own characteristics, which are taken into account when choosing a specific brand and model.
- Sebbin.
Implants of this brand have been known for more than 30 years. The main filler material is medical silicone, which does not leak even if the shell is damaged. Its consistency is available in three versions: soft, dense and classic. The shell is made using special technology. It includes 10 layers with a total thickness of 500 microns, which makes it not only durable and damage-resistant, but also extremely comfortable. The lifetime warranty on the prostheses of this brand is one of the indicators of their high quality. - POLYTECH.
This company has been producing breast implants since 1986, making it one of the largest and most experienced manufacturers. POLYTECH has several lines of round and drop-shaped implants: Meme, Replicon, Optimam, Opticon. The most popular models are those with a Microthane surface, which prevents the formation of fibrous areas. - Motiva.
This company produces implants for breast enlargement. The products are presented in a huge range. Breast prostheses of this brand can be chosen among three filling densities. In addition, the shell of the implants is available in two versions: velvety, which prevents the prosthesis from moving, and silky, which has maximum compatibility with body tissues. Breast prostheses of this brand are equipped with special chips that store all important information: from the series and number to the date of sterilization. - Nagor.
This brand has about 270 models of implants of different shapes and sizes. In addition, Nagor produces endoprostheses for patients with non-standard shapes, which allows both reconstructive plastic surgery and surgery of a purely aesthetic nature with the most natural results. - ARION.
More than 500 models of different shapes, sizes and profiles presented in the company’s assortment are the merit of more than 40 years of experience in the field of manufacturing endoprostheses. They are available in different filler options: hydrogel, cohesive or soft silicone.
HOW TO CHOOSE IMPLANTS USING OTHER METHODS
Despite the apparent complexity of the Body Logic system, in fact, for an experienced surgeon, the process of measuring a patient’s parameters and selecting the appropriate implant takes no more than 15-20 minutes. The presence of sizers (implants for fitting) will greatly facilitate this task and help the patient assess the size and shape of the future breast.
Of course, there are many other ways to select implants, proposed by various authors (for example, the scheme of Dr. Tebbetts and Per Heden and even the computer program developed for this by Dr. Stan). On the contrary, many surgeons rely only on their experience, eye and intuition, and probably have very good results. There cannot be certain dogmas in plastic surgery. The one who has excellent and long-term stable results is right. How he achieves this is the second question.
Clinical cases of the use of thin Straumann Roxolid implants
- Installation of one implant in the area of the front tooth or premolar (a thinner implant in an aesthetically significant area creates more space for the gingival papillae and improves aesthetics);
- Jaw implantation. Installation of 6 thin Roxolid implants instead of 4 standard-diameter implants allows for simultaneous implantation of the entire jaw without bone tissue build-up, even in cases of thin jaws;
- Implantation in the area of chewing teeth. If three teeth are missing in a row, it is possible to install two thin implants with a bridge for three teeth. This method of prosthetics evenly distributes the load between the implants and has the same success rate as installing two standard-sized implants.
Left: All-on-4 implantation of both jaws, standard size implants
Right: All-on-6 upper jaw, All-on-4 upper jaw. Of the 10 installed implants - 7 Straumann Roxolid implants with a diameter of 3.3 mm
Prospects for thin implants
Dental implantation has had positive success for many decades, despite this, we still do not know all the possibilities of using thin implants. For a long time, bone tissue augmentation was an almost mandatory condition for installing implants, which was not suitable for some patients due to trauma, fear of additional operations and possible complications.
Today, implantology is moving along the path of minimally invasive treatment. Even in cases where bone augmentation cannot be avoided, it is increasingly being performed simultaneously with the installation of implants, and not as a separate operation. In some cases, instead of bone grafting, gum grafting is performed, which is again less traumatic and more predictable.
It is also worth noting that the use of thin implants has its own specifics, and in this case the qualifications of the implantologist are especially important. If all recommendations are followed, thin implants can be as reliable as standard-sized implants.