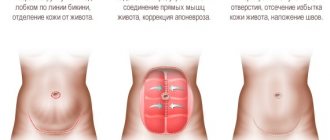
Modern plastic surgery offers great opportunities to achieve your aesthetic ideal. If you cannot get a beautiful flat stomach and thin waist through sports and diet, abdominoplasty comes to the rescue. This is a very effective, but also very difficult operation - for both the doctor and the patient.
Rehabilitation after abdominoplasty takes a long time and requires special attention from the patient. At this time, you will have to observe a number of restrictions and care for the injured area. The final result depends not only on the qualifications of the surgeon, but also on the responsibility of the patient. In addition, it is worth preparing in advance for stiffness of movement, swelling and bruising, which always accompany the patient in the postoperative period.
First days after surgery
The first few days after correction are the most difficult, especially if there is rehabilitation after abdominoplasty with suturing. In the first two days, pain and discomfort are observed, fluid accumulates in the area of intervention, which will result in the appearance of edema. The abdomen becomes hard to the touch. Sometimes you may have problems urinating or a feeling of difficulty breathing - such situations do occur, although they are very rare.
On the first day, it is undesirable to break bed rest. You will have to lie in bed in a certain position: on your back, with your legs slightly bent and raised. This position allows you to reduce the load on the muscles and minimize the risk of seams coming apart. You can usually get out of bed on the second day after the intervention. But this must be done with caution, without sudden movements.
Three to four days after the correction, the patient can leave the hospital and return home. From this moment, long-term rehabilitation after abdominal abdominoplasty begins.
Abdominoplasty technique with suturing.
Complications after abdominoplasty
- 2.1 Abdominal compartment syndrome
- 3.1 Unsatisfactory appearance of the postoperative scar
- 4.1 Swelling after abdominoplasty
From a medical point of view, tummy tuck is not classified as abdominal surgery. However, when performing it there are risks of negative consequences characteristic of this group of surgical interventions. There is a high likelihood of serious side effects and complications after abdominoplasty, especially considering that the operation is performed for aesthetic reasons and not for medical reasons.
Doctors divide complications after abdominoplasty into 2 groups: general and local . The first ones affect several important systems of the body at once and are life-threatening. Their statistical frequency ranges from 0.3% to 1.1%:
- abdominal compartment syndrome;
- thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism;
- pneumonia.
The latter cause local changes in the area of intervention and most often do not threaten the patient’s life, but may not have the best effect on health. They occur much more often - according to various estimates from 10 to 20% of cases:
- hematoma;
- seroma;
- development of infection;
- skin flap necrosis;
- divergence of seams.
Local aesthetic complications after abdominoplasty are not dangerous in themselves, but can significantly spoil the result of the operation:
- unsatisfactory appearance of the suture on the abdomen, as well as other problems associated with scar healing;
- navel changes;
- changes in subcutaneous fat.
In addition, absolutely all patients in the postoperative period experience swelling after abdominoplasty, and also experience significant pain, which can last up to several months. These are expected side effects after tummy tuck that you need to be prepared for. Next, we will talk in detail about each possible complication after abdominoplasty, determine their causes and what to prepare for in each case:
↑ Local complications after abdominoplasty
↑ Postoperative hematoma
This is an accumulation of blood in the area of a surgical wound. Most often it appears in the first days after abdominoplasty. It may be caused by a surgeon’s mistake in not carefully ligating the vessels, or by the characteristics of the body - in particular, the risk directly correlates with the patient’s body mass index. Sometimes bleeding occurs due to a jump in blood pressure or decreased blood clotting, including that caused by anticoagulants, which are used to prevent thrombosis.
Small hematomas most often do not cause any symptoms. As the volume increases, swelling, pain, and darkening of the skin appear. An additional difficulty is that fatty tissue in the abdominal area can absorb a lot of fluid, so it is not always possible to determine the presence of blood loss in time - and it can be very large. This complication after abdominoplasty requires constant monitoring by a doctor: sometimes the situation normalizes on its own, but more often the problem area needs to be drained with a syringe. In the most serious cases, incisions will have to be made to find out the cause of the bleeding and stop it.
↑ Seroma after tummy tuck
It is an excessive accumulation of lymph between the skin-fat flap, separated during abdominoplasty, and the tendon plate of the anterior abdominal wall - aponeurosis. Risk factors:
- large volume of surgery (when combining a tummy tuck with liposuction, the probability of occurrence is 30%);
- damage to lymphatic and vascular pathways;
- loose compression garments, non-compliance with the wearing schedule;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- excessive physical activity in the early postoperative period.
This condition is not dangerous, but can cause discomfort and even pain. The main method of treatment is to remove accumulated fluid. For this purpose, punctures with aspiration (suction) of the contents are usually sufficient.
- Read more: Seroma after abdominoplasty: causes and treatment
It is impossible to reliably prevent lymphatic stagnation, but careful drainage of the postoperative wound significantly reduces the likelihood of its occurrence.
↑ Purulent-infectious complications after abdominoplasty
They occur when harmful microorganisms enter a wound or tissue injured during surgery. The problem can be either a violation of the rules of asepsis on the part of the doctor, or in the initial condition of the patient - with weak immunity and the presence of even slight chronic inflammation in the body, there is a risk that the infection will reach the operated area through the bloodstream (the so-called hematogenous route of spread ). It is curious that such complications occur much more often in smokers - 12.7% versus 5% in non-smokers. Possible flow options:
- External inflammation of a postoperative wound. The symptoms are typical: the suture swells, turns red, becomes hot and painful, and possible fever after abdominoplasty. Treated with antibiotics - a standard prophylactic course is prescribed to each patient immediately after surgery. In the future, it may be necessary to change or adjust it.
- Abscess. Purulent inflammation. It usually occurs at the site of an untreated hematoma or seroma, since the accumulation of biological fluids outside the vessels is an ideal breeding ground for microbes. The problem area may swell and hurt, the temperature usually fluctuates (in the evenings it rises above 38, in the morning it drops to values close to normal). Signs of general intoxication may appear - weakness, headache, chills. Treatment of abscesses is only surgical: the cavity is opened and drained, while increased doses of antibiotics are prescribed.
- Phlegmon. An extremely dangerous pathology. It occurs when a highly aggressive infection enters the body of a patient with an initially weakened immune system. The inflammatory process, starting from a surgical wound on the abdomen, quickly spreads to the surrounding tissues: the pubic area, buttocks, thighs and lower back. It is treated with a combination of intensive antibiotic therapy and surgical methods - it is necessary to open the phlegmon and drain the pus.
Prevention of this group of complications after abdominoplasty by the doctor is careful adherence to the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. From the patient’s side: treat all possible sources of chronic infection - from carious teeth to gynecological inflammations and stop smoking for at least 2-3 weeks before and after surgery.
↑ Necrosis of the skin flap
A consequence of tissue death in the abdominal area. It can be marginal - in the suture area, or central - in the center of the displaced area of skin, around the navel. The main causes of occurrence are impaired blood supply due to technical errors during abdominoplasty or excessive tissue tension.
- In the mild version, it is limited to epidermolysis, which affects only the upper layers of the skin. The problem area looks like a wet abrasion and over time completely recovers on its own.
- When necrosis after abdominoplasty affects the deep layers of the dermis and even subcutaneous tissue, treatment becomes complex and lengthy - at least 3-6 months. If dead tissue is not touched, it will take a long time to “rot”, leaving rough scars on the skin that can be complicated by infection. Usually they are immediately removed in full, and new sutures are placed on the cleaned wound. Sometimes repeated reconstructive surgeries are necessary for best results. To speed up healing, hyperbaric oxygenation is used - additional enrichment of tissues with oxygen.
↑ Dehiscence of seams
Not a common but unpleasant complication after abdominoplasty. It can occur if the wound was initially improperly sutured (this happens extremely rarely) or if the patient grossly violates the surgeon’s recommendations - excessively strains the abdominal muscles, lifts weights, etc. Another possible cause is inflammation, which is accompanied by severe tissue swelling and exudate.
- Read more: How to care for a seam after abdominoplasty and what to do if it breaks
The problem is solved by re-fixing the skin edges; if necessary, the surgeon cleans and drains the wound, and also prescribes a course of antibiotics. There is no great danger to health, but in the future there are often negative aesthetic consequences in the form of rough scarring.
↑ Complications after general abdominoplasty
↑ Abdominal compartment syndrome
This medical term refers to increased intra-abdominal pressure. This may occur if the operation affected not only the skin and fatty tissue, but also muscles and aponeurosis - for example, when, in addition to a tummy tuck, diastasis was corrected. Because of this, the total volume of the abdominal cavity decreases, which causes a sharp increase in pressure in it - by more than 15 mm Hg. – and, as a result, significant negative changes in the entire body:
| System | Problems with ACT |
| Heart and blood vessels | The patency of the inferior vena cava is impaired. Blood stagnates in the legs, which increases the risk of thrombosis and thrombophlebitis. Plus, small capillaries narrow compensatoryly: this, firstly, worsens the blood supply to the tissues, and secondly, increases the already considerable load on the heart. |
| Breath | The increased pressure in the abdominal cavity moves the diaphragm upward, compressing the lungs. A similar effect can be felt after a hearty feast, but in this case it is compensated by stretching the abdomen. However, after abdominoplasty, the anterior abdominal wall is inactive and its compensatory capabilities are small - as a result, the movement of the lungs is significantly hampered and atelectasis occurs in them - areas of collapse. The further you go, the more oxygen supply to the blood is disrupted and respiratory failure increases. |
| Kidneys | The normal functioning of this organ is possible only with full blood flow - only in such conditions does the filtration of toxic metabolic products occur. The narrowing of small arterioles and capillaries disrupts this process, reducing the volume of urine excreted, until signs of renal failure appear. |
| CNS | Following the increase in pressure in the peritoneum, it rises in the chest cavity. Because of this, the superior vena cava is compressed and the outflow of blood from the head is disrupted. Following this, intracranial pressure begins to increase with a whole bunch of corresponding symptoms, in severe cases - up to loss of consciousness. |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Blood flow through the hepatic artery slows down, which leads to compression of the liver vessels and death of its cells. Internal microcirculation in the stomach is disrupted, and this in turn increases the permeability of its walls to microbes. Reduced blood flow to the mucous membrane provokes the formation of ulcers. |
As a result, the complication can lead to failure of several vital organs at once. To prevent this from happening, in the first days after abdominoplasty the patient must have intra-abdominal pressure measured over time. For moderate abdominal compartment syndrome, conservative measures are sufficient:
- temporarily remove compression garments;
- raise your head relative to your body;
- ensure timely bowel and bladder emptying;
- neutralize excessive tension in the abdominal wall muscles with sedatives and painkillers.
In severe cases, the only method of correction is to open the postoperative wound, thus reducing the pressure in the abdominal cavity to normal values.
↑ Thromboembolic pathologies
These include deep and superficial vein thrombosis, as well as pulmonary embolism (PE). The risk group includes patients with the following characteristics:
- obesity;
- age over 40 years;
- phlebeurysm;
- previous thrombosis and thromboembolism;
- taking estrogens, including contraceptives;
- heart rhythm disturbances, especially atrial fibrillation;
- smoking;
- The duration of the operation is more than 2 hours.
With thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins, pain, swelling and redness of the skin appears at the site of blockage. If the deep veins are affected, there may be no pronounced symptoms at all. PE is characterized by:
- chest pain when breathing and/or behind the sternum;
- sudden shortness of breath;
- blue discoloration of the face and upper body;
- sudden cough with blood.
To prevent these complications, patients are given compression stockings immediately after surgery. They must be worn around the clock for at least 5 days. They use drugs to reduce blood clotting - specific names and dosages are individually prescribed by the doctor. Independent experiments are dangerous and can cause severe bleeding. For the normal functioning of the veins, muscle function is important - therefore, after surgery, they try to “put patients on their feet” as soon as possible (even despite the fact that in the first week they will have to move in a half-bent position). Developed thromboembolic complications after abdominal surgery are treated in intensive care.
↑ Pneumonia
Postoperative “congestive” pulmonary infections are more common in obese patients. To prevent them, as well as to prevent thrombosis, it is recommended to start moving regularly from the first days. Breathing exercises are very effective; the simplest option is to inflate balloons. You can do this without getting out of bed.
Any pneumonic complications appear already in the first 3-10 days of the recovery period after abdominoplasty. They are clearly visible on x-rays and in blood tests. Treatment begins with an increased dose of antibiotics, which is then adjusted based on the patient's condition.
↑ Poor aesthetic result of the operation
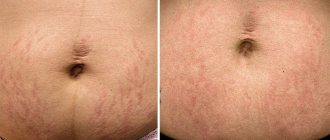
↑ Unsatisfactory appearance of the postoperative scar
The problem can be caused by several factors:
- Surgeon errors: incorrect alignment of wound edges, excessive tension of tissues or suture threads.
- Features of the body. With a tendency to hypertrophy of scar tissue, a large scar of dark or bright red color is formed. It is impossible to prevent such a result, and for those who have previously developed keloids, surgeons, in principle, do not recommend such operations without medical indications.
- Early infection. If the edges of the wound are inflamed, as well as with necrotic complications after abdominoplasty, the mark on the abdomen will be noticeably rougher and without additional corrective procedures will look extremely unaesthetic.
There are methods that have been tested and approved by doctors in most countries of the world, aimed at creating the most accurate, unnoticeable scar possible. First of all, these are silicone-based ointments and patches - they can be used immediately after the stitches are removed, and a little later, if necessary, add cosmetic polishing. For more details, see the article “Suture after abdominoplasty: an inevitable evil and how to deal with it”
↑ Changes in the umbilical region
During abdominoplasty, the navel is separated from the surrounding skin, and after removing excess tissue and fatty tissue, its location is re-formed - usually it is moved 1-2 cm above the original position, which is considered the absolute norm. But due to individual changes in tissue during the recovery process, the displacement can be much greater. Deviations to the right or left are also possible - and this is an obvious cosmetic defect. It can be corrected with a small repeat operation, which is performed approximately six months after the main one.
Another common problem is infection in the wound around the navel with the development of inflammation, including purulent inflammation. Impaired blood supply due to compression of the vascular pedicle can provoke necrosis; in this case, the affected tissue will have to be removed, and after healing, an “artificial” navel will be formed, surgically creating a characteristic pit.
↑ Changes in the condition of the skin and fatty tissue
It happens that at the initial stage of rehabilitation after abdominoplasty, the abdomen looks perfectly smooth, but after a few months, when the swelling goes down, peculiar bumps appear on it, and the overall contour becomes asymmetrical. This complication occurs if the surgeon removes subcutaneous fat unevenly. Liposuction will be required for leveling - in rare cases, non-surgical methods are suitable, but, as a rule, a good result can only be obtained through surgery.
Another common problem is vertical or (less commonly) horizontal ridges above the seam after abdominoplasty. They fully manifest themselves only after the swelling subsides. They are most pronounced in patients who actively lost weight before surgery. The reason is that during classical abdominoplasty the skin is tightened mainly vertically to remove the so-called. "apron". But it is much more difficult to securely suture other excesses; this requires an additional incision in the midline of the abdomen.
Over the course of several months, the skin will tighten a little naturally, and most of the problematic folds will disappear. But how effective the process will be depends on the patient’s age and the general ability of the tissue to contract. If after six months or a year the stomach still does not look its best, the situation can only be corrected through corrective plastic surgery with the same vertical scar. Most patients refuse it, believing that small folds are not worth another anesthesia and an additional scar on the body.
↑ Frequent side effects after abdominoplasty
↑ Edema after abdominoplasty
This is an inevitable consequence of tummy tuck. It occurs due to a combination of two factors: the body’s protective reaction to the injury and impaired blood flow due to a long horizontal incision. The peak occurs in the first few days of the recovery period, then over the course of 1-2 months, fluid stagnation gradually resolves.
- Read more: Why swelling after tummy tuck is inevitable and how to get rid of it quickly
There is no special treatment. It is important to follow basic “safety precautions” - adhere to a diet with a limited amount of fatty and salty foods, give up alcohol, and strictly adhere to the schedule for wearing compression garments. Towards the end of rehabilitation, you can undergo a course of lymphatic drainage procedures, but in most cases there is no particular need for this.
↑ Pain in the abdominal cavity
Discomfort after abdominoplasty is caused by muscle and soft tissue injuries. May be stronger than after other plastic surgeries. Initially, they are localized in the upper abdomen - this is due to the fact that the nerve endings here are practically not damaged during the operation and largely retain sensitivity.
The pain reaches its peak in the first 7-10 days of the rehabilitation period, but noticeable relief often occurs only 3-4 weeks after abdominoplasty. As innervation is restored, unpleasant sensations will appear again, and their emphasis will shift from the upper abdomen closer to the central (umbilical) region. Residual spasms can occur even after several months - they are subjectively felt like tingling with needles, but pass quickly and generally do not cause much inconvenience.
How long does rehabilitation take?
In abdominoplasty, rehabilitation after surgery takes quite a long time due to the complexity and volume of surgical intervention. The exact timing is determined depending on the situation, individual for each patient. The duration of recovery is influenced by anatomical parameters, the type of plastic surgery performed, care in the postoperative period, and even genetic characteristics.
On average, after abdominoplasty, the rehabilitation period is divided into several stages:
- first month,
- six months,
- year.
The first month will be the most difficult, with a number of prohibitions and rules that must be followed for a full recovery. By the fourth week, the health and condition of the operated areas improves significantly.
Over the course of six months, the scars gradually change their appearance - they lighten and become faintly visible against the background of the underlying skin. At this time, intermediate results can be assessed. Finally, a year after the correction, the final results are summed up.
Loss of sensation
During abdominoplasty, the surgeon changes the position of its tissues. This often affects a number of small nerves. Usually the nerve endings in the abdomen and upper thighs are affected. During the first time after surgery, patients complain that sensitivity in these areas is reduced.
There may also be a feeling of numbness, which is aggravated by a combination of liposuction and skin tightening. It is accompanied by a feeling of “goosebumps” or “burning”. This phenomenon means a gradual restoration of sensitivity and disappears about a year after the operation, in some cases earlier.
What to do
After abdominal abdominoplasty, rehabilitation requires the mandatory wearing of compression garments. As with any plastic surgery, compression garments allow the tissues to adapt, locking them into a new position. In addition, the underwear gives a massage effect, stimulating an accelerated reduction of swelling and bruising, and normalizes blood circulation and lymph flow.
But wearing underwear is especially important if you are undergoing rehabilitation after abdominoplasty with suturing of diastasis. Due to the high tissue tension after suturing, there is a risk of sutures coming apart; this is a common complication after surgery if the doctor’s recommendations are ignored. The underwear relieves stress from the muscles and thereby minimizes the risk of divergence of the edges of the incision. You will have to wear it for about a month, in rare cases - a little more.
At first you will have to sleep either on your side or on your back, with your legs tucked under. It is also important to follow a diet, avoiding fried, spicy, pickled and fatty foods.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
Indications:
- unsatisfactory condition of the postoperative scar;
- aesthetic imperfections of the abdomen that were not sufficiently eliminated during the previous intervention or acquired later - overhanging skin, prolapse of the navel.
During repeated abdominoplasty, it is possible to excise a rough scar, as well as eliminate overhangs.
For medical reasons, repeated surgery is performed only in case of serious complications in the form of seromas.
Contraindications:
- diabetes;
- heart and pulmonary failure;
- obesity;
- pregnancy;
- planned pregnancy (in the near future);
- insufficient period from childbirth (6-9 months is the optimal time);
- insufficient time from previous tummy tuck.
What not to do
For three months you should not engage in active sports, especially strength training. Moreover, for two to three weeks after surgery, it is advisable to avoid any activity, including household chores or long trips.
To promote a rapid reduction of edema, thermal procedures should be excluded for two months. This is a visit to a bathhouse, sauna or hot bath. Heat stimulates blood flow to the affected areas and dilation of blood vessels, which can have unpleasant consequences. For normal scar formation, it is also necessary to limit the influence of ultraviolet radiation - do not visit the solarium and the beach, and in the summer, hide the operated areas from the sun.
During rehabilitation after abdominoplasty with suturing of diastasis, the recommendations given are exactly the same as for other types of abdominoplasty. Violation of prohibitions threatens the discrepancy of diastasis, long-term subsidence of edema, and the formation of noticeable scars (hyperpigmentation).
Why the shape of the abdomen is not restored after childbirth
Firstly, hormonal changes, when all the main resources of the body are aimed at further nursing the baby and feeding him. And the body does not have much energy to direct it towards recovery. Also, under the influence of hormones, metabolism changes, and previously unusual deposits of subcutaneous fat reserves may appear on the anterior abdominal wall.
Secondly, weakened abdominal muscles. After all, for 9 months they were not only inactive, but also stretched. And when stretched, they also become thinner, and now it is very difficult for them to recover and begin to function fully.
Thirdly, when overstretching is too strong, for example, during a multiple pregnancy, or a polyhydramnios, or a large fetus, not only the muscles are overstretched, but also the fascia, thin connective tissue areas between the muscles, in which defects can arise during overstretching, further leading to the appearance of hernias.
Fourthly, mommy doesn’t have enough time and energy to go to the gym or work out with a trainer.
And all this leads to the fact that many girls after childbirth have a belly that they do not like.
If the muscles were in good tone before pregnancy, and did not become overstretched during pregnancy, then fitness after childbirth will help restore the stomach to its previous slimness.
Drug treatment and physiotherapy
For abdominoplasty, rehabilitation may also include medication. In the first days, your doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics to prevent possible infection. Antibiotics are also prescribed if the infection appears in the later stages of rehabilitation.
For a faster reduction of swelling and bruising, special ointments are recommended, for example, Traumeel or Troxevasin. If the doctor prescribes several similar drugs at once, the ointments must be applied strictly according to the schedule, without mixing with each other.
After about a month and a half, you can attend some physical therapy treatments, which also help relieve swelling and bruising. This can be electrophoresis, microcurrents, special massage, darsonval and much more. It is important to remember that taking medications and attending procedures must be agreed upon with the surgeon. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable!
Reasons for revision abdominoplasty
It also happens that the operation was done efficiently, but you still have to do a repeat abdominoplasty. This happens when the first abdominoplasty is done early. For example, the patient has not yet lost the number of kilograms and centimeters he needs, but has already convinced the surgeon of the need for tummy tuck. An experienced surgeon will always suggest that you first lose weight to your desired, comfortable weight, and only then perform surgery, since repeated surgeries are no less traumatic.
Sometimes the likelihood of a repeat abdominoplasty can be predicted even before the first operation. This happens if the patient has a large belly, a lot of fat deposits and a narrow pelvis. Then, if it is impossible to remove a large amount of tissue and leave a small seam, abdominoplasty is deliberately carried out in two stages. All this is done to achieve the best aesthetic result. In this case, “additional correction”, it is possible to perform a repeat abdominoplasty under local anesthesia 2-3 months after the first. The appropriateness of using local anesthesia is determined by the doctor: general anesthesia may be required.
When to see a doctor
Abdominoplasty with suturing of diastasis and rehabilitation after it are considered a difficult period. A number of natural postoperative phenomena will accompany the patient in any case. First of all, this is severe swelling, bruising, discomfort when moving, and an unsightly appearance of the incisions. But these phenomena are considered normal and there is no need to worry about them.
In some cases, phenomena such as:
- palpable tissue hardness upon palpation,
- severe swelling and bloating,
- severe pain,
- temperature increase,
- redness in the area of intervention.
The most common complications are the formation of seroma or hematoma, infection and suture dehiscence. The risks of their occurrence can easily be reduced to zero if you follow the rules during the recovery period and contact a specialist at the slightest suspicion of an unusual course of the situation.
Skin "apron"
As a rule, it appears after a significant decrease in body weight. Subcutaneous fat is significantly reduced in volume. But, unfortunately, the previously existing excess skin, unlike fatty tissue, does not tend to decrease. In addition to cosmetic dissatisfaction, the skin “apron” can affect the condition of the musculoskeletal system. In particular, if there is a sufficiently large apron, posture is disturbed, which over time leads to the development of pathological structural changes in the spine. Therefore, abdominoplasty is recommended.
1.General information
The general term “plastics” in surgery refers to a group of surgical techniques aimed at correcting, restoring or giving the desired shape to any organ or part of the human body. In the public consciousness, plastic surgery is firmly associated with aesthetic medicine (for example, facial skin lifting, correction of the shape of lips, nose, and many others are widely known), although in reality it is by no means limited to cosmetic operations. The same methodology is applied, in particular, in clinical abdominal interventions, when it is necessary to eliminate a birth defect or the consequences of a severe injury, reconstruct the normal anatomy of the affected organ, or restore the free flow of biological fluids.
Abdominoplasty (plastic surgery on the abdominal wall) is, as a rule, purely cosmetic; the ultimate goal is to recreate, and sometimes literally sculpture, the so-called. “flat stomach”, coveted and deified by the bodily fashion of recent decades. Abdominoplasty is often confused with liposuction, but these are different procedures, there are fundamental differences between them, and the second most often becomes part of the first.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!