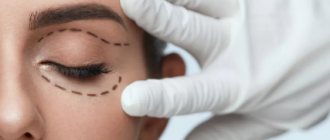
Blepharoplasty surgery formally refers to plastic surgery, but the close proximity of the surgical field to the eyes suggests that blepharoplasty stands at the intersection of aesthetic surgery and ophthalmology. In some cases, this type of intervention has not only cosmetic, but also medical indications, which are mainly dealt with by our ophthalmology center. These include:
- Entropion and eversion of eyelids
- Hernias of the upper or lower eyelid
- Lagophthalmos (hare's eye)
- Disposition of lacrimal openings
- Neoplasms of the eyelids (benign)
- Traumatic injuries
In these cases, it is not recommended to go to plastic surgery clinics, because The experience of aesthetic doctors is sometimes not sufficient to obtain high treatment results.
Cosmetic surgery on the eyelids and in the area around the eyes allows you to tighten the skin and remove excess fat, eliminate age-related changes and improve the appearance of the upper part of the face - remove “bags” and wrinkles around the eyes, remove swelling of the eyelids, give the look youth and freshness.
Blepharoplasty is performed both as an independent procedure and as part of a complex of anti-aging measures.
The shape and condition of the eyelids is what any interlocutor, voluntarily or involuntarily, first of all pays attention to, but the natural role of this organ is much broader. From an evolutionary point of view, the eyelids serve the function of protecting and moisturizing the eyeball. Reflexive closing of the eyelids occurs in case of any danger, which protects the visual organ from dust, drying out, injury, exposure to temperature and chemical unfavorable factors.
Anatomical features of the eyelids
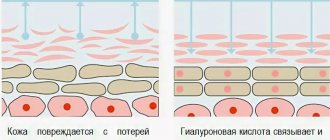
The eyelid is designed in such a “grooved” manner that multiple folds of skin provide a tight closure without any tension or tension on the tissue. The outer layer of the eyelid is represented by the thinnest skin. The dermis of this thickness (less than 1 mm) is not present anywhere else in the body. Under the skin there is a circular muscle, which ensures the mobility of the eyelids. Then, deeper still, a thin membrane separates the muscle from the fatty tissue. Finally, the back layer of the eyelid - the conjunctiva - is in direct contact with the cornea. At the junction of the eyelid with the anterior surface of the eyeball there is a conjunctival sac. The rigidity of the eyelids is given by the cartilaginous plates that make up their frame base.
The eyelids are innervated by branches of the facial nerve, which are woven into the orbicularis oculi muscle along its outer and lower edges. The skin of the eyelids constantly experiences quite significant stress, so its aging begins already at the age of about 30 years. The dermis becomes less elastic, its excess appears, gathering in folds and sagging. Fat deposits and wrinkles appear around the eyes. Together with drooping forehead skin, stretched upper eyelids give the face a tired and heavy expression.
It has been noted that such age-related changes are accompanied by more or less pronounced impairment of peripheral vision and an increase in intraocular pressure. Blepharoplasty, which removes excess fat and skin from the eyelids, prevents the development of these conditions.
In the arsenal of modern plastic surgery, there are many technologies and techniques that are successfully used when performing blepharoplasty. Subjective complaints, study of anamnesis and heredity, objective diagnosis of the condition of the eyelids, analysis of the connection between aesthetic problems and disorders in the visual system - all this together allows an experienced specialist to develop a strictly individual plan for surgery and subsequent rehabilitation.
Types of blepharoplasty surgeries
Plastic surgery is possible on both the lower and upper eyelids. Accordingly, they talk about “lower” or “upper” blepharoplasty.
Upper blepharoplasty is usually aimed at eliminating drooping eyelids. The result of this operation is a wider opening of the palpebral fissure, rejuvenation and liveliness of the look.
Lower blepharoplasty may include removal of excess intraorbital fat or be aimed only at tightening the skin (fat-sparing blepharoplasty), eliminating eyelid hernias, ectropion, repositioning of lacrimal openings, etc.
Plastic surgery of the lower and upper eyelids can be performed percutaneously or through transconjunctival access.
Important elements of blepharoplasty are often canthopexy and canthoplasty - tightening the corners and changing the shape of the eyes. However, these procedures can also be performed as independent plastic surgery.
In some cases, blepharoplasty may include restoration of the lacrimal ducts. Such plastic surgery of the lacrimal punctum is usually performed for medical reasons in the presence of abnormalities in the development of the eye, or to eliminate the consequences of injury.
Among patients with an Asian type of appearance, eyelid surgery is quite common, making it possible to bring the eye shape closer to the European type. This type of blepharoplasty can be performed with or without incisions.
Drooping and drooping eyelids (ptosis) can also be corrected through surgical blepharoplasty.
Pros and cons of the surgical method
Surgical intervention differs from hardware and injection techniques in a wider range of targeted tasks, high efficiency and sustainable results. Surgery helps with severe age-related manifestations, significant congenital anomalies, when minimally invasive procedures are powerless. Unlike fillers, which dissolve in 6–18 months, the operation provides a long-lasting lifting and rejuvenation effect for 5–15 years.
Like any operation, surgical blepharoplasty can cause complications. Among the possible ones are eye infection, hematomas, swelling, hypertrophied scars. By choosing an experienced, qualified surgeon, the risk of side effects is minimized. The relatively high cost of the procedure is justified, because over 5–15 years it is necessary to undergo from 5 to 30 courses of injection plastic surgery of the upper eyelids for a similar result, which will cost more.
Indications for blepharoplasty
Aesthetic blepharoplasty is always caused by the patient’s subjective dissatisfaction with his appearance. Psychological discomfort may be associated with the congenital structure of the eyelids or be a consequence of age-related changes. The most common complaints include:
- dissatisfaction with the shape of the eyes;
- “bags” under the eyes (fatty hernias of the lower eyelids);
- excess skin on the upper eyelids;
- wrinkles in the corners and under the eyes.
Blepharoplasty for medical reasons is performed in the following cases:
- eversion or inversion of the eyelid;
- pathology of the lacrimal opening;
- eyelid ptosis;
- eyelid hernias, etc.
Possible complications
After blepharoplasty, complications in the form of suppuration of wounds, corneal injuries, deterioration of vision, and asymmetry of the eyelids are extremely rare. Swelling, bruising and hematomas of the periorbital area after the intervention are a normal reaction of the body and disappear on their own after 2-3 weeks.
Possible side effects include excessive drooping of the corners of the eyes - this gives the face a sad, dissatisfied appearance. If there is insufficient tone of the lower eyelid or when too much skin is removed, ectropion occurs - inversion of the lower eyelid. In these cases, repeat corrective surgery may be required.
Thanks to the use of modern equipment, the use of gentle techniques and close interaction between the doctor and patients, you can have blepharoplasty of the upper and lower eyelids in our clinic without fear of complications and undesirable consequences.
Preparing for surgery
In order to predict the effectiveness of the planned operation, preparation for blepharoplasty always necessarily includes an assessment of the elasticity of the eyelid skin. In old age, this characteristic is almost always reduced. In such cases, blepharoplasty surgery should include canthopexy to prevent postoperative lower eyelid drooping.
Preparation for blepharoplasty, like any other surgical procedure, requires a comprehensive diagnosis and may include:
- collection of complaints and anamnestic data;
- laboratory tests of blood composition;
- ECG;
- examination by a therapist;
- consultation with specialized specialists (in the presence of comorbid chronic diseases);
- conversation with an anesthesiologist and choice of anesthesia method.
Our ophthalmology center is a highly specialized eye clinic, and therefore the extensive experience of doctors and the availability of the necessary equipment allow us to achieve high results in eyelid surgery for both therapeutic and aesthetic purposes.
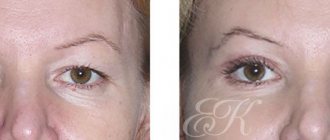
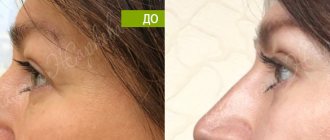
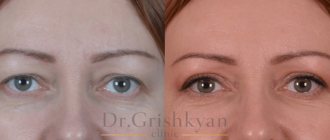
Photos of completed work
Upper eyelid blepharoplasty
Photos "before" and "after"
Photos "before" and "after"
Photos "before" and "after"
Photos "before" and "after"
Blepharoplasty technique
The blepharoplasty operation can last, depending on the initial condition of the eyelids and the wishes of the patient, from 30 minutes to 2 hours. Local or general drugs, as well as their combinations, are used for pain relief.
The surgical plan and optimal methods in each case are purely individual. Careful preliminary diagnosis here is a particularly significant factor in the success of surgical care. The doctor not only tries to delve as deeply as possible into the content of the problems that led the patient to surgery, but also to evaluate the reconstructive possibilities, which, even with the modern development of surgery, are still not limitless, and they are often limited not so much by technology as by the resources of the body itself.
Modern techniques allow for correction without external incisions or sutures, guaranteeing aesthetic results of the highest level. Even if there is a need for excision, the integrity of the skin is disrupted in places of natural folds, which over time makes the traces of surgical intervention invisible.
At the end of the operation, a special aseptic bandage is applied to the eyelids, which can be removed after 4-6 hours. If the patient experiences pain after the end of anesthesia, it can be relieved with appropriate medications, but blepharoplasty, as a rule, does not cause significant discomfort during the rehabilitation period.
Features of the postoperative period
Blepharoplasty is often performed “in one day”, i.e. the patient can leave the hospital in the evening after the operation. In case of a difficult recovery from anesthesia or if there are medical indications, the operated patient remains in the clinic for a day.
If stitches were applied during the operation, they are removed after 4-5 days. During the first week, subcutaneous hematomas may persist, which gradually resolve. Postoperative tissue swelling lasts up to two weeks; in order to reduce it, it is recommended to sleep on high pillows at night.
The eyes are regularly treated with medications that the surgeon will prescribe upon discharge. They relieve inflammation and prevent the formation of crusts on the skin.
In the eyelash growth area after surgery, a decrease in skin sensitivity may be observed, which is restored over time.
Resumption of normal lifestyle and professional activities is recommended no earlier than the 10th postoperative day. From this moment on, you can use decorative cosmetics, although application directly to the eyelids is contraindicated for another two weeks.
Outdoors, it is recommended to protect your eyes with tinted glasses. In addition, in the early postoperative period, it is advisable to stop using contact lenses.
You should avoid physical activity, sports and overwork for a month.
The final effectiveness of blepharoplasty is assessed no earlier than six months later. If necessary, minor re-correction is carried out. The effect of eyelid surgery lasts for 7-10 years or longer. This indicator largely depends on lifestyle, nutrition, and mental state. Postoperative scars are located out of sight.
Contraindications to blepharoplasty
Typical contraindications for eyelid surgery are the same as for other types of surgical treatment. Whether they are absolute or relative (i.e., surmountable or negligible) is determined during preoperative diagnosis. When making a decision, the ratio of possible risks and predicted benefits of the intervention is assessed mainly. Specific restrictions may be imposed, first of all, by diseases of the visual system (acute and chronic diseases of the conjunctiva, lacrimal glands and ducts, dry eye syndrome, blepharochalasis (excessive swelling around the eyes), blepharospasm, hyperthyroidism and a number of other ophthalmopathological conditions. In this case, advisory participation an ophthalmologist is strictly necessary.
Analyzes
To exclude the presence of contraindications to surgery, each patient is required to undergo a series of examinations and tests. The list of necessary studies is given to the surgeons at the first consultation. The list usually includes general tests, blood biochemistry and test results for viral diseases. Diagnostic examinations will require electrocardiography and fluorography. A coagulogram and blood group determination with the Rh factor are also necessary.
In some cases, additional consultations with specialists may be required. So, for blepharoplasty, a consultation with an ophthalmologist may be prescribed. For patients over 45 years of age, a cardiologist's opinion is required. After collecting all the results, the patient must visit a therapist, who will issue a conclusion with a recommendation whether plastic surgery is allowed or not.